무릎 관절이 다쳤을 때와 무릎 관절 속 뼈 골절
Knee injury and fractures of knee bones
무릎 관절이 다쳤을 때의 개요
- 장난, 운동, 또는 교통사고 등으로 무릎 관절이 다칠 수 있고 무릎 관절이 손상될 수 있다.
- 무릎 관절은
-
- 대퇴골 원위 골단(뼈끝),
- 슬개골,
- 경골 근위 골단,
- 비골 근위 골단,
- 연골,
- 인대,
- 건,
- 근육,
- 피부 등으로 구성되어 있다.
- 무릎 관절 속 앞 부위에는 둥글고 납작한 뼈가 하나 있다. 그 뼈를 슬개골(膝蓋骨/Patella)이라고 한다.
- 무릎 관절의 맨 아래 부위에 경골 근위 두부와 비골 근위 두부가 있고 그 무릎 관절의 맨 위 부위에 대퇴골의 원위 두부가 있다.
- 무릎 관절을 심하게 다쳤을 때는 앞서 설명한 무릎 관절을 이루고 있는 여러 종류의 뼈들 중 한개 내지 여러 개가 동시 골절될 수도 있고, 무릎 관절을 형성하는 근육, 인대, 건, 활막, 혈관, 또는 신경 등이 동시 손상될 수 있다.
- 무릎 관절이 다치면 그 관절 주위에 있는 피부, 근육, 측부 인대, 전슬 십자 인대, 활막, 혈관, 신경, 슬개골, 대퇴골 원위 골단, 비골 근위 골단, 경골 근위 골단 중 일부나 또는 몇 가지가 손상될 수 있다.
- 무릎 관절 측부 인대 외상(Collateral ligament injury of the knee)이 생긴 무릎 관절 부위를 만지면 아프고 무릎을 꾸부릴 때 통증이 생기고 무릎 관절 속에 삼출액이 고여 무릎이 붓고 체액이 고인다.
- 무릎 관절 X선 사진 검사로 확진하고 무릎을 고정시켜 치료 하고 필요에 따라 수술로 치료를 한다.
- 무릎 관절에 탈구가 생길 수 있고 탈구와 무릎 관절을 구성하는 뼈의 골절이 함께 생길 수 있다.
- 무릎 관절에 있는 말초 신경과 혈관 이상이 생길 수 있다.
- 무릅 관절을 다치면 정형외과 전문의의 치료를 받아야 한다.
사진 1-154. 무릎 관절. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
슬개골 외상과 탈골
-
외상으로 슬개골이 골절될 수 있고 탈골도 될 수 있다.
-
슬개골 탈골은 사춘기 아이들에게 더 잘 생기고 남아들보다 여아들에게 더 잘 생긴다.
-
걸을 때 무릎 관절의 아래 부위에 있는 다리가 외반 된다.
- 슬개골이 탈골된 무릎부위가 아프고 무릎을 만지면 뽀각뽀각 소리가 나고 압통이 생긴다.
- 자연적으로 제자리로 돌아갈 수 있다.
- 갑자기 탈골될 때는 손으로 만져 복구시킬 수도 있다.
- 의사의 지시에 따라 약 3주 동안 그 무릎을 움직이지 말고 무릎을 쓰지 않는 안정치료를 한다.
- 재발되면 수술로 고정치료를 받는다.
무릎 관절이 다칠 때의 증상 징후
- 무릎 관절을 형성하고 있는 대퇴골의 원위 골단, 비골 근위 골단, 경골 근위 골단, 슬개골 중 어느 뼈가 어느 정도로 골절되었는지에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 무릎 관절 속에 있는 뼈가 골절되면 무릎이 붓고, 아프며, 골절된 무릎 부위를 손으로 누르거나 무릎을 능동적으로나 수동적으로 움직이면 무릎이 상당히 아픈 것이 보통이다.
- 골절된 무릎을 능동적으로나 수동적으로 굽혔다 폈다 하기가 대단히 곤란하다.
- 어떤 때는 골절된 뼈끝이 서로 어긋날 수도 있고, 골절된 뼈끝이 간격을 두고 서로 떨어지고 분리될 수도 있다.
- 골절된 뼈의 양쪽 끝에 생긴 사이를 손으로 만져볼 수도 있고 손가락 하나가 그 간격 사이로 들어갈 수 있을 정도로 골절된 두 뼈끝에 간격이 생길 수도 있다.
- 무릎 관절 뼈 골절이 심하게 생겼을 때는 골절된 뼈끝이 피부 층을 꿰뚫고 피부 밖으로 삐져나올 수도 있다.
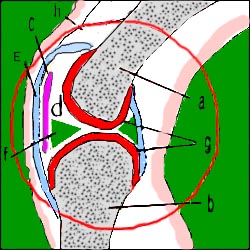
▴ 그림 141. 무릎 관절의 구조
a-대퇴골의 원위골단, b-경골의 근위 골단, c-슬개골, d-관절낭, e-활막, f-메니쿠스(관절반월), g-관절연골, h-인대. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
무릎 관절 속 뼈가 골절될 때의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 무릎 관절의 뼈가 골절되었다고 의심되면 무릎 관절 X선 사진 검사 등으로 진단한다.
무릎 관절 속 뼈가 골절될 때의 치료
- 무릎 관절을 심하게 다쳐 무릎 관절에 있는 뼈(슬개골이나, 대퇴골 원위 골단, 경골 근위 골단, 또는 비골 근위 골단)가 골절됐다고 의심하면 가능한 한 그 무릎을 더 이상 움직이지 말아야 한다.
- 가능하면 다친 무릎을 처음 목격한 상태 그대로 두고 의료구급대, 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 긴급으로 전화해서 그들의 지시에 따라 사고 현장에서 응급치료를 시작한다.
- 우선, 환아를 안정시킨다.
- 의사나 그들의 지시에 따라 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단으로 병원 응급실로 급히 이송한다.
- 무릎 관절 속에 있는 뼈가 골절되었다고 의심되면 그 쪽 다리의 혈액순환이 잘 되는지 체크한다. 다친 무릎 관절의 아래 있는 피부 피부의 혈색을 관찰 한다.
- 그 쪽 발등 동맥 맥박을 정상인지 확인 한다.
- 의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과 의사가 사고 현장으로 올 수 없을 때는 상황에 따라 발목 관절 뼈 골절을 치료할 때와 거의 같이 처음 목격한 상태 그대로 무릎 관절을 계속 유지하면서 골절된 무릎 관절과 그 쪽 위아래 다리 전체에 부목을 대어 무릎을 고정시킨 후에 병원 응급의료실로 이송한다.
- 만약에 골절된 무릎 관절의 아랫다리가 창백하거나 파랗거나 감각 이상이 있을 때는 조금도 지체하지 말고 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 긴급으로 전화해 그들의 도움을 받으면서 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단으로 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 간다.
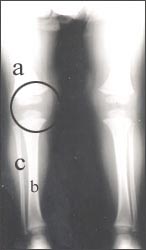
▴ 사진 1-155. ◯로 표시한 부위에 무릎 관절
a-대퇴골, b-경골, c-비골
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
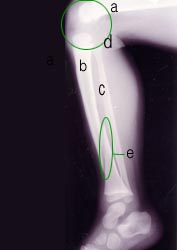
▴ 사진 1-156. ◯로 표시한 부위에 무릎 관절
a-대퇴골, b-경골, c-비골, d-무릎 관절, e ◯내–경골 골절
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
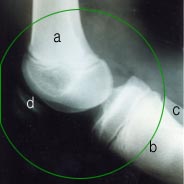
▴ 사진 1-157. 무릎 관절의 측면 X선 사진
◯로 표시한 부위에 무릎 관절
a-대퇴골, b-경골, c-비골, d-슬개골
경골 두부와 비골 두부가 탈구됐다.
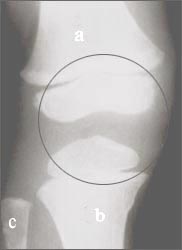
▴ 사진 1-158.정상 무릎 관절의 측면 X선 사진
◯로 표시한 부위에 무릎관절이 있다.
a-대퇴골, b-경골, c-비골, d-슬개골
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
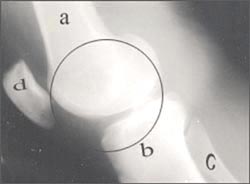
▴ 사진 1-159. 정상 무릎 관절의 전후면 X선 사진
◌내에 무릎 관절
a-대퇴골, b-경골, c-비골
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
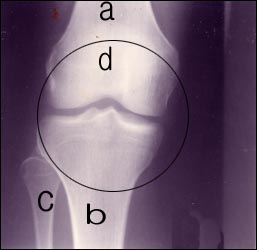
▴ 사진 1-160. 정상 무릎 관절의 전후면 X선 사진
◯내 무릎 관절
a-대퇴골, b-경골, c-비골, d-슬개골
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Knee injury and fractures of knee bones
무릎 관절이 다쳤을 때와 무릎 관절 속 뼈 골절
Overview of injuries to the knee joint
- A playing, exercise, or car accident can injure the knee joint and damage the knee joint.
- Knee joint
1.Distal femur epiphysis (end of bone),
2. patella,
3. Proximal tibia epiphysis,
4 Proximal fibula epiphysis,
5. cartilage,
6. Ligament,
7. tendon.
8 .muscle,
9. It is composed of skin, etc.
- There is a round- flat bone in the front part of the knee joint.
- The bone is called the patella.
- The proximal tibia head and the proximal fibula head at the bottom of the knee joint, and the distal head of the femur at the top of the knee joint.
- When the knee joint is severely injured, one or several of the various types of bones that make up the knee joint may be fractured simultaneously, and the muscles, ligaments, tendons, synovium, blood vessels, or nerves that form the knee joint may be simultaneously damaged.
- Injuries to a knee joint may damage some or some of the skin, muscles, collateral ligaments, anterior knee cruciate ligaments, synovial membranes, blood vessels, nerves, patella, distal femur, proximal fibula, and proximal tibia. have.
- If you touch the area of the knee joint where the collateral ligament injury of the knee has occurred, it hurts and causes pain when bending the knee, and effusion accumulates in the knee joint, causing the knee to become swollen and fluid. It is confirmed by an X-ray examination of the knee joint, the knee is fixed and treated, and if necessary, the treatment is performed with surgery.
- A dislocation may occur in the knee joint, and dislocation and fracture of the bones that make up the knee joint may occur together.
- Peripheral nerve and blood vessel abnormalities in the knee joint can develop.
- If you injure your knee joint, you should seek medical attention from an orthopedic surgeon.

