여러 가지 출혈과 여러가지 지혈 방법
How to stop bleeding in various situations
다음과 같이 여러 종류의 출혈이 있다.
- 피부 층이나 피하 조직 등에서 몇 방울 정도 나는 외출혈,
- 몸속에 있는 동맥이나 정맥에서 대량으로 나는 내출혈, 외출혈 또는 내외출혈
- 신체 내부에서 신체 외부로 나는 외출혈과 내출혈,
- 신체의 내부에서 바로 그 주위에 있는 신체 내부로 나는 내출혈이 있다.
- 출혈이 급성으로 나는 급성 출혈,
- 만성으로 나는 만성 출혈도 있다.
- 혈우병 등 유전성 출혈 질환으로 비정상적으로 출혈이 생길 수 있다. 특발성 혈소판 감소성 자반증 등 후천성, 전신, 출혈성 질병이 있을 때도 비정상적으로 출혈할 수 있다.
- 정상 이상으로 출혈을 하면 응급으로 출혈을 지연시키는 동시에 그 원인을 알아 원인에 따라 치료 한다.
- 원인이 무엇이든지 출혈하면 지혈을 우선 응급으로 하고, 필요에 따라
-
- CBC 피 검사,
- 혈액 응고 인자 검사,
- 프로프롬빈 시간(PT),
- 부분적 트롬보플라스틴 시간(PTT),
- 출혈 시간 검사를 해 출혈의 원인을 알아야 한다(표 20 참조).
- 그 원인에 따라 출혈을 치료 한다.
- 손가락으로 코를 쑤셔 나는 코피는 코의 앞 말랑말랑한 부분(비익)을 엄지와 인지로 살짝 잡으면 지혈된다.
- 그래도 코피가 계속 나면 코피의 나는 원인을 더 알아보는 동시 이비인후과에서 아드레날린제 액 2방울 정도 묻힌 솜 덩어리로 콧구멍 속(비강 속)에 잠시 동안 넣었다 빼면 대개 코피는 멈춘다.
- 때로는 이비인후과에서 초산 은봉으로 비강 점막층의 모세 혈관을 지져 지혈 시켜 치료 할 수 있다.
- 혈소판 감소증, 혈우병 등으로 코피가 날 수 있다. 이때는 우선 두 손가락으로 비익을 전술 한 것 같이 손가락으로 잡아 지혈시키고 의사의 지시에 따라 추적 치료를 받는다.
- 편도 절제 수술 치료를 받은 후나 아데노이드 수술 치료를 받은 후 코피가 날 수 있고 입 안에서 피가 날 수 있다. 이때도 역시 의사의 지시에 따라 치료한다.
- 절상, 열상(찢긴 상처, 찢김, 열창) 등으로 생긴 외출혈은 상처의 크기에 따라, 신체 부위에 따라, 출혈의 정도에 따라 아래 사진 204~210에서 볼 수 있는 치료를 한다.
- 손가락 압박 지혈 치료,
- 손바닥 압박 지혈 치료,
- 출혈되는 상처에 피를 공급하는 동맥 압박 지혈 치료
- 봉합수술 치료 지혈 치료
- 이상 치료 방법을 혼합한 지혈 치료방법 등으로 지혈시킬 수 있다.
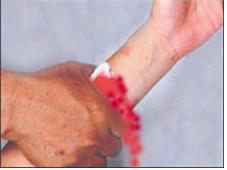
▴사진 1-163. 상처 부분에 거즈 등을 올려놓고 손바닥이나 손가락으로 상처를 직접 꼭 눌러 지혈시킬 수 있다
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
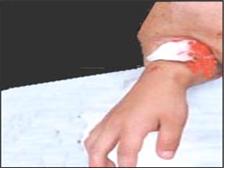
▴사진 1-164. 피나는 상처에 거즈 등을 올려놓고 손으로 상처를 직접 꼭 눌러 지혈시킬 수 있다
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee., MD, FAAP
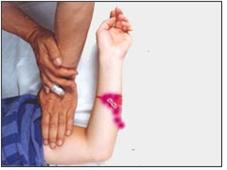
▴사진 1-165. 출혈될 때 나는 피를 공급하는 팔이나 다리 등에 있는 동맥을 손가락이나 손으로 꼭 눌러 지혈시킬 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴사진 1-166. 팔이나 다리에서 피가 많이 날 때는 피가 나는 상처 부분을 손으로 직접 꼭 눌러 지혈하고 그와 동시 출혈 부분에서 심장이 있는 쪽으로 조금 떨어진 팔이나 다리의 한 부분을 붕대나 지혈대 등으로 매어 지혈할 수 있다. 지혈대로 매서 지혈시키는 응급처치법은 다른 지혈 방법으로 지혈시킬 수 없는 응급한 경우에 쓰는 지혈 응급처치방법이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
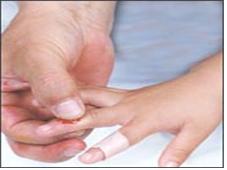
▴사진 1-167. 손가락이나 손으로 피나는 상처 부분을 직접 꼭 눌러 지혈시키거나 밴드를 붙이거나 붕대를 감아 지혈시킬 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
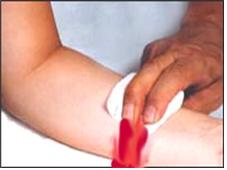
▴사진 1-168. 피가 나는 상처 부분을 손가락이나 손바닥으로 꼭 눌러 지혈시킬 수 있다
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
How to stop bleeding in various situations
여러 가지 출혈과 여러가지 지혈 방
There are several types of bleeding, including:
- External bleeding from a few drops of the skin layer or subcutaneous tissue, Internal bleeding, external bleeding or internal/external bleeding from a large amount of arteries or veins in the body
- External and internal bleeding from inside the body to the outside,
- There is internal bleeding from the inside of the body to the inside of the body right around it.
- Acute bleeding with acute bleeding,
- Chronic, chronic bleeding also occurs.
- Hereditary bleeding disorders such as hemophilia can cause abnormal bleeding.
- Abnormal bleeding can occur when there are acquired, systemic, or bleeding diseases such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
- If you bleed beyond normal, delay the bleeding in an emergency and at the same time find out the cause and treat it according to the cause.
- If bleeding for whatever cause is bleeding, stop bleeding first as an emergency,
1. CBC blood test,
2. Blood clotting factor test,
3. Proformin time (PT),
4. Partial thromboplastin time (PTT),
5. The bleeding time should be checked to determine the cause of bleeding (see Table 20).
