두개골 골절
Skull fractures
두개골 골절의 종류
-
두개골을 두골 또는 머리뼈라고 한다.
-
교통사고나 안전사고 등으로 머리를 다치거나, 운동이나 장난을 하다가 머리를 다치면 두개골이 골절되기도 한다.
-
두개골에 골절이 생길 때 두개골만 골절되기도 하고, 두개강 내에 있는 뇌에 손상이 생길 수 있고, 두개강 내에 있는 혈관이 터져 두개강 내 출혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
머리(두부)를 심하게 다쳤을 때 두개골은 골절되지 않았지만 두개강 내에 있는 뇌가 크게 손상될 수 있고 뇌 내에 출혈이 생겨 그로 인해 사망할 수 있다.
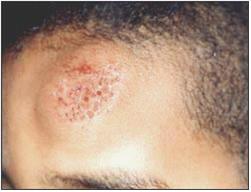
▴ 사진 94. 전두골 두피 좌상
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
1. 함몰 두개골 골절
-
탁구공의 일부분이 깨질 때 깨진 탁구공 껍질 일부가 탁구공 밀려 밀려 들어간 것처럼 골절된 두개골의 일부가 두개골 강 속으로 밀려 들어갈 수 있다. 이런 종류의 두개골 골절을 함몰 두개골 골절(Depressed skull fracture)이라고 한다.
-
그와 반대로, 두개골이 심하게 골절되어도 두개골 강 속에 있는 뇌가 아주 조금 손상될 수 있다.
-
그렇지만 두개골이 골절될 정도로 머리를 크게 다쳤을 때는 두피, 두개골, 뇌 모두가 동시에 손상되는 것이 보통이다.
2. 선상 두개골 골절
-
두개골에 가는 금만 간 골절을 선상(線狀) 두개골 골절(Linear skull fractures)이라 한다.
3. 분쇄 두개골 골절
-
두개골의 일부가 여러 조각으로 골절된 두개골 골절을 분쇄 두개골 골절(Comminuted skull fractures)이라고 한다.
4. 복잡 두개골 골절
-
두개골 골절을 단순 두개골 골절(Simple skull fracture)과 복잡 두개골 골절(Compound skull fracture)로 분류하기도 한다.
-
골절된 두개골 부분의 바로 위 두피가 손상되지 않았을 때의 두개골 골절을 단순 두개골 골절이라고 한다.
-
두피 손상도 있고 두개골 골절도 있을 때 두개골 골절을 복잡 두개골 골절이라고 한다.
5. 두개골 골절의 골절 형태에 따라 두개골 골절을 분류할 수 있다
-
선상 복잡 두개골 골절,
-
함몰 복잡 두개골 골절,
-
분쇄 복잡 두개골 골절 등으로 두개골 골절을 나누기도 한다.
-
두개골의 한 부분만 골절될 수도 있고 여러 부분이 동시에 골절될 수 있다.
6. 두개골 골절을 두개골 부위에 따라 두개골 골절을 분류할 수 있다
-
전두개골 골절 ,
-
측두개골 골절,
-
후두개골 골절,
-
두정골 골절,
-
두개골저 골절(Basal skull fractures) or Basilar skull fractures) 등으로 두개골 골절을 분류할 수 있다.
두개골 골절의 원인
-
분만 중 태어나는 아기의 두부가 엄마의 산도에 눌려 두개골이 골절될 수도 있고, 겸자로 분만할 때도 아기의 두개골이 골절될 수 있다.
-
높은 데서 떨어져 머리를 부딪쳤을 때,
-
어디에 머리를 심하게 부딪쳤을 때,
-
교통사고나 안전사고로 두개골이 골절될 수 있고 아동학대로 두개골이 골절될 수 있다.
두개골 골절의 증상 징후
-
두개골 골절의 종류와 정도, 두개 골절이 생긴 두부 부위, 두개골이 골절될 때 생길 수 있는 두개강 속 뇌 손상의 정도 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
분만 중 태어나는 아기의 머리가 산도에 세게 눌릴 때 생긴 신생아 두개골 골절의 증상 징후는 일반적으로 경미하고 때로는 증상 징후가 거의 없을 수 있다.
-
계단 등 높은 데에서 그 아래로 떨어진다든지, 책상 위나 다른 높은 데에서 바닥으로 떨어질 때 두개골이 경미하게 골절될 수 있고, 심하게 골절될 수 있다.
-
두개골이 골절될 때 까무러치듯이 울 수 있고, 얼굴이 창백해지고, 구토하고 잠시 동안 의식을 잃을 수 있다.