Photo 1-154. Knee joint. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Patella trauma and dislocation
- Trauma can fracture the patella and can lead to dislocation.
- Patella dislocation is more prone to adolescent children and more prone to girls than boys. When walking, the leg in the lower part of the knee joint becomes valgus.
- When the kneecap is dislocated, it hurts, and when you touch the knee, you will hear a popping sound and tenderness.
- It can naturally return to its place.
- Sudden dislocation can be repaired by touching it with your hand.
- Follow the doctor’s instructions for about 3 weeks without moving the knee and provide a stable treatment without using the knee.
- If it recurs, receive fixed treatment through surgery.
Symptoms Signs
- When Injured Knee Joint Symptoms differ depending on the degree of fracture of the distal epiphysis of the femur that forms the knee joint, the proximal fibula, the proximal tibia, and the patella.
- When bones in the knee joint are fractured, the knee is swollen and painful, and when the fractured knee is pressed with the hand or actively or passively moved, the knee is usually quite painful. It is very difficult to actively or passively bend and unfold a fractured knee.
- Sometimes the fractured bone ends may deviate from each other, and the fractured bone ends may be separated and separated from each other at intervals.
- You can touch the gap between the two ends of the fractured bone with your hand, or there may be a gap between the ends of the fractured bones enough that one finger can fit into the gap. When a knee joint bone fracture is severe, the fractured bone tip may penetrate the skin layer and protrude out of the skin.

