가정에서 보관할 수 있는 의료기구와 의료품
Medical instruments and supplies to keep home for home medical cares
청진기, 혈압계, 손전등, 가위, 핀셋, 족집게, 설 압자, 흡입구, 가습기, 찜질 대, 붕대, 탄력붕대, 면봉, 일회용 반창고, 반창고, 약솜 구, 거즈, 체온계, 컵, 젤리, 스포이드, 삼각건, 안전핀, 그 외
청진기 Stethoscope
-
청진기는 의사나 간호사가 주로 쓰는 의료 기구이지만 요즘은 비 의료인들도 때로는 요긴하게 집에서 쓸 수 있는 일반용 의료기구로 되었다.
-
간단한 청진기 하나를 집에 보관하면 필요할 때 요긴하게 쓸 수 있다.
-
요즘 의사도 간호사도 아닌 일반인이 집안 식구들 중에 누군가에게 고혈압이 있으면 집안에서 의사의 지시에 따라 가정 혈압 측정을 할 때 청진기를 쓸 수 있다.
-
드물지만 집에서 소아의 혈압을 자주 재야 할 때도 있고 성인의 혈압을 재야 할 때도 있다.
-
여러 종류의 청진기가 있다.
-
값이 싸고 간단한 청진기 하나를 집안에 보관했다가 혈압을 측정할 필요가 있을 때 쓰면 좋을 것이다.
-
이제 집안 식구 모두가 반의사가 되고 만다.

사진 128. 가정에 보관할 수 있는 의료품.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
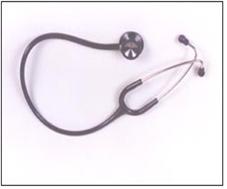
사진 129. 청진기.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
혈압계 Sphygmomanometer
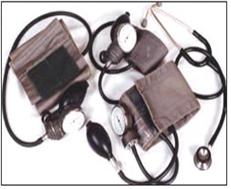
사진 130. 여러 가지 크기의 소아 혈압계.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
의사도 간호사도 아닌 집안 식구 중 누군가가 어린 아이의 혈압을 재야 할 경우는 그리 흔치 않다.
-
그러나 집안 식구들 중 누군가가 고혈압이나 다른 어떤 병으로 오랫동안 누워 앓을 때 의사의 지시에 따라 식구 중 누군가가 혈압을 정기적으로 재야 할 때가 가끔 있다.
-
혈압계의 종류와 크기에도 여러 가지이다.
-
간단한 혈압계 하나를 보관하면 필요할 때에 적절히 쓸 수 있다.
-
요즘은 옴론(OMRON) 혈압기 등 디지탈 혈압기로 보다 쉽게 혈압을 잴수 있다. 심지어는 손목에서도 혈압을 잴 수 있다.
손전등 Flashlight

사진 131. 손전등.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
어두운 곳에서 무엇을 찾을 때 쓸 수 있는 손전등 하나를 집안에 가지고 있어야 한다.
-
손, 발이나 인두 속, 또는 입안 어디가 아프거나 이상 할 경우 어떤 부위에 어떤 병으로 그런지 찾아볼 때 손전등을 요긴하게 쓸 수 있다.
-
손발이나 몸 어디에 박힌 작은 가시나 이물 등을 찾아 빼낼 때도 손전등이 필요하다.
-
그 외로 필요할 때가 더 많다.
가위 Scissors
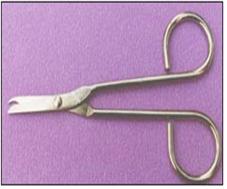
사진 132. 가위.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
보통 가위나 위생용 가위 한 개를 의료용으로 집안에 비치했다가 필요할 때 쓴다.
-
건강 문제로 쓴 붕대, 옷 등을 자를 때도 가위가 필요하다.
핀셋이나 족집게 Forceps and tweezers
-
핀셋 하나 족집게 하나를 가지고 있는 것이 좋다.
-
진드기 주둥이, 그 외 다른 곤충의 주둥이, 벌
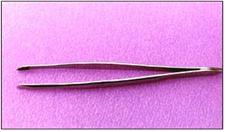
사진 133. 족집게.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

