객혈(각혈)
Hemoptysis(Bleeding from the lower respiratory tract)
객혈의 개요
-
하기도–후두, 기관, 기관지, 세기관지, 폐 등에서 나온 피(혈액이나 혈담)를 밭아 내는 징후를 객혈이라 한다.
-
위장 관에서 난 피나 피 석긴 구토 물을 뱉어 내는 징후를 토혈(Hematemesis)이라 한다.
-
소아청소년들이 여러 자지 원인으로 객혈을 가끔 경험한다. 비강에서 난 피나 구강이나 인두 강에서 난 피를 뱉어 낼 때 피가 하기도 에서 난 객혈로 오진할 수 있다.
-
때로는 객혈과 토혈을 쉽게 감별할 수 없다.
-
뱉은 피 속에 거품이 섞여 있으면 객혈일 가능성이 더 많다.
-
뱉은 피 색이 검붉거나 짙은 갈색일 때, 또는 뱉은 핏속에 음식물 찌꺼기가 섞어 있을 때는 토혈일 가능성이 더 많다.
-
기침하면서 밭은 피는 각혈일 가능성이 더 있다.
객혈의 원인
▴ 사진 1-174. 정상 가슴 X선 사진.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
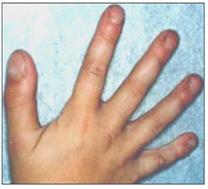
▴ 사진 1-175. 만성 폐병이나 기관지 확장증 등으로 곤봉상지(곤봉 손가락)가 손가락끝 마디에 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
객혈의 원인은 많다.
-
소아청소년들의 객혈의 원인 중 가장 흔한 원인은 기관지염이다.
-
기관지염의 원인 중 가장 흔한 원인은 급성 바이러스 기관 기관지염이다.
-
그 다음으로 소아청소년들의 각혈의 흔한 원인은 박테리아 폐렴이나 폐결핵 등 호흡기 감염병이다.
-
객혈이 다른 여러 종류의 폐 질환으로도 생길 수 있다.
-
그 외 기관 내 이물이나
-
기관지 내 이물,
-
기관절개 기도,
-
기관 기관지 폐 선천성 기형,
-
기관 기관지 내 혈관 종,
-
가슴 타박상,
-
호흡기 외과적 진단 치료 후,
-
혈액응고 이상 등으로 객혈이 생길 수 있다.
-
폐디스토마 등 폐 기생충증, 결핵,
-
기관지 종양이나 기관지 농양,
-
폐농양이나 종양,
-
폐기종,
-
기관지 확장증,
-
전이성 폐종양,
-
기관지 선종양 등으로 객혈이 생길 수 있다1- 참조문헌.
-
그 외
각혈의 증상 징후와 각혈과 토혈의 감별 진단
-
일반적으로 순수한 객혈이 기침할 때 소량 나오거나 각혈이 가래와 섞여 있는 것이 보통이다.
-
드물게 피가 폐나 기관지 등 하기도에서 대량 나올 수 있다.
-
성인의 경우, 하루에 200cc 이상 객혈이 나오면 생명이 위험하다.
-
비강이나 인두강 등에서 나온 피를 뱉을 때 폐, 기관지, 기관, 후두에서 나온 피로 잘못알고 객혈이라고 오진할 수 있다.
-
객혈이라고 진단 붙인 후 뒤 늦게 객혈 아닌 토혈, 비 출혈, 또는 구강이나 인두 강에서 난 피를 객혈이라고 잘못 진단붙이는 경우가 사실상 더 흔하다.
-
피를 뱉기 바로 전 구토나 구역질을 하거나 피를 뱉으면서 구토를 하면 일반적으로 토혈일 가능성이 더 많다.
-
이미 위에서 설명했지만, 토혈 속에 음식물 찌꺼기가 섞여 있을 수 있지만 객혈 속에는 침이나 거품이 섞여 있는 경우가 더 많다.
-
피를 토하는 경우, 간장이나 비장이 부어 있을 수 있고 복통, 구토 등 소화기계통의 질병에서 흔히 볼 수 있는 증상 징후가 있을 수 있다.
-
객혈이 있는 경우, 의사들이 청진기로 가슴을 청진할 때 건성 수포 음, 협착 음, 천명, 수포 음 등 비정상 호흡음을 드릴 수 있다.
-
비정상 숨소리가 기관, 기관지, 폐에서 나기도하고 숨소리가 비정상적으로 적게 들릴 수 있고 더 크게 들일 수 있다.
-
드물게는 손가락 끝 마디에 곤봉 손가락(사진 13 참조)이 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 여러 징후 증상, 진찰 소견 등을 참조해 토혈과 객혈을 감별 진단을 할 수 있으나 때로는 여러 가지 임상검사를 해도 확실히 감별 진단하기가 어렵다.
객혈의 진단
-
증상 징후 병력 진찰 소견 등을 종합해서 객혈이 있는 것 같으면 필요에 따라
-
객담과 객혈로 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사,
-
세균 배양검사를 하고
-
하기도, 폐, 가슴의 X선 사진, MRI 검사, Ct 스캔 검사,
-
혈액 응고 스크린 검사 등을 해서 진단할 수 있다.
