열성 경련(열 경련/열 경기/열 발작)
Febrile convulsions (Febrile seizures)
열성 경련의 개요
-
뇌염, 뇌막염, 뇌손상, 그 외 어떤 기질적 중추 신경 병변이 없는 환아가 뇌 이외 신체의 다른 계통에 생긴 감염병으로 열이 날수 있고 그 열로 인해 생기는 전신 경련을 열성 경련, 경기 또는 열 발작이라 한다.
-
뇌나 중추 신경에 생긴 어떤 종류의 감염병으로 인해 열이 날 수 있고 뇌 감염병으로 인해 뇌가 손상될 수 있고, 뇌 손상으로 전신 경련을 할 수 있다. 이때 생긴 전신경련을 열성 경련이라고 하지 않는다.
-
열성 경련은 어떤 감염병을 앓을 때 생기는 증상 징후이지 병명은 아니다[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제12권 소아청소년 신경, 정신, 정서, 행동, 수면 문제–열성 경련 참조.
|
비 열성 경련
|

▴ 사진 340. 항문 수은 체온계와 구강 수은 체온계
요즘 수은 체온계를 권장하지 않으나, 수은 체온계는 값도 싸고 쓰기 간편해 아주 실용적이다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
열성 경련의 기전과 원인
-
열성 경련이 유발되는 기전은 확실히 모른다.
-
그러나 열이 날 때 중추 신경계가 미숙해서 열성 경련이 유발된다고 한다.
-
독감, 돌발성 발진, 홍역 등 바이러스 감염병,
-
A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상 구균 편도염,
-
폐렴, 이질, 살모넬라 등 박테리아 감염병으로 나는 열로 열성 경련이 유발될 수 있다.
-
어떤 감염병을 앓기 시작할 때 나는 열로 열성 경련이 유발될 수 있고
-
어떤 감염병을 몇 시간 동안 앓고 있는 중, 또는 감염병을 하루 이틀 동안 앓고 있는 중 갑자기 열이 더 나면서 열성 경련이 유발될 수 있다.
-
-
고열이 나면 어떤 아이에게는 열성 경련이 유발되고, 다른 아이에게는 열성 경련이 유발되지 않는 이유는 아직 확실히 모른다.
-
친 부모 형제자매들 중 누군가가 소아기에 생긴 감염병으로 생긴 열로 열성 경련을 경험 했던 병력이 있으면 다른 형제자매에게도 열성 경련이 생길 가능성이 더 있다. 이런 이유로 열성 경련은 유전성 있다고 본다.
-
과거에 어떤 감염병을 앓다가 열성 경련이 유발했던 아이가 또 다른 감염병을 앓을 때 열이 나면 열성 경련이 또 유발될 가능성이 더 높다.
-
연구에 의하면, 생후 6개월에서 8세 이전 영유아이들과 학령기 아이들의 3~8%에게
-
열성 경련이 유발 될 수 있다.
-
열성 경련은 생후 6개월 이후부터 8세 이전까지 즉, 영유아, 초기 학령기 아이에게 주로 유발될 수 있고 생후 6개월 이전 아기들과 8세 이후 학령기 아이들에게는 잘 유발되지 않는다.
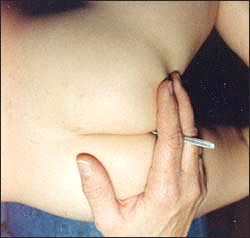
▴ 사진 341. 항문 수은 체온계로 항문 체온을 잰다.
항문체온을 잴 때 장갑을 낀 손으로 항문 체온계를 잡고 체온을 잰다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
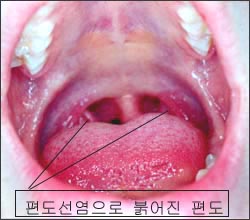
▴ 사진 342. 급성 인두 편도염(편도선염)으로 편도가 부어 있고 혀가 붉다. 이 환아는 급성 인두 편도염과 성홍열을 앓고 있다. 성홍열을 앓을 때도 열성 경련할 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
생후 6개월~3세 이전까지 영유아들에게 열성 경련은 가장 잘 유발된다.
-
생후 6개월 이전 영아나 8세 이후 학령기 아이가 어떤 감염병을 앓다가 열이 나면서 열성 경련이 유발되면 열성 경련을 한다고 바로 진단 붙이기 전에 환아가 뇌염이나 뇌막염 등 다른 어떤 종류의 감염병을 앓고 있는지 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
간질, 테타니, 저혈당증, 또는 그 외 다른 병을 앓을 때도 전신 경련이 유발될 수 있다.
-
따라서 전신 경련을 하면 어떤 병으로 인해 경련이 유발됐는지 확실히 진단해야 한다.
열성 경련의 증상 징후
-
어떤 감염병을 앓을 때 예측할 수 없이 열성 경련이 갑자기 유발될 수 있다.
-
열성 경련으로 나타나는 증상 징후가 비 일률적이다.
-
열성 경련을 할 때 흔히 볼 수 있는 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
-
어떤 감염병으로 열이 날 때 전신 경련이 갑자기 일어나면서 의식을 잃고, 두 눈을 홉뜨고, 이를 악물고, 입 안에서 거품이 나면서 호흡 곤란이 생기고 안색이 창백해지고, 입술이 파래질 수 있다.
-
팔다리 근육 등 전신 근육에 강직성 경련과 간헐적 경련이 유발된다. 이때 팔다리를 오므렸다 폈다 하기도 한다.
-
어떤 감염병을 앓기 시작할 때 열이 나기 시작하면서 열성 경련이 유발되기도 하고. 또는 갑자기 전신 경련이 유발돼서 체온을 처음 측정한 후 비로소 고열이 나면서 어떤 감염병을 앓고 있다는 사실을 처음 아는 경우도 있다.
-
대부분의 열성 경련은 2~3분 계속되다가 저절로 그치는 것이 보통이다. 더러는 15~20분 동안 계속되기도 한다.
-
열성 경련이 다 끝난 후 잠시 동안 온몸의 힘이 다 빠진 듯이 몸이 축 늘어지고 얼굴이 창백해지며 의식이 몽롱해질 수 있다. 그러나 열성 경련을 하는 중 잃었던 의식은 경련이 끝난 후 정상적으로 회복된다.
-
경련이 끝난 후 한두 시간 동안 깊은 잠에 빠질 수 있다. 드물게 열성 경련이 다 끝난 바로 후 신체의 한쪽에 마비가 잠시 동안 생겼다가 정상으로 회복된다. 이런 반신마비를 타드 마비(토드 마비/Todd’s paralysis)라고 한다. 열성 경련을 할 때 열을 나게 한 감염병으로 생긴 증상 징후와 열성 경련으로 생긴 증상 징후가 함께 나타난다.
-
가령 폐렴에 의해서 열이 나고 그 열로 열성 경련이 유발될 때는 열성 경련의 증상 징후와 폐렴으로 생기는 기침과 열 등의 증상 징후가 함께 나타나는 것이 보통이다.

▴ 사진 344. 영유아들의 소변 피 검물을 받을 때 쓸 수 있는 영아용 오줌주머니.
요즘, 영아 오줌주머니로 받은 소변으로 소변세균 검사를 하면 그 검사결과의 가치가 별로 없다고 주장하는 의사들도 있다. 그러나 저자의 오랜 경험에 의하면, 진찰결과, 증상 징후, 병력과 클린 캐치 소변(께끗한 중간 뇨 소변 피검사소변 Clean catch specimen, Midstream specimen)으로 소변 검사한 결과를 총 종합해서 임상 평가를 잘하면 영아용 오줌주머니를 이용해 받은 피검물용 소변으로 소변 검사를 한 결과가 상당히 유용한 임상 가치가 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP.