사진 134. 핀셋.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
독침 등이 살갗에 박혀 있을 때 그 것을 핀셋이나 족집게로 뺄 수 있다.
-
콧구멍 속(비강 속), 입안 이물, 또는 외이도 속에 들어 있는 이물을 집어 낼 때 핀셋이나 족집게를 이용 할 수 있다.
-
살갗이나 신체의 어떤 부위에 박혀 있는 가시, 나무 조각, 또는 쇠붙이 조각 등을 손으로는 뽑아낼 수 없을 때 핀셋이나 족집게 등을 이용해서 뽑아낼 수 있다.
설압자 Tongue depressor
사진 135. 설 압자.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
몸이 아프거나 인두나 입안이 아프거나 건강 문제로 병원에 가면 의사가 입안을 들여다보고 진찰할 때가 많다.
-
입 속이나 목구멍 속을 들여다볼 때 혀로 들여다보는 시야가 막혀 인두 속을 자세히 들여다볼 수 없다.
-
바로 이럴 때 설압자로 혀 바닥을 아래로 누르든지 옆으로 젖히든지 위로 올려 인두강 속 여기저기를 자세히 들여다보는데 설압자를 요긴하게 쓸 수 있다.
-
인두 뿐 아니라 목구멍 속, 잇몸, 편도의 크기를 알아보는데 설 압자로 혀를 여기저기로 눌러 시야를 넓이는 데 이용할 수 있다.
-
입안, 인두, 편도 등에 염증이 있는지 없는지 확실히 알아보는데,
-
입천장, 또는 입안 등을 전등불로 자세히 들여다보는데 혈압자를 이용하면 도움이 된다.
-
집에서 부모가 같은 방법으로 자녀의 혓바닥을 아래로 누르든지, 옆으로 젖히든지 해서 자녀의 입안이나 인두강 속 등을 들여다보아야 할 때 설압자를 이용할 수 있다.
-
입안이나 인두강 속 등을 들여다볼 때 쓸 수 있는 설압자가 없을 때는 숟가락을 이용해서 혀바닥을 아래로 누르든지, 옆으로 젖히고 인두강 속이나 입안 등을 들여다볼 수 있다. 한 번 쓴 설압자는 버리고 숟가락은 살균해야 한다.
-
입안에 어떤 이상이 있을 때도 설압자로 입안의 볼과 혀를 이쪽저쪽으로 밀어젖히고 이상 부위를 찾아보는데 설압자를 쓸 수 있다.
-
때로는 손가락뼈가 골절되거나 손가락 마디가 탈구되었을 때 설압자를 부목으로 쓸 수 있다.
흡입구 Suction blub

사진 136. 흡입구.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
신생아, 영유아, 학령기 아이, 사춘기 아이, 또는 성인이 갑자기 구토를 할 때, 의식을 잃을 때 입안이나 인두강 속, 비강 속에 괸 분비물, 구토물, 또는 이물 등을 흡인해 기도를 확보할 때 쓸 수 있는 기구를 흡입구라고 한다.
-
외이도 내 이물이나 눈에 이물이 들어갔을 때도 멸균 흡입구를 이용해 이물을 흡인하여 빼낼 수 있다.
-
흡입구의 둥근 부분을 손으로 눌렀다 폈다하면 비강 속, 입안이나 인두강 속 구토물 등을 흡인해서 기도를 확보할 수 있는 간단한 흡입구(그림 136)도 있고, 구토물 등을 흡인할 수 있는 전기 흡인기도 있다. 전력 작동 흡인장치는 주로 병원에서 쓴다.
-
가정에서 쓸 수 있는 흡입구 한 개를 집안에 보관하고 있다가 필요할 때 요긴하게 쓸 수 있다.
-
한번 쓴 흡입구는 버리든지 깨끗이 씻고 물에 끓여 살균한 후 보관했다가 또다시 써도 된다.
-
그렇지만 감염성이 강한 병원체 감염병을 앓는 환아에게 썼던 흡입구는 한번 사용한 후 버려야 한다.
-
비강 속에 있는 분비물이나 구토 물을 흡입구로 흡인할 때는 흡입력이 약하고 흡입구의 끝부분이 비강 속 깊숙이까지 들어갈 수 없어 원래 치료하려는 목적을 달성하기 어렵고 쓰기가 불편한 점이 많으나 입안의 구토 물 등을 흡입하는 데는 비교적 쓰기가 간편하고 유용한 치료가치가 있다.
-
병원에 태어난 신생아가 신생아실에서 집으로 퇴원할 때 병원 신생아실에서 썼던 흡입구를 집으로 가지고 와서 집에서 필요할 때 쓸 수 있다. 병원에서 가지고 온 흡입구가 깨끗한 것 같지만 적어도 한번 정도 끓는 물에 살균처리한 후 보관했다가 필요할 때는 쓸 수 있다.
가습기와 실내 습도 Humidifier and room humidity

