손뼈 골절이나 손가락뼈 골절
Fractures of hand bones or finger bones (Hand fractures or finger fractures)
손뼈 골절과 손가락뼈 골절의 개요
-
손뼈는
-
-
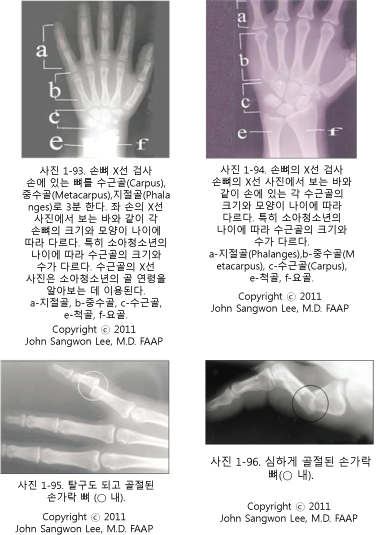
수근골(팔목관절에 연결되는 손목 뼈/Carpus),
-
5개의 중수골(손의 중간에 있는 뼈 손바닥 뼈/손 허리뼈/Metacarpus),
-
지절골(손가락 뼈/Phalanges)로 형성된다.
-
-
둘째, 셋째, 넷째, 5째의 손가락에 있는 지절골은
-
-
근위 지절골과
-
원위 지절골과
-
중간 지절골로 나누어진다.
-
-
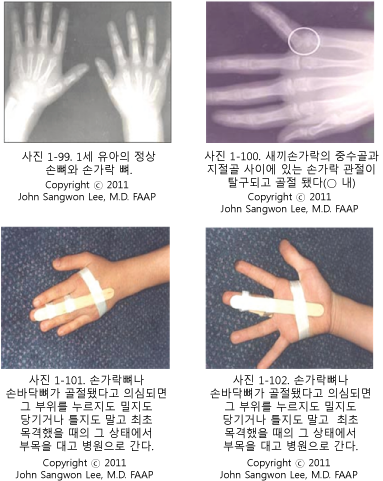
생후 7~8세부터 성인의 수근골의 수는 8개이다. 그 이 전에는 나이에 따라 수근골 수가 다르다.
-
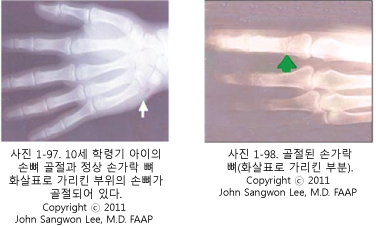
여러 개의 손뼈들 중 어느 손뼈도 골절될 수 있다.
-
손뼈의 골단, 골간 등 어느 부위가 골절될 수 있다.
-
운동, 장난, 또는 사고 등으로 손뼈와 손뼈 관절 또는 손가락 마디에 있는 관절(수지 관절)이 삘 수 있고, 삐고 골절이 동시에 생길 수 있다.
-
특히 소아청소년들이 육체적 운동을 하다가 손바닥이나 손가락, 또는 손목관절에 있는 인대가 손상 되어 삘 수도 있고, 손에 있는 뼈가 골절될 수 있다.
손뼈골절과 손가락뼈 골절의 증상 징후
-
손뼈의 골절의 정도와 골절된 손뼈 부위에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
일반적으로 손뼈 골절이 된 부위가 붓고 만지면 아프며 골절이 되고 외상 입은 손 부위를 정상적으로 움직일 수 없다.
손뼈 골절과 손가락뼈의 골절의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 손바닥뼈(수근골과 중수골)나 손가락뼈(수지골/ 지골)가 골절됐다고 의심되면 손바닥 뼈나 손가락 뼈 X-선 사진 검사로 쉽게 진단한다.
-
손바닥뼈나 손가락뼈 골절이 있을 때의 증상 징후가 있는데도 X-선 검사에는 골절이 보이지 않을 수 있다.