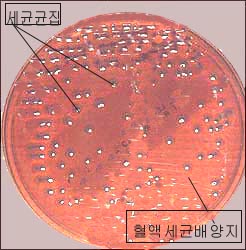
▴ 사진 343. 혈액 세균 배양검사에서 자란 세균 집락.
필요에 따라 피, 소변, 대변, 인두, 뇌척수액 등의 피검물로 세균 배양검사를 할 수 있다. 하얀 점들이 세균 배양지에서 자란 세균 집락들이다.
참고;혈액 세균 배양지(혈액 우무 배지) 세균 군집(세균 집락)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
열성 경련의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 열성 경련을 진단한다.
-
다른 경련 질환을 배제해서 진단한다.
-
대부분의 열성 경련은 2~3분 동안 지속되다가 자연히 그친다. 그 때문에 열성 경련을 하는 환아를 병원 응급실로 데리고 왔을 때는 열성 경련이 이미 다 끝난 상태일 때가 많다.
-
집에서 열성 경련을 할 때 부모가 목격했던 징후와 열성 경련을 더 이상하지 않을 때 의 사의 진찰 소견 등을 종합해서 진단할 때가 많다.
-
열성 경련이 2~3분 이상 계속되고 있는 환아를 병원에 데리고 올 때는 경련하는 상태를 관찰하고 진찰해서 진단할 수 있다.
-
열성 경련을 계속 할 때는 물론이고 열성 경련이 다 끝난 후에도 병원 응급실로 데리고 가서 열성 경련과 그 때 앓고 있는 감염병의 원인을 찾아 그 원인에 따라 치료한다.
-
뇌막염, 뇌염, 뇌막 뇌염(Meningoencephalitis), 뇌종양, 뇌 농양, 뇌출혈, 뇌 손상, 저혈당증, 테타니, 약물 중독, 납 중독, 간질 등으로 생긴 전신 경련과 열성 경련을 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
열성 경련을 할 때 인두 점액, 피, 대소변, 뇌척수액 등의 피검물로 세균배양, 혈 중 전해질 농도, 두개골 X선 사진, 뇌파, 뇌 CT 스캔, 뇌 MRI 등의 검사를 필요에 따라 할 때도 있다. 의사의 판단에 따라 이런 종류의 검사를 하지 않고 열성 경련을 진단 치료할 때도 많다.
다음과 같은 열성 경련을 복합성 열성 경련이라고 한다.
-
한 종류의 감염병을 앓는 동안 열성 경련을 두 번 하거나 그 이상 여러 번 하거나,
-
열성 경련이 20분 이상 계속되거나,
-
열성 경련을 한 후 토드 마비가 생길 때
-
복합성 열성 경련이 아닌 열성 경련은 단순 열성 경련이라고 한다.
-
다음과 같은 열성 경련을 단순 열성 경련이라고 한다.
-
열이 나지 않았는데도 경련 한다든지,
-
열성 경련을 한 후 2주 경 뇌파검사 결과가 비정상으로 나타나면,
-
뇌에 있는 뇌 병변으로 전신 경련을 하면 열성 경련을 한다고 진단하기 전에 다른 병이나 원인으로 전신 경련을 했다고 진단한다.
열성 경련의 치료
-
갑자기 열성 경련이 유발된 환아를 보면 누구든지 몹시 당황한다. 그렇지만 열성 경련을 하는 환아를 목격 할 때 침착하게 대처한다. 걱정스럽고 당황되지만 우선 환아를 안전한 곳으로 침착히 옮겨 눕힌다.
-
그와 동시에 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 전화해서 그들의 지시에 따라 현장에서 적절한 응급치료를 시작하면서 상황에 따라 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단을 이용해 병원 응급실로 급히 이송한다.
-
환아의 기도를 다음과 같이 확보해 열어 준다
-
숨통(기도)을 막히게 할 수 있고 목 기도 부분을 꼭 조이는 목 주위 옷은 느슨하게 풀어준다.
-
머리를 옆으로 살짝 돌리고 상체를 하체보다 좀 낮게 눕혀서 입안, 인두 강, 비강, 기도 속 구토물이나 점액이 중력에 의하여 기도 밖으로 입 밖으로 나오게 하고 구토물이 기도 속으로 들어가지 않도록 처치해 기도를 확보해 준다.
-
-
경련을 하는 중 혀를 깨물까 염려해 숟가락이나 수건 등을 환아의 입 속에 넣어서는 안 된다. 그런 것으로 오히려 입안이 손상될 수 있기 때문이다.
-
뇌염, 뇌막염, 또는 패혈증 등 생명에 위험한 감염병을 앓을 때도 열성 경련과 비슷하게 전신 경련을 할 수 있다. 따라서 응급실에서는 이런 종류의 감염병으로 유발된 경련과 열성 경련을 감별 진단해야한다
-
열성 경련을 하는 동안이나 열성 경련이 다 끝난 후에도 환아를 병원 응급실로 데리고 가서 어떤 종류의 감염병을 앓고 있는지 알아보고 감염병도 치료받고 열성 경련도 함께 치료 받아야 한다.
-
열은 일반적으로 타이레놀이나 모트린 등의 해열제로 해열시킬 수 있다 ([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제21권 소아청소년 가정간호–해열 진통제 참조)..
-
경구용 디아제팜(Diazepam) 항경련제로 열성 경련을 치료하면 단순 경련 발생률이 감소된다. 그 외 항문용 Diazepam, 항문용 Midazolam, 또는 비강용 Midazolam으로 단순 열성 결련을 치료하면 경련 지속 시간이 짧아진다. 부작용 때문에 이런 종류의 항경련제로 통상적으로 치료하지 않는다. 그러나 대부분의 열성 경련은 항경련제로 치료하지 않아도 2~20분 이내에 자연적으로 그친다.
-
열성 경련을 하는 동안 심장이 아주 느리게 뛸 수도 있고 숨을 어렵게 쉴 때도 생길 수 있지만 기본 심폐 소생술 처치를 요하는 경우는 드물다.
-
환아의 입이나 입과 콧구멍에 처치자의 입을 대고 인공호흡을 해 준 사람이나 열성 경련을 하는 환아를 직접 접촉하면서 치료해 준 사람은 열성 경련을 일으킨 감염병의 원인이 되는 병원체에 감염될 수 있다. 열성 경련 응급처치를 해준 후 의사의 지시에 따라 환아가 앓고 있는 감염병의 원인 병원체에 감염되지 않게 예방적 치료를 받아야 한다.
-
열성 경련이 끝 난 후 필요에 따라 2주 경에 뇌파검사를 필요에 따라 할 수 있지만 대개 검사하지 않는다.
-
열성 경련이 끝난 후 얼마동안 깊이 잠들어 잘 때도 있다. 이때 환아가 심하게 아파서 잠을 계속 자는지, 또는 열성 경련을 치료할 때 쓴 밸리움(Valium)이나 다른 종류의 항경련제의 부작용으로 잠을 깊이 자는지 확실히 알 수 없다. 이 경우 병원 입원 치료를 요한다.
-
또 집에서 갑자기 열성 경련을 하다가 더 이상 열성 경련을 하지 않아도 부모 자신이 환아를 집에서 관찰 치료하지 말고 의사에게 문의 치료를 받아야 한다.
-
드물게 열성 경련을 한 후 몇 분 내지 몇 시간 후에 또 다시 열성 경련을 하는 경우도 있고, 열성 경련을 유발 시킨 감염병이 어떤 종류의 감염병인지 경련 후 짧은 시간 내 정확히 진단할 수 없다. 또 이때 생긴 열성 경련과 감염병으로 인한 고열 등으로 쉽게 탈수될 수 있다. 이런저런 여러 가지 이유로 감염병을 앓으면서 열성 경련을 할 때는 1~2일 동안 병원 입원 진단 치료를 받는 것이 더 좋다.
열성 경련의 예후
-
과거에 열성 경련을 한 번이라도 했던 병력을 가지고 있는 아이들 중 2% 정도가 최초 열성 경련을 한 이후 어떤 감염병에 걸려 앓는 동안 열이 날 때 열성 경련을 다시 할 수 있다.