사진 137. 가습기. 요즘은 가습기를 권장 하지 않습니다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
몇 년 전까지 상기도나 하기도에 생긴 바이러스 감염병을 치료할 때, 천식, 폐렴, 모세기관지염 등 호흡기 질병을 치료할 때 가습기를 흔히 사용했지만 요즘 거의 쓰지 않는다.
-
가습기에서 나온 미세 수분 방울이 비강 속을 통과한 후 목안(인두강 속)부위에 들어가서 서로 엉겨 붙어서 후두 부분 기도 이하에 있는 기관 속이나 기관지 속, 또는 모세기관지 속까지 들어가지 못한다.
-
또 멸균되지 않은 가습기나 가습기에 사용되는 물 속에서 상존하는 슈도모나스, 프로테우스, 크레보시엘라 등 수분 호기성 박테리아가 기도 등에 감염되어 슈도모나스, 프로테우스, 또는 크레보시엘라 감염병에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
그 외 여러 가지 이유로 가습기로 환아들의 병을 치료하는데 사용하지 않는다.
-
어떤 병을 앓을 때 실내의 습도가 너무 낮아 실내 공기가 건조해서 기도가 건조하고 건강 문제가 있으면 가습기 등으로 실내 습도를 임시 높일 수 있고 환아에게 수분을 충분히 공급해 환아의 기도가 덜 건조하게 치료 할 수 있다.
-
가습기로 환아가 거처하는 실내 습도를 올리는 방법보다 그 실내뿐만 아니라 집안 전체의 습도를 적절히 높여 주는 방법을 강구해야 한다.
-
환자의 거실의 습도가 다른 방의 습도보다 훨씬 낮아 그 방이 특별히 더 건조해서 여러 가지 방법으로 습도를 높여도 그 이상 더 높일 수 없으면 가습기나 다른 방법으로 그 방안의 습도를 일시적으로 높여 줄 수 있다.
-
가습기가 작동할 때 생기는 잡음으로 환자와 집안 식구들에게 해가 될 수 있다. 가
-
습기를 오랫동안 쓰면 실내 습도가 높아 곰팡이와 몰드가 자랄 수 있고 실내 바닥이 미끄러워 넘어질 수 있다.
-
사실은 가습기를 써야할 때가 그렇게 많지 않다.
찬찜질 대와 더운찜질 대 Hot pack or cold pack
사진 138. 찜질 대
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
찜질에는 더운찜질과 찬찜질, 마른 더운찜질과 습 더운찜질, 어름 물 찬찜질 등이 있다(찜질 참조).
-
고무주머니 찜질대나 플라스틱 주머니 등에
-
얼음 덩어리,
-
얼음 물,
-
찬 물
-
더운 물을 넣어
-
찬 찜질대나 더운찜질대를 약국에서 사서 또는 집안에서 만들어 찬 찜질이나 더운 찜질을 할 수 있다.
-
집안에 찜질용 고무주머니 찜질 대를 한두 개 보관했다가 필요할 때 쓸 수 있다.
-
젤리 형태 화학물질을 넣은 찜질 대(사진 138)를 약국에서 구입할 수 있다.
-
이런 종류의 찜질 대를 약국에서 사서 필요할 때 마다 간편하게 쓸 수 있다.
-
젤리 형태 화학 물질로 만든 찜질 대를 냉장고 속에서 차게 보관한 후 찬 찜질을 할 수 있다.
-
그 찜질 대를 뜨건 물에 담구거나 끓는 물에 담가 따뜻하게 한 후 수건으로 싸서 온도를 적절히 조절해 신체 국소 찜질을 하면 된다. 그 외 다른 방법으로 덥혀 더운찜질을 할 수 있다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료–염좌, 탈구 참조.
붕대 Bandages

