신생아의 열
Fever in newborn infants
표 2-4.나이(일령)에 따른 미숙 신생아와 만삭 신생아의 정상체온
| 출생체중 | 체중 1,500gm
(3 lb, 5 oz) 이하 |
체중 1,501 gm~ 2,500 gm
(3 lb, 5 oz ~ 5 lb, 8 oz) |
임신 36주 이상
2,500 gm (3 lb, 8 oz) 이상 |
|||||||||
| 화씨 또는 섭씨 나이 | 체온 섭씨
평균치±범위 |
체온 화씨
평균치±범위 |
체온 섭씨
평균치±범위 |
체온 화씨
평균치±범위 |
체온 섭씨
평균치±범위 |
체온 화씨
평균치±범위 |
||||||
| 생후 1일 | 34.3 | 0.4 | 93.8 | 0.7 | 33.4 | 0.6 | 92.1 | 1.1 | 33.0 | 1.0 | 91.4 | 1.8 |
| 생후 2일 | 33.7 | 0.5 | 92.7 | 0.9 | 32.7 | 0.9 | 90.9 | 1.6 | 32.4 | 1.3 | 90.4 | 2.3 |
| 생후 3일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.4 | 0.9 | 90.4 | 1.6 | 31.9 | 1.3 | 89.4 | 2.3 |
| 생후 4일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.3 | 0.9 | 90.2 | 1.6 | 31.5 | 1.3 | 89.6 | 2.3 |
| 생후 5일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.2 | 0.9 | 90.0 | 1.6 | 31.2 | 1.3 | 88.1 | 2.3 |
| 생후 6일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.9 | 1.3 | 87.6 | 2.3 |
| 생후 7일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.8 | 1.4 | 87.4 | 2.5 |
| 생후 8일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.6 | 1.4 | 87.5 | 2.5 |
| 생후 9일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.4 | 1.4 | 86.7 | 2.5 |
| 생후 10일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.2 | 1.5 | 86.4 | 2.7 |
| 생후 11일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 29.9 | 1.5 | 85.8 | 2.7 |
| 생후 12일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 29.5 | 1.6 | 85.1 | 2.8 |
| 생후 13일 | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 29.2 | 1.6 | 84.6 | 2.8 |
| 생후 14일 | 33.4 | 0.6 | 92.1 | 1.1 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 15일 | 33.3 | 0.7 | 92.0 | 1.3 | 32.0 | 0.9 | 89.6 | 1.6 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 4주 | 32.9 | 0.8 | 91.2 | 1.4 | 31.7 | 1.1 | 89.0 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 5주 | 32.1 | 0.7 | 89.8 | 1.3 | 31.1 | 1.1 | 87.9 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 6주 | 31.8 | 0.6 | 89.2 | 1.1 | 30.6 | 1.1 | 87.1 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 7주 | 31.1 | 0.6 | 87.9 | 1.1 | 30.1 | 1.1 | 86.2 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
출처 Standards and recommendations for Hospital Care of Newborn Infants, American Academy of Pediatrics. 5th, ed. p.91
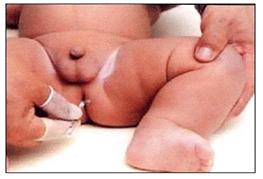
▴ 사진 72. 신생아에게 열이 나면 어떤 종류의 체온계로든 항문 체온을 잰다. 장갑을 끼고 체온을 잰다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 사진 71. 미국에서는 유리로 만든 수은 체온계로 체온을 재는 것을 더 이상 권장하지 않는다. 수은 체온계로 체온을 재면 경제적이고 실용적이고 쓰기에 간편하다. 필요에 따라 항문 수은 체온계와 구강 체온계를 하나씩 보관했다가 필요에 따라 신생아의 항문에서 체온을 잴 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
날씨가 덥거나 실내 온도가 높으면 주위의 온도에 따라 건강한 신생아의 체온이 덩달아 올라가 정상 이상으로 높아 질 수 있다. 어떤 종류의 감염병을 앓지도 않는데 미열 내지 고열이 날 수 있다.