-
단순 열성 경련(Simple febrile convulsion)을 했다고 해서 뇌가 손상되지 않는다.
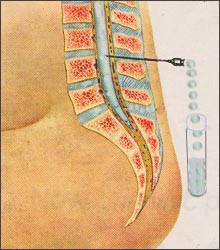
▴ 그림 345. 필요에 따라 뇌척수액을 요추 천자로 뽑아 뇌척수액의 단백, 포도당, 적혈구, 백혈구 등을 검사하고, 그 뇌척수액
피검물로 세균검사 등을 해 뇌막염 등이 있나 진단할 수 있다. 환아가 앉은 자세에서 또는 눈 자세에서 요추천자를 할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
열성 경련을 두 번이나 그 이상 했던 아이는 열성 경련을 한 번 했던 아이보다 간질에 걸릴 가능성은 조금 더 높다. 과거에 열성 경련을 두 번 이상 했던 아이가 그 후에 어떤 감염병을 앓을 때 열성 경련을 또 할 가능성이 조금 더 높다.
-
그 아이가 차후에 감염병을 또 앓을 때 열성 경련을 또 하지 않도록 페노바르비탈이나 다른 종류의 항경련제로 열성 경련을 예방할 수 있다. 그러나 보통 이런 항경련제로 열성 경련 예방 치료를 하지 않는다.
-
열성 경련을 처음 한 후 2년 동안 경구용 페노바르비탈 등 항경련제를 매일 섭취해 열성 경련을 예방해 하라고 권장하지만 그렇게 예방 치료를 해야 할 경우는 드물다.
-
열성 경련을 한 후 2주 경 검사 한 뇌파의 결과가 비정상적으로 나타나는 경우나 열성 경련이 20분 이상 계속되는 경우, 단순 열성 경련이 재발되지 않도록 페노바르비탈, Primidone, 또는 Valproic acid 등 항경련제로 예방 치료를 할 수는 있지만 항경련제로 생기는 부작용 때문에 통상적 예방적 치료를 권장하지 않는다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호–체온, 신생아에게 열이 날 때, 열이 날 때, 해열 진통제,
-
제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 질병–신생아 탈수 열, 신생아에게 열이 나면 어떻게 하나요,
-
제12권 소아청소년 신경, 정신, 정서, 행동, 수면 문제–열성경련
|
다음은 “인공호흡과 심장 마사지(CPR 심폐 소생술), 열성 경련경기에 대한 대처방법”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 인공호흡과 심장 마사지(CPR/심폐 소생술), 경기에 대한 대처방법
Q.
우리아기(남, 28개월)가 경기를 해서 대학병원 응급실에 갔으나, 도착 즉시 의식이 회복(약 5분경과)되어 간단한 진찰(열성경기) 후 퇴원을 하였습니다.
또한, 경기 도중 아이가 숨을 전혀 못 쉬는 것 같아 제가 아이의 입에 손가락을 넣어 갔습니다. 선생님께서 기술하신 내용 중 가만히 있어도 괜찮다고 하셨는데 숨을 전혀 못 쉬는 것으로 보여졌으며, 아이의 얼굴 색깔도 희게 변하는데 경기 도중 아이의 생명에는 지장이 없는지요, 그리고, 만약 경기를 한다면 그냥 가만히 누운 상태에서 애를 들어 병원에 가야 되는지 궁금해서 질문을 드립니다.
A.
혁준님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 더 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
지금쯤 질문에 관한 답변을 이미 얻으셨으리라 믿습니다.
열성 경련을 할 때 상 하기도 내 점액분비, 신경계, 호흡기계와 심장 혈관계의 갑작스런 생리적 변화 등으로 호흡곤란이 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 산소결핍증 내지 저산소증이 생겨 피부가 창백해질 수 있으나 일반적으로 그런 문제들은 자연 회복이 됩니다.
열성 경련을 하는 환아의 구강 내 점액이나 구토물 등을 흡입하기 위한 흡입구 등 이외 아무 것도 넣지 않는 것이 좋습니다.
“가만히 있어도 괜찮다고 하셨는데“의 뜻은 입안에 숫가락 등을 넣지 말고 관찰하라는 뜻이지 구토물 등이 입안에 고여 있을 때 그런 구토물은 흡입해 하기도 속으로 흡인되어 들어 갈 수 있는 구토물을 제거해 내기 위한 흡입구 등을 구강 내 넣지 말고 팔짱을 끼고 있으라는 말은 아닙니다.
의료행위를 의술이라고 말 하는 것같이 열성 경련 치료에 관해 자세히 설명하려면 한 권의 책에 다 쓸 수 없을 정도입니다.
열성 경련을 하다가 호흡곤란 내지 호흡 정지도 생길 수 있고 그때 적절히 기본 심폐소생술로 응급처치를 하지 않으면 사망할 수 있습니다.
그렇기 때문에 부모가 적어도 반의사가 될 정도로 의학공부를 평소에 많이 해야 하고 필요할 때는 평소에 배운 기본 심폐소생술로 죽어가는 자녀를 소생시켜야 할 때도 있습니다.
배운 의술로 때로는 소중한 자녀의 생명을 구하는 데 쓸 수 있습니다. 부모는 이런 응급한 상황에서 의사 역할을 책임지고 1차적 치료를 할 수 있어야 합니다.
그렇지 않으면 의료 응급상황에 따라 의사와 응급 전화 진료를 받고 응급 치료를 하는 것이 가장 좋은 치료입니다.
만일 소아청소년과 의사가 없는 두메산골에서 살 때나 의사의 도움을 전화 진료 또는 다른 방법으로 전혀 받을 수 없는 때는 부모가 응급처치를 해야 합니다. 수수방관하고 죽어가는 어린 자녀를 보고만 있을 수 없습니다.
일반적으로 열성 경련을 하면서 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못하는 경우 의사 아닌 부모가 집에서 1차적으로 대처할 수 있는 응급 치료는 기본 심폐소생술 처치법 이 외 특별히 할 수 있는 응급치료는 별로 없습니다.
열성 경련을 할 때 균혈증이나 패혈증 등 감염병으로 인해 열성 경련을 할 수도 있고 사망할 수도 있습니다.
따라서 열성 경련을 하면 항시 그런 종류의 감염병이 있나 알아서 치료받는 것이 중요합니다.
열성 경련을 할 때 입안에 물고 있던 이물로 상⦁ 하기도가 폐쇄되어 생명에 위험을 받을 수 있기 때문에 열성 경련을 하면서 호흡곤란이 생기면 그에 적절한 응급처치도 해야 합니다. 이런 처치는 그때그때 상황에 따라 적절히 해야 합니다.
열성 경련, 인공호흡과 심장 마사지(CPR 심폐 소생술 처치법) 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
소아청소년과에서 이 문제에 관해 더 상담하시기 바랍니다. 그리고 질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
다음은 “열 경기를 했는데요”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A.열 경기를 했는데요
Q
수고 많으십니다.
제가 판단해야 할 문제지만 선생님의 자문을 얻고 싶어 여쭤봅니다.
우리애가 21개월 여자아인데요 2일정도 기침을 조금씩하고 그럭저럭 잘 놀아서 걱정을 안 했는데요. 자다가 일어나서 우는데 열이 조금 있었어요.
그래서 종합감기약을 먹이고 재웠는데 계속 울다 자다 했거든요.
계속 이불차면 덮어주고 하면서 —그런데 새벽에 쉬라 해서 변기에 데리고 갔는데 열이 많이 나더라구요. 그런데 변기에 앉아서 갑자가 몸이 끄덕끄덕 애가 정신을 잃더니 2분 정도 후에는 입에 거품이 입술을 다 덮을 만큼 나와서 119타고 병원에 가는 도중에 정신이 들면서 엄마를 불렀어요.