사진 139. 여러 가지 크기의 붕대.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
신체 어떤 부위에 자상, 열상 또는 찰과상 등 상처를 감아 줄 때 붕대를 쓸 수 있다.
-
이미 생긴 상처가 더 이상 손상되지 않게 보호하기 위해,
-
상처에서 나는 출혈이 더 이상 나지 않게 지혈시키기 위해,
-
화농성 환부에서 흘러나오는 고름 속에 있는 박테리아가 본인의 신체 다른 부위로나 다른 사람들에게 감염되지 않게 예방할 때,
-
피부 상처에 병원균이 감염되지 않게 예방할 때 환부를 붕대로 감아 치료하는 데 붕대를 사용할 수 있고,
-
상처를 거즈로 덮고 그 위에다 붕대로 감아 거즈를 고정시킬 수 있다.
-
골절, 탈골, 또는 삔 상처에 부목을 대고 고정시킬 때 붕대를 이용할 수 있다.
-
여러 가지 크기의 붕대를 몇 개를 집안에 보관했다 필요할 때마다 쓰면 좋을 것이다.
-
보통 붕대 이 외 탄력 붕대 한두 개를 보관한다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아 응급 의료–염좌
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아 응급 의료–탈구 참조
탄력 붕대 Elastic bandages
-
팔다리에 생긴 탈구 등을 응급 처치할 때 쓸 수 있다.
-
탄력붕대를 쓸 때는 의사의 지시에 따라 써야 한다.

사진 140. 여러 종류의 일회용 반창고와 탄력 붕대.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

사진 141. 탄력 붕대.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
면봉과 Q-팁스 Cotton tipped applicators and Q-tips

사진 142. 면봉.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
젓가락보다 더 짧고 더 가늘고 직경이 3mm 정도 되는 나무나 플라스틱 등으로 만든 봉의 한쪽 끝 또는 양쪽 끝에 솜 등을 감은 의료용 품을 면봉이라 한다.
-
종기 등 환부에서 나오는 고름, 출혈 또는 점액 등을 닦아내는 데도 면봉을 쓸 수 있고,
-
인두 점막층에서 점액을 채취해 세균 검사를 할 피 검물을 얻을 때 면봉을 쓴다.
-
눈의 결막 표면에 들어간 곤충이나 티를 꺼내는 데도 면봉을 쓸 수 있다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아 응급의료–눈의 이물 참조.
-
그 외 외이도 속 또는 비강 속에서 나오는 고름, 피 등을 후벼내는 데도 면봉을 쓸 수 있다. 면봉을 외이도 속 깊숙이 넣어서는 절대로 안 된다.
-
그 외 여러 가지 치료 용도로 면봉을 쓸 수 있다.
-
멸균 면봉과 비 멸균 면봉이 있다. 집안에 비 멸균 면봉을 보관했다가 필요할 때 쓰면 좋을 것이다.
일회용 반창고 Band-aids
-
일회용 반창고를 밴드 에이드라고 한다.
-
원형, 정사각형, 직사각형, 길쭉한 직사각형 등 여러 가지 형태와 여러 가지 크기 일회용 반창고가 있다(사진 143 참조).
-
피부에 생긴 물집, 찰과상, 열상, 자상, 화상 등의 피부 상처 위에 일회용 반창고를 직접 붙여 치료하든지,
-
비눗물로 깨끗이 씻은 피부 환부위에 일회용 반창고를 붙이든지,
-
베타다인 살균제로 살균 치료한 피부 상처위에 일회용 반창고를 붙여 치료할 수 있다.
-
외상으로 생긴 피부 상처에 박테리아 감염이 생기지 않게 일회용 반창고로 상처를 덮어 박테리아 감염병을 예방하는 데 쓸 수 있다.
-
농가진이나 화농성 종기 등에서 나는 피 고름 속 박테리아가 환아 자신이나 다른 사람에게 감염되지 않게 일회용 반창고로 환부를 덮어 박테리아에 감염되지 않게 예방하는 데 쓸 수 있다.
-
각종 일회용 반창고 다수를 필요에 따라 쓸 수 있게 가정에 보관하는 것이 좋다.
-
가능하면 여러 형태의 일회용 반창고를 보관했다가 필요에 따라 적절히 쓰면 더 편리할 것이다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료–찰과상,
-
자상, 절상 참조.
반창고 Adhesive plaster