-
이런 때는 골절이 있다고 추정 진단을 하고 손바닥뼈 골절이나 손가락뼈 골절 치료를 하는 것과 같이 우선 적절히 치료하고 첫 X-선 검사를 한 후 7-10일 후에 추적 X선 검사를 해서 손뼈 골절을 확진할 때도 있다.
손바닥 뼈 골절과 손가락 뼈 골절의 치료
-
손바닥 뼈 골절이나 손가락뼈의 골절의 정도에 따라 치료한다.
-
삐거나 골절된 손바닥뼈나 손가락 뼈, 또는 손가락 관절을 적절히 치료하지 않으면 손바닥이나 손가락에 기형이 생길수도 있고 기능장애가 생길 수 있다. 그 기형이나 기능 장애가 일생 동안 지속 될 수 있다.
-
이런저런 이유로, 손바닥 뼈, 손가락 뼈, 손목 관절뼈가 골절되거나 손에 외상이 생기면 손바닥 뼈나 손가락 뼈 문제를 특별히 전문하는 손 전문 정형외과 전문의의 적절한 치료를 받는다. 손에 외상을 입으면 가능하면 우선 환아를 안정시키고 안전한 곳으로 옮긴다.
-
손가락 뼈나 손바닥 뼈가 골절되었다고 의심되면 의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년 의사나 병원 응급실에 긴급으로 전화해서 그들의 지시에 따라 사고 현장에서 응급치료를 시작한다.
-
손바닥 뼈 골절의 정도에 따라 적절한 교통수단을 이용해서 종합 병원 응급실로 데리고 간다.
-
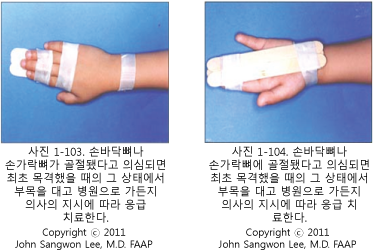
손바닥 뼈가 골절이 됐다고 의심하면 골절이 됐다고 추정되는 손가락과 그 주위의 정상 손가락, 손바닥, 팔목, 아래팔을 부목으로 우선 임시 고정처치 한다.
-
부목을 대기 전과 대는 중, 댄 후에 골절된 손가락과 손의 피부색, 그쪽 손톱 밑 혈색, 손이나 손가락에 분포된 말초신경 기능이 정상인지 체크해 본다.
-
손이나 손가락이 파랗거나 거기에 아무 감각이 없거나 자유자재로 움직일 수 없으면 현장에서 단골 소아청소년과 의사나 병원 응급실에 긴급 전화 문의 진료 상담을 해 그들의 지시대로 응급처치를 한다.
-
그렇지 않으면 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 간다.
-
손바닥 뼈나 손가락 뼈가 골절되었을 때 적절한 시기에 적절히 치료하지 않으면 손이나 손가락의 기능 장애가 생겨 평생 불구자가 될 수 있다고 이미 언급했다.
-
특히, 소아 지골 골절을 적절히 치료하지 않으면 회전변형이 생길 수 있다.
-
금만 간 지골 골절은 2~3주 동안 부목으로 치료하고 3~4주 동안 골절된 지골의 바로 옆에 있는 다음 손가락을 함께 테이프 고정으로 치료한다.
-
중수골이 골절됐을 때는 중수골이 골절된 정도에 따라 캐스트 고정 치료를 하거나 부목으로 치료하든지, 또는 수술로 치료 할 수 있다.
-
따라서 손바닥 뼈나 손가락 뼈가 골절되었거나, 마디가 탈구되었거나, 삐었을 때는 일반 정형외과 전문의나 손뼈 골절 전문 정형외과 전문의의 치료를 받는다.
다음은 “손가락 좌상, 새끼손가락 좌상”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 손가락 좌상, 새끼손가락 좌상
Q.
생후 8개월 된 여아입니다.
방문 틈에 세끼손가락이 껴있는 상태에서 오빠가 문이 닫힐 정도로 세게 닫았습니다.