이런 일이 있은 지 1주일이 되었는데요, 지금은 아무 일도 없었다는 듯이 잘 놀거든요. 그런데 경기가 있은 후 2주일 뒤에 뇌파검사를 받아보라는 얘기가 있던데요. 검사를 받아볼까요. 받아야겠다는 생각도 많은데 괜히 애 고생시킬까봐 망설여지네요 . 바쁘시더라도 자문 좀 부탁드립니다.
A.
박정희님
안녕하세요. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
열성 경련을 단순 열성 경련과 복합 열성 경련으로 분류합니다.
열성 경련을 한 후 뇌파검사를 꼭 할 필요는 없습니다.
특히 단순 열성 경련을 한 후 뇌파검사를 할 필요가 없습니다.
열성 경련을 했는지 다른 종류의 경련을 했는지 확실치 않을 때는 경련한 후 어느 때든지 뇌파검사를 할 수 있습니다.
이때 응급하지 않으면 경련 후 2~3주 후 선별적 뇌파검사를 하는 것이 좋습니다.
아무 이상이 없는 정상 소아청소년들의 뇌파검사의 결과의 약 15%는 비정상적일 수 있고 또 간질이 있는 아이들의 뇌파검사의 결과의 15%가 정상적으로 나타날 수 있습니다(간질의 종류에 따라서 다릅니다).
단순 열성 경련을 한 후 2주까지 아무 증상 징후가 없으면 뇌파검사를 꼭 할 필요가 없습니다.
그러나 환아의 신경계에 어떤 문제가 있거나 열성 경련을 했는지 다른 종류의 경련을 했는지 확실치 않을 때는 뇌파검사를 하는 것이 좋습니다.
열성 경련, [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호 백과]-제12권 소아청소년 신경계, 정신, 정서, 행동,수면문제–열성 경련]을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
다음은 “5살 여자 아이인데 열경기를 가끔 해요”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 5살 여자 아이인데 열 경기를 가끔 해요
Q.
3살.4살에 한 번씩 했고 올해 들어서 열이 38도에 2달 간격으로 2번했습니다.
병원에서는 6.7세쯤 되면 괜찮아진다고는 하는데 걱정입니다. 의사선생님께서는 자주하면 뇌파검사를 한 번 받아보라고 하시던데 어떻게 해야 하는지 가르쳐주세요. 부탁드립니다.
안녕히 계세요. 충북 제천에서 보냅니다.
A.
선생님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다.
나이, 성별, 과거, 현재, 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 많은 정보가 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 그러나 주신 정보를 토대로 답변을 드립니다.
열성 경련은 8-9세 이후 아이들에게는 잘 유발되지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
열성 경련을 단순 열성 경련과 복합성 열성 경련으로 분류합니다. 이 두 종류의 열성 경련은 다 양성입니다.
자녀가 했던 열성 경련은 단순 열성 경련에 속합니다.
열성 경련을 한 아이들의 뇌에 이상이 생기지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
열성 경련을 한 후 1-2주 후 머리끝부터 발끝까지 자세히 한 진찰결과에 아무 이상이 없고 증상 징후가 없으면 아무 검사를 더 할 필요가 없습니다.
그러나 혈중 칼슘 농도, 마그네슘 농도, 혈당 농도 등을 검사할 수 있습니다.
진찰 결과가 모두 정상이면 뇌 MRI 검사나 CT 스캔 검사를 꼭 할 필요가 없습니다.
건강한 아이들의 뇌파검사가 비정상적으로 나타날 때도 있고 간질을 하는 아이의 뇌파검사가 정상적으로 나타날 수 있습니다.
열성 경련을 한 바로 후나 열성 경련을 한 후 약 10일까지 뇌파검사를 하면 열성 경련을 한 결과로 인해서 뇌파검사의 결과가 비정상으로 나타 날 수 있습니다. 그런 이유로 뇌파검사의 결과으로만 열성 경련을 했다 안했다고 진단하는 데 별 가치가 없습니다.
뇌에 어떤 이상이 있고 열이 나지 않고 경련을 했을 때 뇌파검사는 진단 가치가 있습니다.
일반적으로 단순 열성 경련을 진단 치료하는 데 뇌파검사를 통상적으로 하지 않습니다.
열성 경련을 한 후 환아의 뇌파검사를 꼭 하고 싶을 때는 열성 경련이 끝난 후 2주경 검사하는 것이 보통입니다.
열성 경련을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
그리고 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단을 받으시고 그 문제에 관해 상담하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림 5/22/12
|
다음은 “제아이가 1시간 30분 동안의 열성 경련이 있었는데요”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 제아이가 1시간 30분 동안의 열성 경련이 있었는데요
Q.
나이: 28개월 성별: 남
과거병력: 목이 부어 열이 나서 7개월 때 1번, 돌을 앞두고 하루 2번, 16개월쯤 1번 까지는 정확하게 시간을 재지 못했고 119불러 응급실 도착하면 깨어난 경우가 대부분.. 후유증도 크게 없었음..
가족력: 아빠가 백일 지나면서부터 한 달에 2번씩 6살 때까지 열성 경련이 있었다고 함, 엄마도 어릴적 한 번의 열성 경련이 있었음
진찰소견: 열성 경련, 뇌파이상 없음
하지만 최근 27개월 때 일으킨 경련은 여느 때와 달라 엄마로서 당혹스럽습니다. 여느 때와 다름없이 목이 부어 열이 났구요.. 아이가 경기하는 것을 보고 맘먹고 이번엔 시계부터 보았습니다..5분가량 거품을 물고 의식이 없고 호흡곤란을 보이다가 이내 신음소리를 내면서 우는 듯 변화를 보여 깨어나나 싶었는데 눈을 감고 신음소리를 내며 의식 없이 1시간 30분 가량을 경련을 지속했습니다..
어떠한 사례를 보아도 1시간 넘어가는 경우를 보지 못해 충격은 더욱 큽니다.
의사는 후경련으로 여기는듯합니다.. 경련시간은 5분인데.. 후경련을 1시간 넘게 할 수 있는지요? 119로 경련 20분 경과 후 응급실 도착.. 간호사들은 아이가 깨어났다며 걱정 말라고 하더니 경련이 지속됨을 보고 담당 의사를 불러 응급처치로 좌약, 진정제 3회 투여.. 그래도 아이는 깨어나지 않고 경련(주먹을 꼭 쥐고 두 다리는 뻣뻣.. 눈은 감은 상태 신음소리가 작게 남)이 지속됨.. 1시간 30분이 경과한 후에야 고통스러워 울다 자다를 반복했습니다..
의사는 좋지도 않은 진정제를 3번 맞춰 놓고 그제서야 후경련이라는 무책임한 말만을 추측으로 내뱉더군요… 어찌 되었던 후경련이면 안심할 수 있는 건가요? 어디에도 후경련에 대한 자세한 설명이 없어서 궁금합니다.. 경련 후 걸음을 걷지 못했구요.. 술 취한 사람이 균형을 못 잡고 부딪치고 넘어지듯이 마비증세를 보였습니다.. 이것이 간질 후 나타난다는 todd마비는 아닌지요? 경련을 지켜본 응급실 담당의사는 경험이 없어 보이고 신뢰가 가지 않습니다..
소아신경과 전문의는 단순열성경련으로 보는지 1시간 30분의 경련 시간을 믿지 못하는 듯.. 아니면 안심시키려는 듯.. 뾰족한 치료방법이 지금으로선 없기 때문일 수도 있다는 생각이 듭니다. 뇌파검사 결과 정상인 점과 지금현재로서는 잘 걷고 후유증을 보이지 않는 것만으로 긍정적으로 말합니다.. 재발 가능성만을 보고 발륨 좌약을 경련 시 넣는 것을 권합니다.. 의학적인 지식이 부족한 엄마로서 의사를 믿지도 안 믿지도 못하는 답답한 심정을 적어봅니다..