-
때로는 전신경련을 할 수 있다. 두혈종, 두부 외상 참조.
-
단순 선상 두개골 골절이 경미하게 생길 때 증상 징후가 거의 없거나 증상 징후가 경미하게 나타날 수 있다.
-
골절이 생긴 두개골 부위 바로 위에 있는 두피가 붓고 그 두피를 손으로 만지면 좀 말랑말랑하고 아플 수 있다.
-
태어날 때 신생아에게 생긴 단순 선상 두개골 골절은 두혈종을 동반할 때가 많다.
-
두개골이 경미하게 골절되었을 때는 머리가 아프고 구토하고 어지럽고 기운이 없고 얼굴이 창백할 수 있다.
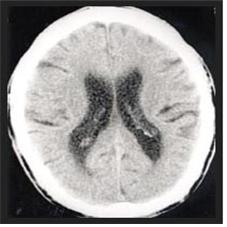
사진97. 두부 CT 스캔
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
-
두개골이 심하게 골절되었을 때는 두개골이 변형될 수 있다.
-
두개골의 밑 부위–두개골 기저(頭蓋骨基底) 골절이 생기면 두개골 강 내에 있는 뇌척수액이나 두개 강 내 피가 골절된 두개골 사이를 통해서 콧구멍 속, 목구멍 속, 귓구멍 속, 또는 안구 속 등으로 흘러나올 수 있다.
-
두개골이 골절되었을 때 귓바퀴의 바로 뒤에 있는 유양돌기 부위에 피가 맺히고 멍들 수 있다. 이런 징후를 “배틀 징후(Battle sign)”라고 한다.
-
두개골저 골절이 있을 때 유양돌기의 부위에 피가 맺힐 수 있고 두개강 내 피나 척수액이 안구 속이나 안구 주위 속으로 흘러나와 두 눈이 래쿤(너구리 비슷한 북아메리카 산 포유동물)의 눈과 같이 보일 수 있다. 이런 징후를 래쿤 눈 증후(raccoon eye sign)라고 한다.
-
코구멍 속에서, 귓구멍 속에서 척수액과 피가 흘러나올 수 있다.
-
12개의 뇌신경들 중 일부가 마비될 수 있다.
-
뇌척수액이 귓구멍 속으로 흘러나올 때 귀젖이 흘러나오는 것으로 오진할 수 있다.
-
뇌척수액이 비강 속으로 흘러나올 수 있다.
-
두개골이 골절되면서 이런 증상 징후가 있을 때는 상당히 위험한 건강 상태에 있는 두개골 기저 골절이 있다는 것을 의미한다.
-
1 뇌신경 손상이 생기면 냄새를 잘 맡지 못한다.
-
두개골이 아주 심하게 골절되었을 때는 전신경련을 할 수 있고 혼수될 수 있다.
-
양쪽 동공의 크기에 차이가 날 수 있다.
-
이 정도로 여러 종류의 증상 징후가 있으면서 두개골이 심하게 골절되었을 때 응급으로 적절히 치료하지 않으면 생명에도 위험할 수 있다.
두개골 골절의 진단
-
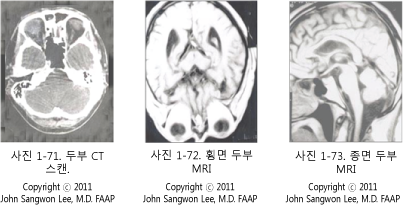
증상 징후와 진찰 소견 등을 종합해서 두개골(두개골)이 골절되었다고 의심되면 두개골 X선 사진 검사, CT 스캔 검사, MRI 검사 등으로 확진할 수 있다.
-
복잡 두개 골절이 있을 때는 뇌 일부가 골절된 두개골 사이로 삐져나올 수 있다. 이 경우, 언뜻 보고서도 두개골이 골절됐다는 것을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
-
경미하게 골절되었을 때는 육안으로 두부를 보고 두개골 골절이 있다는 것을 쉽게 진단할 수 없다.
-
두개골 기저(頭蓋骨基底)에 경미한 골절이 있을 때는 두개골 X선 사진 검사로 골절된 부위를 찾기가 힘든 경우도 있다.
두개골 골절의 치료
-
두개골 골절의 종류와 정도, 두개골이 골절될 때 생긴 다른 외상의 유무 등에 따라 치료가 다르다.
-
두개골 골절이 의심되면 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과에 긴급히 전화해서 그들의 지시에 따라 구급차나 다른 교통수단으로 종합병원 응급실로 빨리 이송한다.