사진 144. 여러 가지 크기의 반창고.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
한쪽 면은 부착성이 있고 다른 쪽 면은 부착성이 없이 만든 붕대와 비슷한 의료용품을 반창고라 한다.
-
피부에 생긴 찰과상, 절상, 자상 등의 피부 외상을 응급으로 살균 치료하고 일회용 반창고로 덮어 치료하거나,
-
그 피부 환부를 덮은 거즈를 반창고로 고정시켜 치료하든지,
-
그 피부 외상을 붕대로 우선 감고 그 붕대를 더 고정시킬 때 반창고를 사용할 수 있다.
-
부목을 댈 때도 반창고를 이용할 수 있다.
-
반창고의 종류와 크기에도 여러 가지가 있다.
-
크고 작은 반창고 한두 개를 보관했다가 필요할 때 적절히 쓰면 편리할 것이다.
약솜구 Cotton balls

사진 145. 약솜구.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
직경이 1~3cm 정도 크기로 둥글게 만든 약솜 덩어리를 약솜구라 한다.
-
약솜구는 크고 작게 만든 여러 종류의 약솜구가 있다.
-
살균 처리를 한 약솜구도 있고 살균 처리를 하지 않은 깨끗한 약솜구도 있고,
-
큰 뭉치로 만들어 파는 약솜 뭉치도 있다.
-
피나 고름, 또는 체액 등은 약솜구에 잘 흡수되기 때문에 피나 고름 등을 씻을 때 약솜구를 주로 이용한다.
-
살균 제 등을 약솜구에 묻혀 피부나 점막층 상처를 치료할 때 약솜구를 이용 할 수 있다.
-
살균된 작은 약솜구를 다소 사서 보관했다가 필요에 따라 쓰면 좋을 것이다.
| 요즘 약솜구 대신 화학섬유로 약솜구와 비슷하게 만든 의료품을 많이 쓴다. |
거즈 Gauze
-
거즈는 화학 섬유나 면 등으로 만든 일종의 천 조각이다.
-
거즈의 크기 모양 두께가 여러 가지다.
-
멸균 거즈, 멸균 되지 않았지만 깨끗하게 만든 거즈가 있고, 5x5cm, 8x8cm 등 여러 가지 크기의 거즈가 있다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료–찰과상, 자상, 절상 참조.
-
찰과상, 열상, 자상 등의 피부 상처를 비눗물로 깨끗이 씻은 후 상처를 거즈로 덮어 치료할 수 있고 그 상처를 비눗물로 씻은 후 베타다인 액으로 살균 치료 한 후 그 상처를 거즈로 덮어 치료할 수 있다.

사진 146. 거즈.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
상처에 세균이 감염되지 않게 상처를 보호할 때 상처를 멸균 거즈나 일회용 반창고로 덮어 치료할 수 있다.
-
피부 상처를 깨끗이 씻고 살균 치료를 할 때 멸균 거즈를 주로 쓸 수 있다.
-
그 외 상처를 보호하기 위해서 거즈로 덮을 수 있다.
-
화농성 종기 등에서 나오는 피고름 속에 있는 박테리아가 환아 본인이나 다른 사람에게 감염되지 않게 조치 할 때도 거즈를 쓸 수 있다.
-
크고 작은 멸균 거즈 다소를 보관했다가 필요할 때 쓸 수 있다.
체온계 Thermometer