선생님의 아이라면 어떻게 판단하고 어떻게 대처하시겠습니까?
명쾌한 답변 부탁드립니다..
A.
정아 맘께
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 그리고 병력 증상 등을 자세히 주셔 고맙습니다.
마치 아침에 대학병원 소아청소년과 병실에서 회진을 돌 때 인턴이 담당한 환아의 밤새 병 경과를 주임교수와 레지던트나 의학도에게 보고하는 것처럼 아주 잘 하셨습니다. 감사합니다.
부모가 앓는 자녀의 병력과 그때 생긴 증상 징후 등을 자세히 요약해서 의사에게 잘 전달해 줄수록 자녀가 가지고 있는 병을 더 쉽게 진단할 수 있고 더 쉽게 치료할 수 있습니다.
그래서 환아는 병으로 덜 고생할 것이고 결과적으로 의료비도 적게 들고 부모는 덜 고생할 것입니다.
“용한 의사는 없다”는 신문 기사를 최근 읽은 적이 있습니다.
그 동안 걱정을 많이 해셨습니다.
여러 고명하신 의사로부터 치료 받으시고 상담하시고 그 동안 많이 연구를 하셨는데 제가 그 분들 보다 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있을까 걱정합니다.
오늘 제가 신경 정신 질환에 “경련 중적상태“란 제목으로 경련에 관한 글을 올렸습니다. 꼭 읽어보시기 바랍니다.
제 생각으로 자녀는 경련을 할 때마다 열이 났었고 이번도 경련할 때 열이 났고 열이 나지 않을 때는 경련을 했던 병력이 없고 뇌파검사 결과가 정상인 것을 종합해 보면 열성경련을 했다고 진단하고 싶습니다.
열성 경련에는 단순 열성 경련이 있고 복잡 열성 경련이 있습니다.
정의상으로 20분 이상 경련했고 거기다가 한 시간 반까지 경련이 지속되었고 토드 마비(타드 마비, Todd’s paralysis)가 생겼기 때문에 자녀는 복잡 열성 경련을 한 것 같습니다. 거기다가 30분 이상 계속 전신 경련을 하고 경련하는 동안 의식이 회복되지 않은 것을 보니 경련 중적상태에 빠졌던 것 같습니다.
경련 중적상태에는 3가지 종류가 있습니다.
자녀에게 열성 경련 중적상태가 생겼던 것 같습니다. 약 5% 열성 경련에서 열성 경련 중적상태가 생길 수 있습니다.
적절하게 치료를 잘 받으신 것 같습니다. 그러나 지금부터 열성 경련을 또 생기지 않게 예방 치료를 하는 것에 관해 소아 신경내과 전문의와 상의해 보시기 바랍니다.
열성 경련 예방 치료에 관해 찬반론 때문에 일률적으로 예방하는 방법이 없습니다.
제 자녀라고 하면 어떻게 치료하겠느냐고 물으셨는데 저 역시 제 자식에게 열성 경련 지속 중적성태가 생겼을 때는 응급실에서 적절한 치료를 받고 병원 입원치료를 받고 다른 어떤 병으로 경련을 했는지 알아보고 소아 신경내과 전문의의 치료를 받고 그 분의 지시에 따라 치료하고 예방하겠습니다.
제가 읽은 재미있는 기사를 하나 소개해 드리니 읽어주시기 바랍니다.
|
환자의 비밀을 지키는 원칙 Dr. Ann Bruner’s Principles of confidential care 1. 나는 당신의 건강과 안녕을 위해서 봉사하기 위해서 여기에 있습니다. 2. 나는 당신에게 가장 적절한 치료와 의료봉사를 해드리려고 항상 노력하겠습니다. 3. 누구든지 때로는 조그마한 도움이 필요하다고 나는 믿습니다. 4. 나는 모든 병을 다 고칠 수는 없습니다. 5. 나는 당신의 의사이지 당신의 친구는 아닙니다. 6. 나는 당신에게 거짓말은 하지 않습니다. 7. 나는 당신을 위해서 거짓말은 하지 않습니다. 8. 나는 당신의 건강 증진을 위해 최선을 다해서 의료봉사를 합니다. 9. 나는 무엇이 옳고 무엇이 그르다는 것을 판단하려고 여기에 있는 것이 아닙니다. 10. 부모는 자녀들의 도덕, 윤리, 사회성, 문화적 품행에 관헤 책임져야 합니다. 출처와 저자– Dr. Ann Bruner 저자 번역 |
Febrile convulsions (Febrile seizures) 열성 경련(열 경련/열 경기/열 발작)
Overview of febrile seizures
- A patient without encephalitis, meningitis, brain injury, or any other organic central nerve lesion may have a fever due to an infectious disease in the body other than the brain, and systemic convulsions caused by the fever are called febrile convulsions, competition, or fever seizures.
- Some types of infectious diseases in the brain or central nerve can cause fever, brain infectious diseases can damage the brain, and brain damage can cause systemic convulsions.
- The general convulsions that occur at this time are not called febrile convulsions. Febrile convulsions are symptomatic symptoms that occur when suffering from any infectious disease, not a disease name [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatrics and Family Nursing]-Vol. 12 Pediatric and Adolescent Neurology, Psychiatry, Emotions, Behavior, Sleep Problems-Febrile convulsion
Non-febrile convulsions
- Systemic convulsions without fever,
- Systemic convulsions caused by fever when you have meningitis or encephalitis, Systemic convulsions resulting from meningitis, encephalitis, or cerebral sequelae of meningeal encephalitis
- Systemic convulsions caused by any other lesion in the brain are not considered febrile convulsions.
- Systemic convulsions that result from this are called non-febrile convulsions.

▴ Photo 340. Anal mercury thermometer and oral mercury thermometer These days, a mercury thermometer is not recommended, but a mercury thermometer is very practical because it is cheap and easy to use. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Mechanism and causes of febrile seizures
- The mechanism by which febrile seizures are triggered is not clear.
- However, it is said that when fever occurs, the central nervous system is immature, causing febrile seizures.
1. Viral infectious diseases such as flu, Roseola rash, measles,
2. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal tonsillitis,
3. Fever from bacterial infections such as pneumonia, dysentery, and salmonella
can cause febrile convulsions.
4.When to start to get some infectious disease, fever can trigger febrile seizures.
- While suffering from the infectious disease for several hours, or during a day or two of infectious disease, a fever suddenly develops, which can lead to febrile seizures.
- It is not yet clear why fever does not cause febrile convulsions in some children and febrile convulsions in others. If any of the siblings of the biological parents have a history of febrile seizures due to fever caused by childhood infectious diseases, the other siblings are more likely to develop febrile seizures.
- For this reason, febrile seizures are considered hereditary. If a child who has had a febrile convulsion in the past has had a febrile convulsion and has another infectious disease, a fever is more likely to result in another febrile convulsion.
- According to a study, it was found that children aged 6 months to 8 years old and 3~8% of school-age children Febrile convulsions can be triggered.
- Fever convulsions can be caused mainly in infants and early school-age children from 6 months to 8 years of age, and are less likely to occur in babies before 6 months of age and school-age children after 8 years of age.

▴ Photo 341. Anal body temperature was measured with an anal mercury thermometer. When measuring the anal temperature, hold the anal thermometer with a gloved hand and take the temperature. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Picture 342. Acute pharyngeal tonsillitis (tonsillitis) with swollen tonsils and red tongue. This patient suffers from acute pharyngeal tonsillitis and scarlet fever. You can also have febrile convulsions when you have scarlet fever. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- From 6 months to 3 years old, febrile seizures are most often induced in infants and toddlers. If an infant before 6 months of age or a school-age child after 8 years of age suffers from some kind of infectious disease and fever causes febrile seizures,
- it is necessary to differentially diagnose whether the child is suffering from any other type of infectious diseases, such as encephalitis or meningitis.