동네 의원에서 엑스레이를 찍었는데 애기가 가만히 있지를 않아 뼈 상태는 확실하지 않다고 하고 괜찮을 거라고 합니다.
손가락 마디 마디가 부어있고 멍이 들어있으며 손 끝은 핏기가 있습니다.
성장판이 손상되면 손가락도 자라지 않는다고 하는데 어떻게 하면 확인을 할 수 있는지요. 혹시 뼈에 이상이 있을 수 있나요. 꼭 답변 부탁드립니다.
A.
지원님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
자세한 정보를 주셔서 감사합니다.
8개월 된 영아들의 신체의 어떤 부위의 X-사진을 찍는 것은 때로는 여간 힘든 일이 아닙니다.
그래서, 아기가 낮잠을 자는 동안에 X선 사진을 다시 한 번 찍어보는 것이 좋을 것입니다.
드물게는 정신안정제로 안정시키고 뼈 X-사진 검사를 할 때도 있습니다.
손가락 뼈에 골절됐다고 추정하고 골절 됐다고 추정하는 손가락 뼈 골절이 있는 손가락과 손에 부목을 대어 고정 치료를 하는 것이 좋을 것입니다.
요즘 정형외과가 소아 정형외과, 성인 정형외과로 크게 나누어져 있습니다.
또 소아 정형외과 전문의들 중 손 정형외과만 전공하는 전문의도 있습니다.
필요하면 단골 소아청소년과에 부탁해 손만 전문으로 하는 소아 정형외과 전문의에게 의뢰해 달라고 하세요.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환–손뼈와 손가락 뼈의 골절, 골절 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 그리고 질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Hand Bone Fractures and Finger Bone Fractures
손뼈 골절이나 손가락뼈 골절
Overview of Hand Bone Fractures and Finger Bone Fractures
Hand Bone
-
The carpal bone (the wrist bone that connects to the wrist joint/Carpus),
-
5 metacarpals (bone metacarpal in the middle of the hand/vertebrae of the hand/Metacarpus),
-
It is formed by phalanges (finger bones/Phalanges).
The phalanges of the second, third, fourth, and fifth fingers
-
Proximal phalanx
-
Distal phalanges
-
It is divided into middle phalanges.
-
From 7 to 8 years old, the number of carpal bones in adults is 8.
-
Before that, the number of carpal bones differed depending on age.
-
Any of the multiple hand bones can be fractured.
-
Any area such as the epiphysis of the hand bone or the bone stem can be fractured.
-
Exercise, play, or accident can sprain the hand bone and the hand bone joint or the joint in the knuckle (the hand joint), and the sprain and fracture may occur at the same time.
-
In particular, during physical exercise in children and adolescents, ligaments in the palms, fingers, or wrist joints may be damaged and sprained, and bones in the hands may be fractured.
Symptoms of a fracture of the hand bone and a fracture of the finger bone
Symptoms and signs differ depending on the degree of fracture of the hand bone and the area of the fractured hand bone.
In general, the fractured part of the hand bone is swollen and painful when touched, and the fractured hand cannot be moved normally.
Diagnosis of fractures of the hand bones and finger bones
-
If it is suspected that the metacarpal bone (carpal bone and metacarpal) or finger bone (carpal bone/phalangeal) is fractured, it is easily diagnosed with an X-ray examination of the metacarpal bone or finger bone.
-
Although there are signs of symptoms when there is a fracture of the metacarpal or finger bone, the fracture may not be visible on the X-ray examination.
-
In such a case, when a fracture is presumed to be diagnosed and a fracture of the hand bone is confirmed by performing a follow-up X-ray test 7-10 days after the first, appropriate treatment, such as a metacarpal fracture or a finger bone fracture treatment, the first X-ray test is performed. have.
Treatment of metacarpal fractures and finger bone fractures
-
Treatment depends on the degree of metacarpal fracture or fracture of the finger bone.