사진 147. 구강 체온계와 항문 체온계.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
체온계에 관해서 이미 p.00에서 설명했다. 여기서는 주로 요즘 흔히 쓰는 체온계에 관한 정보를 제공하고 있다.
-
체온을 잴 수 있는 온도계를 체온계라고 한다.
-
체온을 잴 수 있는 체온계에는 여러 종류가 있다.
-
오래 전부터 많이 써왔던 재래식 유리로 만든 수은 체온계도 있다.
-
신체의 각 부분의 체온을 잴 수 있는
-
액와 체온(Axillary temperature),
-
신체 체온(Body temperature),
-
직장 체온(Rectal temperature),
-
고막 체온(Tympanic temperature),
-
이마 체온(Forehead temperature),
-
귀 체온(Ear temperature),
-
복부 체온(Abdomen temperature),
-
아기체온 (Baby temperature),
-
구강 체온(Oral temperature) 등을 잴 수 있는 전자체온계(Electronic thermometer)도 있다.
-
귀 체온을 재는 귀 체온계,
-
고막 체온을 재는 고막체온계,
-
이마 체온을 재는 이마체온계 등 여로 종류의 전자 체온계가 있고 가격도 상당히 다르다.
여러 종류의 상품 전자 체온계 VARIOUS ELECTRONIC THERMOMETER
-
ThermoScan pro 4000 ear Thermometer,
-
Super Temp plus Thermometer,
-
Genius Tympanic Thermometer,
-
MooreBrand,
-
Digital Thermometer,
-
Digital Thermometer,
-
ZooTemp Thermometer,
-
Instant Ear Thermometer,
-
Temporal Scanner,
-
Temporal artery
-
Thermometer,
-
Filac 3000 Electronic Thermometer,
-
ADTEMP ll Digital Thermometer,
-
ADTEMP v Digital Thermometer,
-
ADTEMP 1 mercury replace Digital Thermometer 등 여러 종류의 전자 체온계가 있다.
-
일회용 반창고와 같이 생긴 체온계도 있다.
-
일회용 반창고와 같이 생긴 체온계는 1~2분 동안 이마에 붙였다가 떼면 체온을 잴 수 있다.
-
외이도 속 체온을 잴 수 있는 전자 체온계(컴퓨터 체온계)도 있고 그 값이 상당하나 사용하기가 간편하다.
-
영유들이 입으로 빠는 노리개 젖꼭지 속에 넣은 체온계도 있다. 그 노리개 젖꼭지를 빨게 해 체온을 잴 수 있다.
-
항문, 입안, 또는 겨드랑에서 잴 수 있는 유리로 만든 재래식 수은 체온계는 쓰기에 간편하고 가격도 싸고 실용적이다.
-
유리로 만든 수은 항문 체온계 하나와 수은 구강 체온계 하나를 가지고 있다가 필요에 따라 쓰면 좋을 것이다.
-
체온계의 장점 단점이 있다.
-
단골 의사에게 물어 전자 체온계를 하나를 사서 보관했다가 쓸 수 있다
-
열이 날 때 참조.
-
체온계의 종류와 체온 측정 참조.
컵 Cups

사진 148. 컵.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
소변 또는 대변 등 피 검물로 각종 임상 검사를 할 때 필요한 검사용 피 검물을 담아 병원이나 소아청소년과에 가지고 갈 수 있는 한 번도 쓰지 않은 깨끗한 컵이나 멸균 컵을 한두 개 보관하는 것이 좋다.
-
가능한 한 120~240cc 정도 액체를 담을 수 있는 깨끗하고 멸균 플라스틱 컵을 한두 개 보관하는 것이 더 좋다.
-
때로는 종이컵 한두 개를 집안에 보관했다가 필요에 따라 쓸 수 있다.
-
가래, 피, 대변, 소변, 고름, 구토 물 또는 그 외 진단용 피검물을 집에서 컵에 받아가지고 병원으로 가지고 가면 피검물을 이용해 필요한 임상 검사를 하는 데 요긴하게 쓸 수 있다.
-
가능하면 멸균 플라스틱 컵 하나를 비치하면 더 좋을 것이다.
-
액체 형태의 약물을 먹을 때, 그 약물의 용량을 측정할 수 있는 플라스틱 컵이나 종이컵, 투약용 컵 한두 개를 보관한다.
사진 149. 물약을 먹일 때 쓸 수 있는 물약 측정 스푼.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

사진 150. 물약을 먹일 때 약의 용량을 측정할 때 쓸 수 있는 플라스틱 측정 컵.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제10권 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기계 질환–소변검사 참조.
젤리 Jelly