-
신체에 아무 이상도 감염병도 없는 신생아를 두꺼운 담요나 포대기로 너무 꼭 싸 주거나 옷을 너무 많이 입히면 신생아의 체온이 정상 이상으로 올라갈 수 있고 열이 날 수 있다.
-
신생아가 탈수되면 그로 인해 미열 내지 고열이 날 수 있다. 이렇게 생긴 열을 신생아 탈수 열이라 한다.
-
신생아의 생명을 위협할 수 있는 폐렴, 뇌막염, 패혈증 등으로 미열 내지 고열이 날 수 있다.
-
감염병이나 그 외 다른 어떤 병이 있어도 열이 날 수 있다.
-
드물게는 생명을 위협할 수 있는 위중한 감염병을 앓고 있는 신생아에게 고열이 나지 않고 오히려 미열이 나거나 체온이 정상 이하로 떨어져 저체온증이 생길 수 있다.
|
다음은 “아기체온이 41도까지”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 아기체온이 41도까지
Q.
안녕하세요. 이렇게 좋은 사이트를 알게 되어 넘 기쁩니다.
10월1일에 태어난 여자아기입니다.
3일에 병원에서 퇴원하여 몸조리를 한다고 따뜻한 방에서 아기와 함께 있었습니다.
낮에는 편히 자던 아기가 늦은 저녁이 되어 잠을 안자고 보채며 우는 것이었어요.
입을 자꾸 벌리며 먹을 것을 찾기도 하면서요.
하루 동안에 변을 3번이나 봤어요. 샛노란 변에 두부를 으깨놓은 듯한 묽기였어요.
새벽3시까지 안자고 보채는 아기를 저는 안고 얼러 주며 있다가 아기가 지쳐 힘이 없어 보이며 경기를 하는 것이었어요. 얼굴이 빨게 지고 눈을 크게 뜨며 부르르 떨었어요. 그때 체온을 재어보니 41도였어요.
저는 그때 상황의 심각성을 인식하고 종합병원응급실로 갔습니다.
아기의 옷을 벗기고 열부터 식히더니 1주일정도 입원해야 한다는 것이었습니다.
열만 내리면 다 인줄 알았는데 갓 태어난 아길 1주일의 입원이라니 병원이 의심되더군요.
지금까지 나온 검사 결과는 방사선사진과 뇌수막염에는 이상이없다고 합니다.
그리고 소변배양검사결과 세균이 3가지가 나왔는데 아기에게서 나온 건지 용기에서 나온 건지를 다시 검사해봐야겠다는 어처구니없는 답변을 주더군요.
다음 주 화요일쯤에 퇴원이 가능하다는데…
도대체 어떤 검사를 하고 정말 필요한검 사인지 알고 싶습니다.
불친절한 병원이 의심스럽기도 하구요.
선생님의 답변 부탁드립니다.
A.
이청님
안녕하세요. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
아기 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 더 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
신생아 탈수 열,
선천성 폐렴,
뇌막염,
골수염,
패혈증,
요로 감염 등 박테리아 감염병 또는 바이러스 감염병으로 고열이 날 수 있습니다.
주위 온도가 너무 높거나 아기를 너무 싸주거나 탈수됐을 때도 고열이 날 수 있습니다.
인터넷으로 무엇 때문에 열이 났었는지 확실히 말씀드릴 수 없으나 혹시 신생아 탈수 열로 고열이 났었는지 의심해 봅니다.
신생아에게 고열이 나면 뇌척수액 검사, 혈액검사와, 피, 소변, 대변과 척수액 등 피검물로 세균배양검사 등을 하는 것이 보통입니다.
가슴 X선 사진 검사 등 적절한 영상 검사를 하는 것도 중요합니다. 그 검사의 결과를 알면 제가 답변 드리는 데 많은 도움이 됩니다.
질문이 더 있으시면 담당 의사선생님께 하시고 상담하시기 바랍니다.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 질병–탈수 열, 신생아에게 열이 날 때, 신생아 전신경련. 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요–열, 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교간호 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다.
이상원 드림
| 참고로, 미 소아청소년과학회는 생후 28일 이전 신생아들에게 화씨 100.4도 이상 또는 섭씨 38도 이상 열이 나면 병원에 입원을 시키고 열나는 원인을 찾으면서 적절히 치료해 주라고 권장한다. |
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호–고열이 날 때, 제12권 소아 신경, 정신, 정서, 행동, 심리, 수면 문제–열성 경련, 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 질병–신생아 체온, 신생아 탈수 열, 신생아가 열이 나면 어떻게 하나요, 열이 날 때 참조.
신생아의 열 Fever in newborn infants
Table 2-4. Normal body temperature of immature and term newborns according to age
표 2-4.나이(일령)에 따른 미숙 신생아와 만삭 신생아의 정상체온
| 출생체중 Birth weight Weight | 체중 1,500gm
(3 lb, 5 oz) 이하 1,500 gm (3 lb, 5 oz) or less |
체중 1,501 gm~ 2,500 gm
(3 lb, 5 oz ~ 5 lb, 8 oz) Weight: 1,501 gm~ 2,500 gm (3 lb, 5 oz to 5 lb, 8 oz) |
임신 36주 이상
2,500 gm (3 lb, 8 oz) 이상Pregnancy 36 weeks or more 2,500 gm (3 lb, 8 oz) or more |
|||||||||
| 화씨 또는 섭씨, 나이 Fahrenheit or Celsius age | 체온 섭씨
평균치±범위 Body temperature Celsius Mean ± range |
체온 화씨
평균치±범위 Body temperature Fahrenheit Mean ± range |
체온 섭씨
평균치±범위Body temperature Celsius Mean ± range |
체온 화씨
평균치±범위Body temperature Fahrenheit Mean ± range |
체온 섭씨
평균치±범위Body temperature Celsius Mean ± range |
체온 화씨
평균치±범위Body temperature Fahrenheit Mean ± range |
||||||
| 생후 1일
1 days after birth |
34.3 | 0.4 | 93.8 | 0.7 | 33.4 | 0.6 | 92.1 | 1.1 | 33.0 | 1.0 | 91.4 | 1.8 |
| 생후 2일
2 days after birth
|
33.7 | 0.5 | 92.7 | 0.9 | 32.7 | 0.9 | 90.9 | 1.6 | 32.4 | 1.3 | 90.4 | 2.3 |
| 생후 3일
3 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.4 | 0.9 | 90.4 | 1.6 | 31.9 | 1.3 | 89.4 | 2.3 |
| 생후 4일
4 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.3 | 0.9 | 90.2 | 1.6 | 31.5 | 1.3 | 89.6 | 2.3 |
| 생후 5일
5 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.2 | 0.9 | 90.0 | 1.6 | 31.2 | 1.3 | 88.1 | 2.3 |
| 생후 6일
6 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.9 | 1.3 | 87.6 | 2.3 |
| 생후 7일
7 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.8 | 1.4 | 87.4 | 2.5 |
| 생후 8일
8 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.6 | 1.4 | 87.5 | 2.5 |
| 생후 9일 9 days after birth | 33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.4 | 1.4 | 86.7 | 2.5 |
| 생후 10일
10 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 30.2 | 1.5 | 86.4 | 2.7 |
| 생후 11일
11 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 29.9 | 1.5 | 85.8 | 2.7 |
| 생후 12일
12 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 29.5 | 1.6 | 85.1 | 2.8 |
| 생후 13일
13 days after birth |
33.5 | 0.5 | 92.3 | 0.9 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | 29.2 | 1.6 | 84.6 | 2.8 |
| 생후 14일
14 days after birth |
33.4 | 0.6 | 92.1 | 1.1 | 32.1 | 0.9 | 89.8 | 1.6 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 15일
15 days after birth |
33.3 | 0.7 | 92.0 | 1.3 | 32.0 | 0.9 | 89.6 | 1.6 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 4주
4 weeks after birth |
32.9 | 0.8 | 91.2 | 1.4 | 31.7 | 1.1 | 89.0 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 5주
5 weeks after birth |
32.1 | 0.7 | 89.8 | 1.3 | 31.1 | 1.1 | 87.9 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 6주
6 weeks after birth |
31.8 | 0.6 | 89.2 | 1.1 | 30.6 | 1.1 | 87.1 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
| 생후 7주
7 weeks after birth |
31.1 | 0.6 | 87.9 | 1.1 | 30.1 | 1.1 | 86.2 | 1.9 | – | – | – | – |
Source; Standards and recommendations for Hospital Care of Newborn Infants, American Academy of Pediatrics. 5th, ed. p.91

▴ Photo 72. When a newborn child has a fever, take the anal body temperature with any type of thermometer. Put on gloves and take your temperature. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 71. In the United States, it is no longer recommended to measure the temperature with a mercury thermometer made of glass. Measuring body temperature with a mercury thermometer is economical, practical, and easy to use.
If necessary, an anal mercury thermometer and an oral thermometer can be stored, and if necessary, the body temperature can be measured in the anus of the newborn. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- If the weather is hot or the room temperature is high, the body temperature of a healthy newborn baby can rise above normal depending on the surrounding temperature.
- You don’t suffer from any kind of infectious disease, but you may have a mild or high fever. If a newborn baby with no abnormality or infectious disease on the body is wrapped too tightly with a thick blanket or bag, or if too much clothes are worn, the newborn’s body temperature may rise above normal and may cause fever. When a newborn baby is dehydrated, it can result in mild to high fever. This fever is called newborn dehydration fever. Low or high fever may occur due to pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis, etc., which can threaten the life of newborns. An infectious disease or any other disease can also cause fever.
- Rarely, a newborn with a serious, life-threatening infectious disease may not develop a high fever, but rather a mild fever or hypothermia due to a lower body temperature than normal.
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer for “baby body temperature up to 41 degrees”.
Q&A.
Baby body temperature up to 41 degrees Q. Good morning.
I am very happy to know such a great site.
This is a baby girl born on October 1st.
She was discharged from the hospital on the 3rd day and stayed with her baby in a warm room to take care of herself.
The baby, who was sleeping comfortably during the day, was late in the evening, and she was not sleeping and crying.
She keeps opening her mouth and looking for something to eat. She saw her stool three times during the day. It was thin, like crushing her tofu on her stool.
She was holding and freezing a baby that didn’t sleep until 3 a.m., and then the baby looked tired and weak and played.
Her face was flushed and her eyes wide open and trembled. She then took her body temperature and found that she was 41 degrees.
At that time, I recognized the seriousness of the situation and went to the emergency room of a general hospital.
They said that they had to take off their clothes, let them cool down from the heat, and then be hospitalized for about a week.
I thought it would be all if only fever fell, but she was suspicious of the hospital for a week’s hospitalization for a newborn baby.
The results of the tests so far have shown that there is no abnormality in radiographs and meningitis.
And as a result of the urine culture test, three kinds of bacteria were found, but he gave a ridiculous answer that I should test again whether it came from a baby or from a container. You can be discharged from the hospital about next Tuesday…
I’d like to know what kind of test it is and what kind of sword it really needs. I’m also suspicious of an unfriendly hospital.
Please answer from the teacher.
A.
Lee Cheong Good morning.
Thanks for the great question.
The more information you know about your baby’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer.
We will respond based on the information you provided. Newborn dehydration fever, Congenital pneumonia, Meningitis, Osteomyelitis, blood poisoning, Bacterial infections, such as urinary tract infections, or viral infections can cause high fever.
High temperatures can also occur when the ambient temperature is too high, when the baby is wrapped too much, or when it is dehydrated.
I can’t tell you for sure what caused the fever on the Internet, but I wonder if the newborn had a high fever due to dehydration fever.
When a newborn has a high fever, it is common to do a cerebral spinal fluid test, a blood test, and a bacterial culture test with the specimens such as blood, urine, feces and spinal fluid. It is also important to perform appropriate imaging tests, such as chest X-ray examination. Knowing the results of that test will help me a lot to answer.
If you have any further questions, please consult with your doctor in charge. [Parents should also be a
at last the half-doctors-Pediatrics and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 6 Diseases with good growth and development of newborns- Dehydration fever, when a newborn baby has a fever, a newborn baby’s general convulsions.
Please refer to Volume 22, Sons and Daughters, Love and Raise-Yeol, Volume 21, Children and Adolescents, Family School Nursing, etc. If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won, MD
For reference, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents recommends that newborns before 28 days of age have a fever of more than 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit or more than 38 degrees Celsius to be admitted to the hospital and treated appropriately while finding the cause of the fever. [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatric Family Nursing]-Volume 21 Child and Adolescent Home School Nursing-When High Fever, Vol. 12 Pediatric Neuros, Mental, Emotion, Behavior, Psychology, Sleep Problems-Fever convulsions, Part 6 Kwon Newborns with good growth and development disease-Newborn baby’s body temperature, Newborn dehydration fever, What should I do if a newborn baby has a fever? Refer to When you have a fever.
출처 및 참조 문헌
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th& 19th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Ambulatory Pediatrics, Green and Haggerty, Saunders
-
School Health: A Guide For Health Professionals, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
How to really love your child Ross Campbell
-
Good Behavior Stephen W. Garber, Ph.D. and other
-
Adolescent Medicine and The Media Adolescents Medicine
-
AM: Stars Adolescent Medicine: State of the Art Reviews, Asthma, and Diabetes in A
-
The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Adolescent Gynecology, Part II THe Sexually Active Adolescent, August 1999
-
Fueling the Teen Machine, Ellen Shanley and Colleen Thompson
-
Why Teenagers Act the Way They Do, Eight Adolescent Personality Types: Understanding and Dealing With Them, Dr. G. Keith Olson
-
The Pregnancy bible Joan Stone, Keith Eddleman
-
Pediatric and Adolescent Endocrinology, The Pediatric Clinics of North America in August 1987
-
Adolescent Gynecology, Ross Round table
-
Female Reproductive Health, Adolescent Medicine Patricia S. Simmons, M.D., Marc. Laufer, M.D.
-
The Adolescent Male: Adolescent Medicine, David S. Rosen, M.P.H., Michael Rich, M.D.
-
Lesbian and Gay Youth: Care And Counseling, Adolescent Medicine, Caitlin Ryan, M.S.W, A.C.S.W., Donna Futterman, M.D.
-
Medical and Gynecologic Endocrinology: Joseph S. Sanfilippo, M.D., Jordan W. Finkelstein, M.D., Dennis M. Styne. M.D., Adolescent Medicine Clinics, Oct. 2005 Vol. 16
-
Robert T. Brown, M.D., Paula K. Braverman, M.D.
-
Preparing for Adolescence, Dr James Dobson
-
Dr, Ruth’s Guide to GOOD SEX Ruth Westheimer
-
Dating Sex &Friendship Joyce Huggett
-
진정한 자녀 사랑 나비게이터
-
10대 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키워라 이상원 역
-
소아과학 안효섭 대한교과서
-
의학 용어사전 대한 의사 협회
-
제24권 사춘기 성교육 출처 참조 문헌
-
그 외
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026