-
박테리아, 곰팡이, 결핵균, 또는 기생충 등 병원체 감염으로 인한 호흡기 감염병으로 객혈이 생겼다고 의심하면 세균 검사를 필요에 따라 한다.
-
필요에 따라 기관 기관지 내시경 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
객혈의 치료
-
치료는 원인에 따라서 한다.
Hemoptysis(Bleeding from the lower respiratory tract)
객혈(각혈)
Overview of hemoptysis Lower respiratory tract
- A sign that plucks blood (blood or blood glands) from the larynx, organs, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs, etc. is called hemoptysis.
- Blood or bloody vomit from the gastrointestinal tract is a sign of expelling water called hematemesis. Children and adolescents occasionally experience hemoptysis due to multiple cocks.
- Blood from the nasal cavity or from the oral cavity or pharyngeal cavity can be misdiagnosed as hemoptysis from the lower respiratory tract. Sometimes hemoptysis cannot be easily differentiated between hematopoiesis.
- If the spitting blood contains bubbles, it is more likely to be hemoptysis. When the color of spit blood is dark red or dark brown, or when food debris is mixed in the spit blood, it is more likely to be hematopoiesis.
- The field is more likely to be bleeding blood while coughing.
Causes of hemoptysis

▴ Photo 1-174. Normal chest X-ray picture. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-175. Chronic lung disease or bronchiectasis can cause the upper club limb (club finger) to appear on the fingertips. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- There are many causes of hemoptysis.
- The most common cause of hemoptysis in children and adolescents is bronchitis.
- The most common cause of bronchitis is acute viral bronchitis.
- The next common cause of keratinocytes in children and adolescents is respiratory infections such as bacterial pneumonia or pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Hemoptysis can also result from several other types of lung disease.
- Other internal organs Foreign bodies in the bronchi, Tracheostomy airway,
- Bronchial pulmonary congenital malformations,
- Hemangiomas in the bronchi,
- Chest bruise,
- After respiratory surgical diagnostic treatment,
- Hemoptysis can occur due to abnormal blood clotting.
- Pulmonary parasites such as pulmonary dystomosis,
- tuberculosis,
- Bronchial tumor or bronchial abscess,
- Lung abscess or tumor, heaves,
- Bronchiectasis,
- Metastatic lung tumor,
- Hemoptysis may occur due to bronchial adenoma, etc.
- 1- Reference.
- etc
Symptoms of hemoptysis and differential diagnosis between hemoptysis and hematopoietic
- In general, when pure hemoptysis is coughed, a small amount of hemoptysis comes out, or hemoptysis is mixed with phlegm.
- Rarely, large amounts of blood can come out of the lower respiratory tract, such as the lungs or bronchi. In the case of adults, if more than 200 cc of hemoptysis occurs per day, life is at risk. When spitting blood from the nasal cavity or pharyngeal cavity, blood from the lungs, bronchi, organs, and larynx may be mistaken and misdiagnosed as hemoptysis.
- In fact, it is more common to misdiagnose hemoptysis as hemoptysis, nasal bleeding, or blood from the oral or pharyngeal cavity later after diagnosis as hemoptysis. Vomiting or nausea right before you spit blood or vomiting while spitting blood is generally more likely to be hematopoietic.
- As already explained above, there may be food debris mixed in hematopoietic blood, but there are more cases where saliva or foam is mixed in hemoptysis.
- In the case of vomiting blood, the liver or spleen may be swollen, and there may be symptoms commonly seen in diseases of the digestive system, such as abdominal pain and vomiting.
- In the case of hemoptysis, when doctors auscultate the chest with a stethoscope, they may give abnormal breathing sounds such as dry blister sound, constriction sound, thousand people, blister sound, etc.
- Abnormal breath sounds may come from organs, bronchi, and lungs, and breath sounds may be unusually low or louder. In rare cases, a club finger (refer to photo 13) may appear on the tip of the finger.
- It is possible to differentially diagnose hematopoietic and hemoptysis by referring to these various signs, symptoms, and examination findings, but sometimes it is difficult to reliably diagnose differentiation even if various clinical tests are performed.
Diagnosis of hemoptysis
- Symptoms, medical history, examination findings, etc.
- If it seems that you have hemoptysis, Gram staining microscopic bacterial examination with sputum and hemoptysis,
- Do a bacterial culture test Lower respiratory tract, lungs,
- chest X-ray photo, MRI, Ct scan,
- It can be diagnosed by doing a blood clotting screen.
- If you suspect that hemoptysis has occurred due to a respiratory infection caused by an infection with a pathogen such as bacteria, fungi, tuberculosis, or parasites, a bacterial test is performed as necessary.
- If necessary, it can be diagnosed by bronchoscopy.
Treatment of hemoptysis
- Treatment depends on the cause.
출처 및 참조문헌
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Red book 29th edition 2012
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
소아과학 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026