- Systemic convulsions can also be triggered when suffering from epilepsy, tetany, hypoglycemia, or other diseases.
- Therefore, if you have systemic convulsions, you should definitely diagnose which disease caused the convulsions.
Symptoms signs of febrile seizures
- With certain infectious diseases, febrile seizures can be triggered suddenly and unpredictably. Symptoms of febrile seizures are non-uniform. Symptoms that are common when having febrile seizures include:
- When a fever occurs due to an infectious disease, a whole-body convulsion suddenly occurs and you lose consciousness, open your eyes, clench your teeth, and foam in your mouth, resulting in difficulty breathing, pale complexion, and blue lips. Ankylosing and intermittent convulsions are induced in the muscles of the whole body, such as the muscles of the limbs and legs.
- At this time, it is sometimes said that the arms and legs are closed and unfolded. When you start suffering from an infectious disease, you start to have a fever, causing febrile seizures.
- Or, there are cases in which the first person knows that they are suffering from an infectious disease due to a high fever only after measuring their body temperature for the first time due to a sudden systemic convulsion.
- Most febrile seizures usually last for 2-3 minutes and then stop on their own. In some cases, it may last for 15 to 20 minutes.
- After the febrile convulsion is over, the body may become droopy, the face becomes pale, and consciousness may become hazy for a while, as if all of the body’s strength has been exhausted.
- However, consciousness lost during febrile seizures returns to normal after the seizures are over. You can fall into a deep sleep for an hour or two after the convulsion is over. Rarely, just after the febrile seizure is over, paralysis occurs on one side of the body for a while and then returns to normal.
- Such hemiplegia is called Todd’s paralysis.
- When you have a febrile seizure, you may have symptoms caused by the infectious disease that caused the fever and symptoms caused by the febrile seizure. For example, when a fever is caused by pneumonia and a febrile convulsion is caused by the fever, symptoms of febrile convulsions and cough and fever caused by pneumonia are usually present together.

▴ Photo 344. Infant urine bag that can be used to receive urine blood samples from infants. Nowadays, some doctors argue that the value of the test result is not very good when a urine bacterium test is performed with urine received in an infant’s urine bag.
However, according to the author’s long experience, if a good clinical evaluation is performed by synthesizing the results of a urine test with a medical examination result, symptom signs, medical history and clean catch urine (clean catch specimen, Midstream specimen), it is for infants. The result of a urine test with urine for a specimen received using a urine bag has a very useful clinical value. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP.

▴ Photo 343. A colony of bacteria grown in a blood bacterial culture test. If necessary, a bacterial culture test may be performed with specimens such as blood, urine, feces, pharynx, and cerebrospinal fluid. The white dots are colonies of bacteria grown in a bacterium culture. Reference; Blood bacteria culture medium (blood broth medium): Bacteria colony (Bacterial colony) Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of febrile seizures
- Diagnose febrile convulsions by synthesizing medical history, symptom signs, and medical examination findings.
- Diagnosis by excluding other convulsive diseases. Most febrile seizures last for 2-3 minutes and then stop spontaneously.
- For that reason, when a child with febrile seizures is brought to the hospital emergency room, the febrile seizures are often over.
- The diagnosis is often made by combining the symptoms parents witnessed when having febrile seizures at home and the doctor’s findings when the febrile seizures are no longer present.
- When bringing a patient with a febrile seizure for more than 2 to 3 minutes to the hospital, it can be diagnosed by observing and examining the convulsive condition.
- When the febrile seizures continue, as well as after the febrile seizures are over, take them to the hospital emergency room to find the cause of febrile seizures and the infectious disease you are suffering from, and treat them according to the cause.
- Systemic and febrile convulsions caused by meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, brain tumors, brain abscess, cerebral hemorrhage, brain injury, hypoglycemia, tetany, drug addiction, lead poisoning, epilepsy, etc. should be differentially diagnosed.
- When febrile convulsions, tests such as pharyngeal mucus, blood, feces, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. with specimens such as bacterial culture, electrolyte concentration in the blood, skull X-rays, brain waves, brain CT scans, brain MRI, etc. are sometimes performed as needed.
- In many cases, febrile seizures are diagnosed and treated without this type of testing at the discretion of the doctor.
The following febrile seizures are called complex febrile seizures.
- Having two or more febrile seizures while having one type of infectious disease,
- Febrile convulsions continue for more than 20 minutes, When Todd’s paralysis occurs after a febrile convulsion A febrile convulsion that is not a complex febrile convulsion is called a simple febrile convulsion.
- The following febrile convulsions are called simple febrile convulsions. Convulsions even though you don’t have a fever,
- If the EEG result is abnormal around 2 weeks after febrile convulsion, If you have systemic convulsions with brain lesions in the brain, you are diagnosed with systemic convulsions due to other diseases or causes before being diagnosed with febrile convulsions.
Treatment of febrile seizures
- Anyone who sees a child whose febrile convulsion is suddenly triggered is very embarrassing.
- However, when you see a child with febrile seizures, he responds calmly. It is anxious and embarrassing, but first, calmly move the child to a safe place and lay it down.
- At the same time, call a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrician, and follow their instructions to initiate appropriate emergency treatment at the site and promptly transfer to the hospital emergency room using an ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation, depending on the situation.
- Secure and open the patient’s airways as follows It can block breathing (airway) and loosen the clothes around the neck that tightly tighten the neck airway.
- Turn your head slightly to the side and lay your upper body a little lower than your lower body so that vomit or mucus in your mouth, pharyngeal cavity, nasal cavity, and airways come out of your mouth by gravity, and prevent vomiting from entering your airways to secure your airways.
- Do not put a spoon or towel in the child’s mouth because he or she may bite his tongue during convulsions. That’s because it can damage your mouth. When suffering from a life-threatening infectious disease such as encephalitis, meningitis, sepsis, etc., systemic convulsions can occur similar to febrile convulsions. Therefore, in the emergency room, it is necessary to differentiate between convulsions and febrile convulsions caused by this type of infectious disease.
- During febrile seizures or even after febrile seizures are over, the patient should be taken to the hospital emergency room to find out what kind of infectious disease he is suffering from.
Infectious diseases are also treated, and febrile seizures are also treated. In general, fever can be antipyretic with antipyretic drugs such as Tylenol or Motrin (refer to [[Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing]-Volume 21, Child and Adolescent Home Care-Antipyretic analgesics).
- Treatment of febrile seizures with oral diazepam anticonvulsants reduces the incidence of simple seizures. In addition, treatment of simple febrile convulsions with anal diazepam, anal midazolam, or nasal midazolam shortens the duration of the spasm.
- Because of the side effects, these types of anticonvulsants are not usually treated. However, most febrile seizures naturally stop within 2 to 20 minutes without treatment with anticonvulsants.
- During febrile seizures, the heart may be beating very slowly or breathing may be difficult, but basic CPR treatment is rarely required.
- Persons who have given artificial respiration by placing the patient’s mouth on the patient’s mouth, mouth, and nostrils, or those who have been treated with direct contact with a patient with febrile convulsions may be infected with pathogens that cause the infectious disease that caused febrile convulsions.
- After giving first aid treatment for febrile seizures, the patient should receive preventive treatment according to the doctor’s instructions to avoid being infected with the pathogen that causes the infectious disease the child is suffering from. After the febrile seizures are over, electroencephalography may be performed as needed around 2 weeks as needed, but it is usually not tested.
- There are times when you sleep deeply for some time after the febrile seizure is over. At this time, it is not clear whether the patient is seriously ill and continues to sleep, or whether he sleeps deeply due to the side effects of Valium or other types of anticonvulsants, which were used to treat febrile seizures.
- In this case, hospitalization treatment is required. In addition, even if you suddenly have a febrile convulsion at home and you no longer have febrile convulsions, parents should not observe and treat the child at home and consult a doctor for treatment.