-
If sprained or fractured metacarpals, knucklebones, or knuckle joints are not properly treated, the palms or fingers may be deformed and dysfunctional.
-
The malformation or dysfunction can persist throughout life.
-
For one reason or another, fractures in the metacarpal bones, knucklebones, or wrist joints or trauma to the hand should be treated appropriately by a hand specialist orthopedic specialist specializing in metacarpal or finger bone problems.
-
If hand trauma occurs, first of all, if possible, stabilize the child and move it to a safe place. If you suspect a fracture of a finger bone or metacarpal bone, call a medical paramedic, a regular pediatrician or hospital emergency room, and follow their instructions to initiate emergency treatment at the accident site.
-
Depending on the severity of the metacarpal fracture, take the appropriate means of transportation to the emergency room of the general hospital.
-
If you suspect that the metacarpal bone has been fractured, the finger, which is believed to have been fractured, and the normal fingers, palms, wrists, and forearms around them are first temporarily fixed with a splint.
-
Before and after applying the splint, check whether the skin color of the fractured finger and hand, the color underneath the fingernail, and the peripheral nerve function distributed in the hand or finger are normal.
-
If your hand or finger is blue, there is no sensation in it, or you cannot move freely, call a regular pediatrician or hospital emergency room at the site for medical advice and take first aid according to their instructions.
-
Otherwise, they are taken to the hospital emergency room in a hurry.
-
It has already been mentioned that when a fracture of the metacarpal or finger bone is not properly treated at the right time, the dysfunction of the hand or finger can result, resulting in lifelong disability. In particular, if the pediatric phalanx fracture is not properly treated, rotational deformation may occur.
-
A fracture of the phalanx that has cracked is treated with a splint for 2-3 weeks, and the next finger next to the fractured phalanx for 3-4 weeks is treated with a tape fix.
-
When the metacarpal bone is fractured, it can be treated with a cast fixation treatment, a splint, or surgery, depending on the degree of the metacarpal bone fracture.
-
Therefore, when the metacarpal or finger bone is fractured, the joint is dislocated or sprained, seek treatment by a general orthopedic specialist or an orthopedic specialist specializing in hand bone fracture.
-
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer on “spinning of the finger and sitting of the little finger”.
Q&A.
-
Upper left of the finger, upper left of the little finger
Q.
I have a girl who is 8 months old.
With her three fingers stuck between the door, her brother closed the door hard enough to close it.
She had an x-ray at the local clinic and she said the baby wasn’t still so her bones weren’t sure and she would be fine.
Her knuckles are swollen and bruised, and the tips of her fingers are bloody.
It is said that when her growth plate is damaged, her fingers do not grow.
How can she check it?
Could she ever have something wrong with her bones.
Please answer me.
A.
Support Good morning.
Thanks for asking.
That’s a good question.
The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer.
We will respond based on the information you provided.
Thanks for the detailed information.
Taking X-pictures of any part of the body of 8-month-old infants is sometimes difficult.
So, it would be a good idea to take another X-ray picture while your baby is taking a nap.
Rarely, it is stabilized with a tranquilizer and a bone X-photo examination is sometimes done.
It is advisable to perform a fixation treatment with a splint on the finger and hand with a fractured finger bone, which is presumed to be fractured in the knuckle bone and is presumed to be fractured.
These days orthopedics are largely divided into pediatric orthopedics and adult orthopedics.
Also, among the pediatric orthopedic specialists, some specialists only specialize in hand orthopedic surgery.
If necessary, ask your regular pediatrics and adolescents department to refer you to a pediatric orthopedic specialist who specializes in hand only.
[Parents should also be at least the half-i-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 16 Children and Adolescents Orthopedic Diseases-Please refer to the fractures and fractures of the bones of the hands and fingers. And if you have more questions, please contact us again.
Thank you. Lee Sang-won dream
출처 및 참조문헌
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.160-161
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.536-537
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured,3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.129, 275-276
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons -
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other