-
의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과 의사가 환아가 있는 현장으로 도착하기 전이나 병원 응급실에 환아를 데리고 가는 중에도 의사의 지시에 따라 적절히 1차 응급치료를 한다.
-
뇌가 손상되지도 않고 증상 징후도 거의 없는 경미한 두개골 골절은 특별한 치료가 요하지 않고 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 지시에 따라 관찰 치료만 해도 된다.
-
두개골 골절의 종류와 정도에 상관없이 전신경련이나 두개강 내에 출혈이 생기는지 조심히 관찰 치료를 해야 한다.
-
두개골 골절과 뇌 손상이 심하게 생겨 있을 때는 의식의 일부 또는 전부를 잃고 쇼크에 빠질 수도 있다.
-
이때는 침착하게 급히 인간 기본 생명 유지 기본 심폐 소생술 처치법으로 응급치료를 해야 한다. 이때 가능한 한 환아를 현장에서 다른 곳으로 함부로 옮겨서도 안 된다.
-
인간 기본 생명 유지 기본 심폐 소생술 처치법을 할 때, 맨 먼저 숨을 정상적으로 쉬는지 확인하고 만약 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못하면 기도를 확보하고 환아의 입 또는 입과 코에 처치자의 입을 대고 인공호흡을 시작하고, 심장이 뛰지 않거나 아주 느리게 뛸 때는 심장 마사지도 동시 해야 한다.
-
즉 숨을 쉬게 하고 심장이 뛰도록 하는 기본 심폐소생술 처치법을 필요에 따라 해야 한다.
-
최근에는 성인의 경우, 인공호흡 응급처치를 최초로 하는 대신 심장 마사지를 제일 먼저 하라고 한다.
-
목을 꼭 죄게 해 기도를 막히게 하는 옷을 느슨하게 풀어주고 두피나 신체 다른 부위에 생긴 열상이나 자상 등에서 나는 출혈을 지혈시켜야 한다.
-
두개골이나 뇌가 교통사고 등으로 크게 다쳤을 때는 신체의 다른 부위에도 외상이 있을 수 있다. 그런 외상이 발견되면 그것도 동시에 적절히 응급치료해야 한다.
-
쇼크가 생겼을 때도 산소호흡, 인공호흡, 심장 마사지 등으로 인간 기본 생명 유지 심폐 소생술 처치법으로 치료한다. 이런 치료의 순서를 일률적으로 정하기 어려우나
-
기도를 확보하고, 숨쉬기 복구(AB),
-
혈액순환과 심장 기능회복(C),
-
진단(D) 치료(D) 등의 순서로 처치한다.
-
즉 ABCD 또는 ABCDD 순서로 응급처치한다.
-
-
심하게 출혈하면 지혈시키는 동시에 호흡이 곤란하면 숨을 쉬게 하는 처치가 우선순위이다.
-
그와 동시에, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과나 의료구급대에 긴급으로 전화해서 그들의 지시에 따라 응급처치를 시작하면서 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단으로 환아를 급히 종합 병원 응급 의료실로 이송 한다.
-
두개골 골절의 75%는 단순 선상 두개골 골절에 속하고, 합병증이 없는 단순 선상 두개골 골절은 특별한 치료가 요하지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
그렇지만 단순 선상 두개골 골절을 입었을 때 두부에 심한 타박상을 입었을 수 있고 뇌가 심하게 손상될 수 있다. 따라서 아무런 증상 징후가 없을지라도 적어도 이틀 동안 입원해서 관찰 치료를 받는 것이 좋다.
-
두개골이 골절되어 두개골의 일부가 두개골강 속으로 함몰되었을 때는 함몰 두개골 골절이 생긴 두개골의 바로 밑에 있는 뇌실질이 찢어지거나 뇌실질이 타박상을 입을 수 있다.
-
함몰 두개골 골절이나 다른 종류의 두개골 골절이 다 나은 후에 후유증으로 간질(뇌전증)이 유발될 수 있다.
-
함몰 두개골 골절의 정도에 따라서 함몰 두개골 골절이 생긴 두개골을 수술 복구 치료를 하는 것이 보통이다.
-
찢어지거나 찔린 두피는 멸균 거즈로 피를 깨끗이 닦고 베타다인액 살균제 등으로 살균치료를 하고 필요에 따라 찢어진 두피를 봉합 수술 치료를 한다.
-
필요에 따라 파상풍 백신 예방접종을 받는다.