▴ Figure 141. The structure of the knee joint a-distal epiphysis of the femur, b-proximal epiphysis of the tibia, c-patella, d-articular capsule, e-synovial, f-meniscus (articular meniscus), g-articular cartilage, h-ligament. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Diagnosis when bones in the knee joint are fractured
- If it is suspected that the bones of the knee joint have been fractured by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, it is diagnosed with a knee joint X-ray photograph.
- Treatment when bones in the knee joint are fractured If you suspect that the knee joint is severely injured and the bone in the knee joint (patella, distal femur, proximal tibia, or proximal fibula) is fractured, the knee should not be moved as much as possible.
- If possible, leave the injured knee as it was first seen, call a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or a regular pediatrician in an emergency and follow their instructions to initiate emergency treatment at the accident site.
- First of all, stabilize the patient.
- Urgently transported to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation, as directed by the doctor or theirs.
- If you suspect that a bone in the knee joint is broken, check that the blood circulation in that leg is good.
- Observe the skin color of the skin under the injured knee joint. Check that the pulse of the dorsal artery on that side is normal.
- When a medical paramedic or a regular pediatrician cannot come to the accident site, depending on the situation, the fractured knee joint and the entire upper and lower leg of the fractured knee joint and the entire upper and lower legs are maintained while maintaining the knee joint as it was first witnessed, almost as when treating an ankle joint bone fracture. The knee is fixed by applying a splint to it, and then transported to the hospital emergency room. If the lower leg of the fractured knee joint is pale, blue, or numb, do not delay at all and call the hospital emergency room or a regular pediatrician in an emergency to get their help and go to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation. I take it in a hurry.

▴ Picture 1-155. Knee joint at the area marked with ◯ a-femur, b-tibia, c-fibula Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-156. Knee joint at the area marked with ◯ a-femur, b-tibia, c-fibula, d-knee joint, e ◯intra-tibia fracture Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

▴ Picture 1-157. Lateral X-ray picture of the knee joint Knee joint at the area marked with ◯ a-femur, b-tibia, c-fibula, d-patella The tibia head and fibula head were dislocated.

▴ Picture 1-158. Lateral X-ray picture of normal knee joint There is a knee joint in the area marked with ◯. a-femur, b-tibia, c-fibula, d-patella Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-159. X-ray image of the front and rear of the normal knee joint ◌in the knee joint a-femur, b-tibia, c-fibula Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-160. X-ray image of the front and rear of the normal knee joint ◯ My knee joint a-femur, b-tibia, c-fibula, d-patella
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026