Treat the bleeding according to the cause.
- Nose bleeding caused by pricking the nose with your fingers is bleeding when you slightly hold the soft part (fly) in front of the nose with your thumb and finger.
- If the nosebleed continues, then the cause of the nosebleed is further investigated, and at the same time, the nosebleed usually stops if the otolaryngologist puts it in the nostril (in the nasal cavity) for a while with a cotton lump moistened with 2 drops of an adrenaline solution.
- Otorhinolaryngology can sometimes treat capillaries in the nasal mucosa with silver acetate sticks to stop bleeding.
- Thrombocytopenia and hemophilia can cause nosebleeds. In this case, first, hold the fly with two fingers as described above, stop the bleeding, and receive follow-up treatment according to the doctor’s instructions. After receiving a tonsillectomy or adenoid surgery, you may have nosebleeds and bleed in your mouth. At this time, it is also treated according to the doctor’s instructions.
- External bleeding caused by cuts and lacerations (torn wounds, tears, fissures), etc., is treated as shown in pictures 204 to 210 below according to the size of the wound, the body part, and the degree of bleeding. Finger compression hemostasis treatment,
- Palmar compression hemostasis treatment,
- Arterial compression hemostasis treatment that supplies blood to bleeding wounds Suture surgery treatment hemostasis treatment
- Hemostasis can be stopped by a hemostatic treatment method that combines abnormal treatment methods.

▴Picture 1-163. You can stop bleeding by putting gauze on the wound and pressing the wound directly with your palm or fingers. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

17.jpg ▴Picture 1-164. Put gauze on the bleeding wound and press the wound directly with your hand to stop bleeding. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee., MD, FAAP

▴Picture 1-165. When bleeding, I can stop the bleeding by firmly pressing the arteries in the arms or legs that supply blood with my fingers or hands. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴Picture 1-166. When the arm or leg is bleeding a lot, hemostasis can be stopped by pressing the bleeding wound directly with your hand, and at the same time, a part of the arm or leg slightly away from the bleeding area toward the heart is tied with a bandage or tourniquet have. The first aid method of stopping bleeding with a tourniquet is a first aid method for hemostasis that is used in emergency cases that cannot be stopped with other hemostatic methods. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴Picture 1-167. You can stop the bleeding by pressing down on the bleeding wound directly with your finger or hand, attaching a band, or wrapping a bandage to stop the bleeding. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴Picture 1-168. You can stop bleeding by pressing firmly on the bleeding wound with your finger or palm. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처와 참조문헌
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.75-76, 209-209
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.221-233
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.18, 60-66, 117-118, 195-196
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th-21st ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st Ed 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026