Skull fractures두개골 골절
Types of skull fractures
-
The skull is called the head bone.
-
The skull may be fractured if the head is injured in a traffic accident or safety accident, or if the head is injured while exercising or playing games. When a fracture occurs in the skull, only the skull is fractured.
-
Fractures of the skull and damage to the brain in the cranial cavity may occur, and blood vessels in the cranial cavity may burst, resulting in intracranial bleeding.
-
When the head (head) is severely injured, the skull is not fractured, but the brain in the cranial cavity can be severely damaged and bleeding within
the brain can result in death.
▴ Picture 94. Spit of the frontal bone scalp Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP‘
-
Depressed skull fracture
-
When part of a ping pong ball is broken, part of a fractured skull can be pushed into the skull cavity, just as a part of the ping pong ball’s shell is pushed into the inside of the ping pong ball.
-
This type of skull fracture is called a depressed skull fracture.
-
Conversely, a severe fracture of the skull can damage the brain in the cranial cavity very slightly. However, when the head is severely injured enough to fracture the skull, it is common for the scalp, skull, and brain to be simultaneously damaged.
-
Linear skull fracture
-
Fractures of fine line cracks in the skull are called linear skull fractures.
3. Crushed skull fracture
-
Fractures of the skull in which a portion of the skull is broken into pieces are called comminuted skull fractures.
4. Complex skull fracture
-
Skull fractures are sometimes classified as simple or compound.
-
A fracture of the skull when the scalp immediately above the fractured part of the skull is intact is called a simple skull fracture.
5. When there is a scalp injury or a skull fracture, it is called a complex skull fracture.
-
Skull fractures can be classified according to the type of skull fracture.
-
Linear complex skull fracture,
-
Indented complex skull fracture,
-
Fractures of the skull are sometimes classified as comminuted, complicated skull fractures. Only one part of the skull may be fractured, or several parts may be fractured simultaneously.
6.Skull fractures can be classified according to the skull area.
-
Frontal skull fracture,
-
Temporal skull fracture,
-
Fracture of the epiglottis,
-
Parietal fracture,
-
Skull fractures can be classified as such as Basal skull fractures or Basilar skull fractures.
Causes of skull fracture
-
During delivery, the baby’s head may be pressed against the mother’s birth canal and the skull may be fractured.
-
and the baby’s skull may also be fractured when delivered with forceps. When you fall from a high place and hit your head,
-
When you hit your head badly somewhere,
-
The skull can be fractured in a traffic accident or a safety accident,
-
Child abuse can lead to a fracture of the skull.
Symptoms and Signs of a Skull Fracture
-
Symptoms differ depending on the type and degree of skull fracture, the area of the head where the skull fracture occurred, and the degree of brain damage in the cranial cavity that can occur when the skull is fractured.
-
Symptoms of a newborn skull fracture, when the baby’s head is pressed hard against the birth canal during delivery, are usually mild, and sometimes there may be few symptoms.
-
When falling from a high place, such as a staircase, to the floor from a desk or other high place, the skull can be slightly fractured or severely fractured.
-
When the skull is fractured, it may cry lot, the face may become pale, vomiting, and loss of consciousness for a while.
-
Sometimes, you can have a general convulsion.
-
See cephalohematoma, head trauma.
-
When a simple linear skull fracture occurs, there may be few or mild symptoms.
-
The scalp just above the fractured skull area is swollen, and if you touch the scalp with your hand, it may be soft and painful.
-
Simple linear skull fractures in newborns at birth are often accompanied by cephalohematomas.
-
When the skull is slightly fractured, the head may be sore, vomiting, dizzy, light-headed, and a pale face.
Picture 97. CT scan of the head Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
-
When the skull is severely fractured, it can deform.
-
When a fracture of the base of the skull–cranial base (頭蓋骨基底) occurs, cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity or blood in the cranial cavity can flow through the fractured skull into the nostrils, into the throat, into the ear canal, or into the eyeball.
-
When the skull is fractured, blood may form and bruise in the mastoid process immediately behind the auricle.
-
These signs are called “Battlle signs.”
-
When there is a cranium fracture, blood may form in the area of the mastoid process, and blood or spinal fluid in the cranial cavity may flow into or around the eyeball, making the eyes look like the eyes of a raccoon (a North American mammal similar to a raccoon).
-
These signs are called raccoon eyes. Spinal fluid and blood can flow out of the nose hole and the ear canal.
-
Some of the 12 cranial nerves can be paralyzed.
-
When cerebrospinal fluid flows into the ear canal, it can be misdiagnosed as oozing out of the ear.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid can flow into the nasal cavity.
