Fracture of the humerus
상완골 골절
Overview and causes of humerus fractures
- Here, it is mainly explained because it is okay for a fracture of the humerus, and a description of a fracture of the ulna, radius, or elbow joint is omitted.
- The bone that connects the shoulder joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint (elbow joint) is called the humerus.
- The upper arm bone may be fractured due to exercise, traffic accidents, or safety accidents.
- If a humerus fracture occurs due to an accidental fall while the hand and forearm are stretched out, the upper part of the humerus is likely to be fractured.
- Fractures can occur in the head of the humerus, interosseous fractures can occur, and epiphysis fractures can occur.
- Symptoms and signs are different, and treatment is different depending on which part of the humerus is fractured.
- When the middle part of the humerus is struck, it is easy to fracture the middle part of the humerus.
- When you fall on the elbow, it is easy to fracture the humerus in the elbow area.
- When the humerus is fractured, blood vessels and peripheral nerves around the fractured humerus may be damaged.
- In this way, the humerus can be fractured in various forms.
- For information on fractures other than the humerus fracture, see “Fractures”.
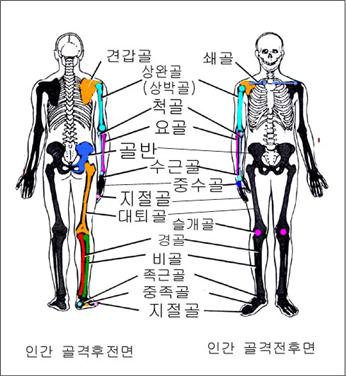
▴ Picture 112. A picture of the human skeleton from the front and back.
Source-Emergency Care, By Grant And Murray
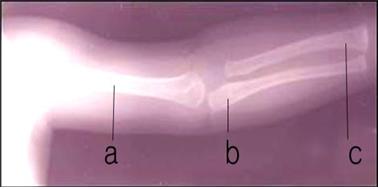
Photo 1-83. X-ray picture of the humerus (a), ulna (b), and radius (c) of a child
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Symptoms and signs of a fracture of the humerus
- Symptoms and signs differ depending on where the humerus is fractured and the degree of fracture.
- The signs of the accompanying symptoms differ depending on the type and severity of the trauma associated with the fracture.
- When the fractured upper arm is swollen and painful, and the arm is actively or passively moved, the pain increases and the arm may become unable to move. It hurts when you press the fractured upper arm with your hand.
- The fractured upper arm cannot be moved normally.
- The end of a fracture of the humerus may damage peripheral nerves, blood vessels, or muscles around it.
- Damage to the peripheral nerve in the arm can cause paralysis of some of the muscles that the peripheral nerve controls.
- At this time, depending on the type of paralyzed nerve and its distribution, the upper arm cannot be actively moved, and some or all of the lower arm may have abnormal sensations.
- If the blood vessels at the fracture site of the humerus are damaged, blood circulation in the upper and lower arms may be impaired, causing changes in skin color and sensation.
Diagnosis of a fracture of the humerus
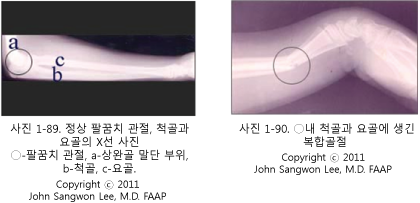
- If you suspect that a fracture of the humerus has occurred by combining symptoms, examination findings, and X-ray, you can take an X-ray of the humerus to confirm it.
Treatment of fractures of the humerus
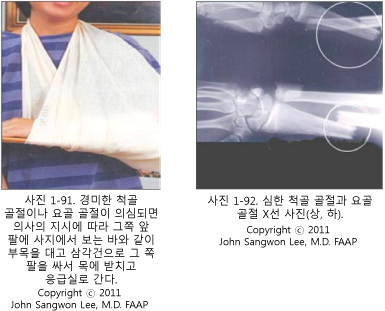
- At the accident site, first stabilize the patient as much as possible and move the child to a safe place.
- Depending on the degree of the humerus fracture, emergency treatment is initiated at the accident site according to the phone instructions from the medical paramedic, the hospital emergency room, or a regular pediatrician.
- As soon as possible, check whether the blood circulation of the arm and hand on the side where the humerus fracture occurs is normal and whether there is a peripheral nerve paralysis of the arm.
- Depending on the situation, before a regular pediatrician or medical paramedic arrives at the scene, keep the fractured arm in the same position as when first seen and stop moving the humerus.
- When the humerus is slightly fractured, according to the doctor’s instructions, wrap the upper arm, lower arm, wrist, and hand together with a triangular tendon and place the other part of the triangular tendon over the neck.
- The upper arm with a fractured humerus can be placed on the child’s torso, and the torso and the fractured upper arm can be fixed with another triangular tendon and transferred to a hospital. At this time, you are using the torso as a splint.
출처 및 참조문헌
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.160
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.524-532
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. p.25, 148-155
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics: A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D., with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan Stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding, by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th-21st ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook, 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey, 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP