아프타스 궤양(아프타 구내염)
Aphthous ulcer (Canker sores)
아프타스 궤양(아프타 구내염)의 원인
- 혀, 입술, 입천장, 인두, 잇몸 등의 점막층에 한두 개의 궤양이 생겼다가 자연히 낫는 궤양을 아프타스 궤양 또는 아프타 구내염이라고 한다.
- 아직도 원인은 확실히 모른다.
- 그러나 이 병이 음식물 알레르기 질환으로 인해서 생긴다는 설도 있고, 바이러스 감염이나 박테리아 감염, 정신적인 요인, 자가 면역, 또는 외상 등에 의해서 생긴다는 설도 있다.
- 피로할 때나, 많이 긴장할 때에 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 또 여러 종류의 알레르기 질환을 앓는 소아청소년들에게 이 병이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
아프타스 궤양(아프타 구내염)의 증상
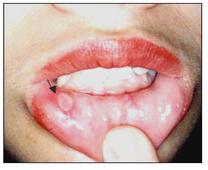
사진 151. 바른 쪽 아래 입술 점막층에 난 아프타스 궤양.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
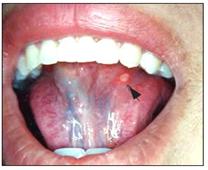
사진 152. 혓바닥 밑 점막층에 난 아프타스 궤양(아프타 구내염)
화살 표시로 가리킨 붉은 반점이 아프타스 궤양이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
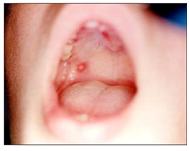
사진 153. 아프타스 궤양이 오른쪽 연구개 점막층에 나 있다. 이 환자에게는 편도염도 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
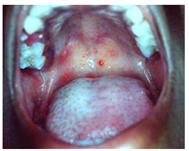
사진 154.헐판자이나(헤르팡기나, Herpangina)로 인해 연구개 점막층에 난 발진. 아프타스 궤양과 헤르팡기나는 다른 병이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
이 병이 발생되기 1, 2일 전부터 아프타스 궤양이 나타날 점막층 부위가 화끈거리고 성가시게 아플 수 있다.
-
아프타스 궤양이 한두 개 나는 것이 보통이다.
-
그러나 그 이상 여러 개가 동시 날 수 있다.
-
궤양의 직경이 2~10mm 정도 된다.
-
궤양의 가장자리는 빨갛고 좀 붓고 둥글다.
-
궤양 표면은 붉은 재색이거나 하얀 곱으로 덮여 있다.
-
이 궤양이 1~2주일간 계속 생겨 있다가 아무런 흉터를 남기지 않고 자연히 낫는다.
-
남아들보다 여아들에게 더 잘 생긴다. 자주 재발되는 경향이 있다.
아프타스 궤양(아프타 구내염)의 치료
-
아플 때에는 타이레놀이나 코데인 등 진통제로 진통시킨다.
- Benzoin Tincture나 Kenalog orabase 등을 궤양에 직접 발라 치료하기도 한다.
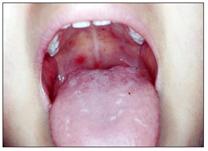
사진 155. 헐판자이나(헤르팡기나)로 인해 구개 점막층에 난 발진. 헐판지아나와 아프타 구내염은 다른 병이다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Aphthous ulcer (Canker sores) Causes of aphthous ulcers (Aphtha stomatitis) 아프타스 궤양(아프타 구내염)
• An ulcer that develops on the mucous layer of the tongue, lips, palate, pharynx, and gums and then heals naturally is called naphthas ulcer or aphtha stomatitis
. • Still not sure of the cause.
• However, some say that this disease is caused by a food allergic disease, and some say that it is caused by viral or bacterial infection, mental factors, autoimmunity, or trauma.
• You may get better when you are tired or when you are very nervous. • It can also be more prevalent in children and adolescents with several types of allergic disorders. Symptoms of aphthous ulcer (Aphtha stomatitis)

Picture 151. Aphthous ulcer on the mucous membrane of the lower lip on the right side. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 152. Aphthous ulcer on the mucous layer under the tongue (Aphtha stomatitis) The red spot indicated by the arrow mark is an aphthous ulcer. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 153. An aphthous ulcer is located on the mucosa of the soft palate on the right. This patient also has tonsillitis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 154. A rash on the soft palate mucosa due to Herpangina. Aphthous ulcer and herpangina are different diseases. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• From 1 or 2 days before the onset of the disease, the area of the mucous membrane where an aphthous ulcer appears may be burning and annoying.
• It is common to have one or two aphthous ulcers.
• However, more than one can fly at the same time. • The diameter of the ulcer is about 2~10mm.
• The edges of the ulcer are red, slightly swollen, and rounded.
• The surface of the ulcer is reddish or covered with white product.
• This ulcer continues to develop for 1 to 2 weeks and heals spontaneously without leaving any scars.
• You look better with girls than boys. It tends to recur frequently.
Treatment of aphthous ulcer (Aphtha stomatitis )
• When you are sick, pain relievers such as Tylenol or Codeine are used.
• Benzoin Tincture or Kenalog orabase may be applied directly to the ulcer for treatment.

Photo 155. A rash on the palatine mucosa due to herpangina. Halpangia and aphtha stomatitis are different diseases. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026