-
When the skull fractures and signs of these symptoms are present, it means that there is a fracture of the base of the skull, which is a very dangerous health condition.
-
1 If there is damage to the brain nerve, the smell is not good.
-
When the skull is very severely fractured, it can cause general convulsions and coma.
-
There may be differences in the size of both pupils.
-
When there are so many signs of symptoms and a severely fractured skull, it can be dangerous to life if not properly treated as an emergency.
Diagnosis of skull fracture
-
If you suspect that the skull (skull) is fractured by combining symptoms and examination findings, it can be confirmed with a skull X-ray scan, CT scan, MRI scan, etc.
-
In complex cranial fractures, part of the brain may protrude through the fractured skull.
-
In this case, at first glance, it is easy to diagnose that the skull has been fractured. In the case of a minor fracture, it is not easy to diagnose that there is a skull fracture by looking at the head with the naked eye. When there is a minor fracture at the base of the skull, it may be difficult to find the fractured area with an X-ray of the skull.
Treatment of skull fractures
-
Treatment differs depending on the type and extent of skull fractures, and the presence or absence of other traumas caused when the skull is fractured. If a skull fracture is suspected, call the medical paramedics, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrics department in an emergency and follow their instructions to quickly transfer them to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other means of transportation.
-
Before the medical paramedics and regular pediatricians arrive at the site where the patient is present or while taking the child to the hospital emergency room, appropriate primary emergency treatment is provided according to the doctor’s instructions.
-
Minor skull fractures with no brain damage and few signs or symptoms require no special treatment and can only be treated with observation according to the instructions of a regular pediatrician.
-
Regardless of the type and severity of skull fractures, careful observational treatment should be performed for general cramps or bleeding in the cranial cavity.
-
When skull fractures and brain damage are severe, you may lose some or all of your consciousness and fall into shock. In this case, it is necessary to calmly and urgently perform emergency treatment with basic CPR to maintain basic human life.
-
At this time, the patient should not be moved from the site to another place as much as possible.
-
Maintaining Basic Human Life. When performing basic CPR treatment, first check whether you are breathing normally. If you cannot breathe properly, secure an airway, place the patient’s mouth on the child’s mouth or mouth and nose, and start artificial respiration. When this is not running or running very slowly, you should also do a heart massage at the same time. In other words, basic CPR procedures that allow you to breathe and make your heart beat must be performed as needed. In recent years, adults are advised to do heart massage first instead of artificial respiration.
-
Tighten the neck to loosen clothes that block the airways, and stop bleeding from lacerations or cuts on the scalp or other parts of the body. When the skull or brain is severely injured in a car accident, other parts of the body may also be traumatized. If such trauma is found, it should be treated appropriately at the same time.
-
Even when shock occurs, it is treated with basic human life-sustaining cardiopulmonary resuscitation, such as oxygen breathing, artificial respiration, and heart massage.
-
Is it difficult to uniformly determine the order of these treatments?
-
Secure airways, restore breathing (AB), Blood circulation and recovery of heart function (C), Treatment is performed in the order of diagnosis (D) treatment (D), and the like.
-
That is, first aid is given in the order of ABCD or ABCDD. The priority is to stop bleeding when severe bleeding and to breathe when breathing is difficult.
-
At the same time, urgently call the hospital emergency room, a regular pediatrics department or medical paramedic to initiate first aid according to their instructions, and hurriedly transfer the child to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation. 75% of cranial fractures belong to simple linear cranial fractures, and simple linear cranial fractures without complications usually do not require special treatment.
-
However, if you have a simple linear skull fracture, you may have severe bruises in the head and severe damage to the brain.
-
Therefore, even if there are no signs of symptoms, it is advisable to stay in the hospital for at least two days and receive observational treatment.
-
When the skull is fractured and part of the skull is recessed into the cranial cavity, the brain parenchyma immediately underneath the skull where the indented skull fracture has occurred may be torn or bruise to the brain parenchyma.
-
Epilepsy (epilepsy) can occur as a sequela after a depressed skull fracture or other types of skull fractures have healed.
-
Depending on the severity of the indented skull fracture, it is common to perform surgical repair treatment on the skull with the indented skull fracture. • For torn or stabbed scalp, clean the blood with sterile gauze, sterilize with betadine solution, etc., and suture the torn scalp if necessary.
-
Get tetanus vaccine as needed.
출처 및 참조문헌
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics: A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D., with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan Stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding, by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook, 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey, 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other