- In rare cases, febrile convulsions occur several minutes to several hours after febrile convulsions, and the type of infectious disease that caused febrile convulsions cannot be accurately diagnosed within a short time after convulsion.
- In addition, it can be easily dehydrated due to febrile convulsions and high fever caused by infectious diseases.
- For various reasons, when suffering from an infectious disease and having febrile seizures, it is better to undergo hospital admission diagnosis treatment for 1-2 days.
The prognosis of febrile seizures
- About 2% of children who have had a history of febrile seizures in the past can resume febrile seizures when they have a fever while suffering from some infectious disease after the first febrile seizure.
- Simple febrile convulsion does not damage the brain.

▴ Picture 345. If necessary, the cerebrospinal fluid is extracted with a lumbar puncture to examine the protein, glucose, red blood cells, white blood cells, etc. of the cerebrospinal fluid, and the cerebrospinal fluid It is possible to diagnose whether there is meningitis or the like by performing a bacteriological test on the specimen. You can perform a lumbar recommender in the sitting position of the child or in the eye position. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Children who have had two or more febrile seizures are slightly more likely to develop epilepsy than children who have had one febrile seizure.
- A child who has had two or more febrile seizures in the past is a little more likely to have another febrile seizure when he later develops an infectious disease.
- You can prevent febrile seizures with phenobarbital or some other type of anticonvulsant so that the child will not have febrile seizures again when he or she has an infectious disease later on.
- However, these anticonvulsants are not usually treated to prevent febrile seizures. • It is recommended to take anticonvulsants such as oral phenobarbital daily for two years after the first febrile seizures to prevent febrile seizures, but such preventive treatment is rare.
- If the result of an EEG that was examined 2 weeks after febrile seizures is abnormal, or if febrile seizures continue for more than 20 minutes, preventive treatment with anticonvulsants such as phenobarbital, Primidone, or Valproic acid to prevent recurrence of simple febrile seizures.
- Although it can be done, conventional prophylactic treatment is not recommended because of the side effects of anticonvulsants.
- [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Vol. 21 Child and Adolescent Home School Nursing-Body temperature, fever, fever, antipyretic analgesics,
- Volume 6 Neonatal Growth and Developmental Disease-Newborn Dehydration Fever, What should I do if my newborn has a fever,
- Volume 12 Pediatric and Adolescent Neuro, Mental, Emotional, Behavioral, and Sleep Problems-Fever Seizures
The following is an example of online pediatric and adolescent health counseling questions and answers about “Artificial Respiration and Heart Massage (CPR CPR), How to Cope with Fever Seizures”.
Q&A. Artificial respiration and heart massage (CPR/CPR), how to cope with competition
Q.
- My baby (male, 28 months old) played a game and went to the emergency room of a university hospital, but upon arrival, consciousness recovered (approximately 5 minutes elapsed) and was discharged after a brief examination (febrile game).
- Also, during the game, the child seemed to be unable to breathe at all, so I put my finger in the child’s mouth.
- The teacher said that it was okay to stay still, but it was shown that he couldn’t breathe at all, and the child’s face color also turned white. I was wondering if I should go to the hospital to hear, so I ask a question.
A.
Hyeok-jun Good morning.
Thanks for asking.
That’s a good question.
The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, clinical examination, etc., the more helpful it is to give you an answer.
We will respond based on the information you provided. I am sure you have already answered your question by now.
During febrile convulsions, respiratory difficulties may occur due to sudden physiological changes in the injured respiratory tract, nervous system, respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and oxygen deficiency or hypoxia may result, resulting in pale skin.
However, in general, such problems are natural. It will recover.
It is not recommended to put anything other than a suction port for inhaling mucus or vomit in the mouth of a child with febrile seizures.
“You said it’s okay to stay still” means to observe without putting a spoon in the mouth. When vomit is stuck in the mouth, such vomit is inhaled, such as a suction port to remove vomit that may enter the lower respiratory tract.
I’m not saying that you don’t put it in your mouth and keep your arms folded. Just like referring to medical practice as medical treatment, it is hard to write all of them in a single book to elaborate on the treatment of febrile seizures.
Difficulty breathing or arrest of breathing may occur during febrile seizures, and then death may result if first aid is not provided properly with basic CPR.
For this reason, parents need to study medicine a lot so that they can at least become anti-doctors, and when necessary, sometimes they need to resuscitate their dying children with basic CPR they have learned.
The medicine you have learned can sometimes be used to save the life of your precious child. Parents should be able to take on the role of doctors and provide primary care in these emergencies.
Otherwise, depending on the medical emergency, the best treatment is to seek emergency phone care with your doctor and provide emergency treatment.
If you live in Dumesangol where there is no pediatrician or doctor’s help, parents should provide first aid when you cannot get help from a doctor by phone or other means at all. You can’t just watch out and see your little ones dying.
In general, if you have a febrile seizure and you cannot breathe properly, there is not much emergency treatment that can be specifically treated other than basic CPR treatment, which is the primary treatment for parents who are not doctors at home.
When you have febrile seizures, you may have febrile seizures or die due to infectious diseases such as bacteremia or sepsis.
Therefore, it is important to always take care of whether you have that type of infectious disease if you have febrile seizures.
When you have febrile seizures, if you have difficulty breathing while having febrile seizures, you should also take appropriate first aid measures because the upper respiratory tract is blocked by a foreign body in your mouth.
These treatments should be done appropriately depending on the situation.
Please refer to febrile seizures, artificial respiration, and heart massage (CPR CPR treatment).
Please consult with the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents further on this matter. And if you have more questions, please contact us again.
Thank you. Lee Sang-won. MD
The following is an example of a question-and-answer on the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling on “Febrile convulsion”
Q&A. Febrile convulsion
Q
you worked hard.
It’s a matter for me to judge,
but I’d like to ask for advice from the teacher.
My child is a 21-month-old girl.
I coughed a little for 2 days and played well, so I wasn’t worried. I woke up and cried, but I had a little fever.
So, I was given a general cold medicine and went to sleep, but I kept crying and sleeping. If I keep getting full, I cover it up and take it to the toilet because I told him to rest at dawn, but I got a lot of heat.
However, the child suddenly nodded while sitting on the toilet, and after two minutes or so, a bubble in her mouth came out enough to cover her lips, and on the way to the hospital for 119, her mind woke up and called her mother. It’s been a week since this happened, and now I play well as if nothing had happened.
However, there was a talk of asking to have an electroencephalogram two weeks after the game. Let’s take a test.
I have a lot of thoughts that I should take it, but I’m hesitating that I’ll have to suffer. Even if you are busy, please ask yourself.
A.
Park Jung Hee Good morning.
Thanks for the great question.
We will respond based on the information you provided.
The febrile seizures are classified as simple febrile seizures and complex febrile seizures. It is not necessary to have an electroencephalogram after a febrile seizure.
In particular, there is no need to do an electroencephalogram after a simple febrile convulsion.
If you are not sure whether you have had a febrile seizure or another type of seizure, you can do an EEG at any time after the convulsion.
At this time, if it is not an emergency, it is recommended to perform a selective EEG test 2-3 weeks after the convulsion
. About 15% of the EEG results of normal children and adolescents with no abnormalities may be abnormal, and 15% of the EEG results of children with epilepsy may be normal (depending on the type of epilepsy). If there are no signs of symptoms for up to two weeks after a simple febrile seizure, it is not necessary to do an EEG.
However, it is advisable to do an electroencephalogram when you are unsure of any problems with your child’s nervous system, a febrile convulsion, or other types of convulsions.
Please refer to febrile convulsions, [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing]-Vol. 12 Pediatric and Adolescent Nervous System, Mental, Emotional, Behavioral, Sleep Problems-Febrile Convulsions]. If you have more questions, please contact us again.
Thank you. Lee Sang-won. MD
The following is an example of a question-and-answer on the pediatric and adolescent health counseling on “I’m a 5-year-old girl and I have febrile convulsions
.Q&A
She is a 5-year-old girl and she did have febrile convulsions occasionally.
Q. 3 years old. She did febrile convulsions once at 4 years old, and this year she had a febrile convulsion at 38 degrees, 2 times every 2 months.
At the hospital, the doctor says she’ll get better at around 6.7 years old,
but I’m worried.
The doctor often asked me to take an EEG test. Please tell me how to do it. Please. Good-bye. Sent from Jecheon, Chungbuk.
A.
Teacher Good morning.
Thank you for asking.
If you have a lot of information such as age, sex, past, present, family medical history, medical examination findings, clinical test results, etc.,
we can give you a better answer. However, we will respond based on the information you provided. Febrile seizures are usually less likely to be triggered in children after the age of 8-9.
The febrile seizures are classified as simple febrile seizures and complex febrile seizures. Both types of febrile seizures are benign.
The febrile convulsions your child had are a simple febrile convulsion. It is common for children with febrile seizures to have no brain abnormalities. 1-2 weeks after febrile seizures, if there is no abnormality in the detailed examination results from head to toe and there are no signs of symptoms, no further examination is required.
However, blood calcium, magnesium, and blood sugar levels can be tested. If the results are all normal, there is no need to do a brain MRI or CT scan. EEG in healthy children may appear abnormal, and EEG in children with epilepsy may appear normal.
If you do EEG immediately after you have a febrile convulsion or until about 10 days after you have a febrile convulsion, the result of the EEG may be abnormal due to the result of the febrile convulsion.
For that reason, it is not worth diagnosing that you have had febrile convulsions only as a result of the electroencephalogram.
When there is something wrong with the brain and you don’t have a fever and you have convulsions, electroencephalography is of diagnostic value. In general, electroencephalography is not routinely used to diagnose and treat simple febrile seizures.
If you absolutely want to have a child’s electroencephalogram after having a febrile convulsion, it is common to do it around 2 weeks after the febrile convulsion is over. See febrile convulsions. In addition, please consult with the child and adolescent department for medical examination and consultation about the problem. If you have more questions, please visit again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won. MD
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer for “My child had a febrile convulsion for an hour and 30 minutes”.
Q&A
.My child had a febrile convulsion for an hour and 30 minutes.
Q.
Age: 28 months Gender: Male Past medical history:
I couldn’t accurately time the time until 7 months after my throat was swollen and feverish, 2 times a day before the stone, and 1 time about 16 months, and most of the time I woke up when I arrived at the emergency room by calling 119.
There were no significant aftereffects.
.Family history: Her dad reportedly had a febrile seizure after 100 days until the age of 6, twice a month, and her mother also had one febrile seizure as a child. Examination findings: febrile convulsions, no brain damage But she’s been embarrassed as a mother because the convulsions she had in the last 27 months haven’t been common.
As usual, my throat was swollen and feverish.
I decided to watch the child play, and this time I started looking at the watch..After biting a bubble for about 5 minutes,
I was unconscious and had trouble breathing, and then I groaned and changed as if crying. I wanted to wake up to see you, but I closed my eyes and made a groaning sound and continued to convulse for about an hour and 30 minutes without consciousness.
No matter what case she sees, the shock is even greater, as she hasn’t seen any case past an hour. Doctors seem to regard it as a post-convulsion.. The seizure time is 5 minutes.. Can the post-convulsion last more than 1 hour?
Arrive at the emergency room after 20 minutes of convulsions on 119. The nurses said that the child woke up and not worry. When the convulsions persisted, they called the doctor in charge and administered suppositories and sedatives 3 times as first aid. Hold tight and both legs stiff.
Eyes closed and moaning remained quiet.) Continued.
After 1 hour and 30 minutes, I was in pain, so I cried and went to sleep. The doctor set the bad sedative three times and only then spit out the irresponsible word of post-convulsion… What can I be relieved of with post-convulsion? I am curious because there is no detailed explanation of the post-convulsion..
I couldn’t walk after convulsions.
A drunk person showed signs of paralysis as if they were unable to balance and bump and fall. Is this not a todd paralysis that appears after epilepsy?
The emergency room doctor who has watched the convulsion looks inexperienced and is unreliable. Pediatric neurologists don’t seem to believe in the 1 hour and 30 minute convulsion time as simple febrile seizures.
Or seem to reassure them.
I think it may be because there is no sharp treatment method right now.
As a result of the EEG test, they say positively just because they walk well and do not show any aftereffects. As a mother who lacks medical knowledge, it is recommended to use Valium suppositories when convulsing. Write down the frustrating feeling that you can’t..
If she was the teacher’s child, how would she judge and cope?
She asks for a clear answer.. A. I like Jung Ah Good morning. Thanks for asking. And thank you for giving her medical history and symptoms in detail. Y
ou did a great job as if you were going round in the morning in the pediatrics and adolescents department of a university hospital and reported the progress of the patient’s illness overnight to the head professor, the resident, or the medical doctor in charge of the intern. Thank you.
The more detailed summaries the parents have of their child’s medical history and the symptoms and signs that occurred at that time and communicated to the doctor, the easier it will be to diagnose the child’s illness and the easier it will be treated. So the child will suffer less from the illness, and consequently, the medical bill will be less and the parents will suffer less. I recently read a newspaper article saying,
“There is no useless doctor.”
She has been worried a lot in the meantime. You have been treated and consulted by many famous doctors, and you have done a lot of research in the meantime, but I am worried that I will be able to give you a better answer than those of you.
Today I posted a post about convulsions in neuropsychiatric disorders under the title of “Convulsive-Severe State”.
Please read it. In my opinion, my child had a fever every time he had a convulsion, and again when he had a convulsion, he had no history of convulsions and the EEG results was normal.
In febrile seizures, there are simple febrile seizures and complex febrile seizures. By definition, my child seems to have had complex febrile convulsions because it had a convulsion for more than 20 minutes, and the convulsion lasted up to an hour and a half, and Todd’s paralysis occurred.
In addition, as I continued to convulse for more than 30 minutes and did not recover consciousness during convulsions, it seems that I fell into a convulsive-moderate state. There are three types of convulsive-moderate conditions.
The child seems to have developed a febrile seizure-neutral condition. About 5% of the febrile convulsions may result in a severe febrile convulsion.
You seem to have received adequate treatment. However, from now on, you should talk to your pediatric neurologist about preventing another febrile seizure from occurring. There is no uniform way to prevent febrile seizures because of the pros and cons of preventing febrile seizures. When it comes to my child, I asked how he would treat it, but when my child had a persistent febrile convulsion, he was treated appropriately in the emergency room, was hospitalized, and what other diseases he had convulsed, and then he was treated by a pediatric neurologist.
We will treat and prevent it according to his instructions. Let me introduce you to an in
interesting article I read, so please read it.
The principle of keeping patient confidentiality Dr. Ann Bruner’s Principles of confidential care
1. I am here to serve for your health and well-being.
2. I will always try to provide the most appropriate treatment and medical service for you.
3. I believe that everyone needs a little help from time to time.
4. I cannot cure all diseases. 5. I am your doctor, not your friend.
6. I will not lie to you.
7. I will not lie for you.
8. I do my best to provide medical service to improve your health.
9. I am not here to judge what is right and what is wrong.
10. Parents are responsible for their children’s morality, ethics, sociality, and cultural behavior.
Source and Author-Dr. Ann Bruner Author translation
출처 및 참조문헌
-
Manual of emergency pediatrics 4th edition, Robert M. Reece, M.D., p.110, 354
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.24-25
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Mose Grossman, M.D., p.23-24
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.187-188, 252-253, 277
-
Nelson textbook, 14 edition p.1495-1496
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition, p.550-551, 552
-
Journal watch pediatrics and adolescent medicine, october 2008. p.73
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding, by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026