사진 151. 젤리.
Copyright ⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
젤리는 윤활제의 일종으로 여러 가지 치료 목적으로 널리 쓰인다.
-
유리로 만든 항문 체온계로 항문 체온을 잴 때나 전자 체온계로 항문체온을 잴 때 항문 속으로 들어가는 체온계의 끝 부분을 덮는 프로부에 젤리를 발라 체온계 프로부 끝 부분 매끄럽게 할 목적으로 젤리를 쓸 수 있다.
-
장갑을 낀 손가락으로 항문 속을 진찰할 때 장갑을 낀 손가락에 젤리를 바를 수 있다.
-
항문이나 직장 또는 질 강을 검진할 때 쓰는 의료 기구에 발라 그 의료 기구가 쉽게 들어갈 수 있게 할 때도 젤리를 이용한다. 신생아의 체온 재는 법 참조.
-
젤리 튜브 한 개를 집안에 보관했다 필요에 따라 쓰면 좋을 것이다
스포이드 Spoid
사진 152. 스포이드.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
시럽 약(시럽제)이나 방울 약(점적 약, 점적 약제)의 양을 측정할 때,
-
시럽 약(시럽제)이나 방울 약을 영유아에게 먹일 때,
-
외이도 속이나 비강 속 또는 눈에 점적약제를 넣을 때 쓸 수 있다.
-
크고 작은 스포이드 한두 개를 보관했다가 필요할 때 쓰면 좋을 것이다.
-
한 방울을 드롭(A drop)이라 하고 전 스포이드(점정기)의 양을 드로퍼(Dropper)라고 한다.
-
이 드롭이나 드로퍼의 양을 혼동해서는 안 된다.
삼각건 Sling

사진 153. 삼각건.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
삼각건은 삼각형 직물 의료 용품이다.
-
골절 된 팔뼈나 다리뼈가 있는 신체 부위, 또는 탈구가 되거나 삔 부위를 고정시켜 응급 치료를 할 때 쓸 수 있다.
-
한두 개의 삼각건을 집안에 보관했다가 필요에 따라 쓰면 좋을 것이다
안전 핀 Safety pin
사진 154. 안전핀.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
-
골절, 탈골, 자상 등 외상을 응급으로 처치할 때 쓴 붕대나 삼각건 등을 고정시키기 위해 안전핀을 쓸 수 있다.
-
필요에 따라 찢어진 옷을 임시 고정 하는 데도 쓸 수 있다.
-
천 기저귀를 채울 때도 안전핀을 이용할 수 있다.
-
크고 튼튼한 안전핀 몇 개를 보관했다가 필요할 때 쓰면 좋을 것이다.
Medical instruments and supplies to keep home for home medical cares
Stethoscope,
blood pressure monitor, flashlight, scissors, tweezers, tweezers, tongue depressor, suction port, humidifier, compress, bandage, elastic bandage, cotton swab, disposable band-aid, band-aid, cotton ball, gauze, thermometer, cup, jelly, eyedropper, triangle gun, safety pin, etc Stethoscope
• The stethoscope is a medical device mainly used by doctors and nurses, but these days, it has become a general medical device that non-medical people can sometimes use at home.
• Keeping a simple stethoscope at home will come in handy when you need it. • Nowadays, ordinary people who are neither doctors nor nurses can use a stethoscope to measure blood pressure at home according to the doctor’s instructions if someone in the household has high blood pressure.
• In rare cases, it is often necessary to have children’s blood pressure taken at home and sometimes adults’ blood pressure.
• There are several types of stethoscopes.
• A cheap, simple stethoscope is a good idea to keep at home and use it when you need to measure your blood pressure.
• Now everyone in the family becomes an anti-doctor.

Picture 128. Medical supplies can be stored at home. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 129. Stethoscope. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Sphygmomanometer

Photo 130. Pediatric sphygmomanometers of different sizes. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• It is not uncommon for someone in the household who is neither a doctor nor a nurse to take a young child’s blood pressure.
• However, when someone in your household has been bedridden for a long time with high blood pressure or some other illness, sometimes it is necessary for someone in your household to have their blood pressure checked regularly as directed by a doctor.
• There are many different types and sizes of blood pressure monitors.
• Keep one simple sphygmomanometer so you can use it properly when you need it.
• Nowadays, you can measure your blood pressure more easily with a digital blood pressure device such as an OMRON blood pressure monitor. You can even measure your blood pressure from your wrist.
Flashlight

Photo 131. Flashlight. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• You should have a flashlight in your house that you can use to find something in the dark.
• If your hands, feet, in pharynx, or in your mouth hurts or feels strange, you can use a flashlight to find out which part is the cause of the disease.
• A flashlight is also needed to find and remove small thorns or foreign objects embedded in limbs or other parts of the body.
• More often than not.
Scissors

Photo 132. Scissors. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• I usually have a pair of scissors or sanitary scissors at home for medical use and use when needed.
• Scissors are also needed to cut bandages, clothing, etc. worn for health reasons.
Forceps and tweezers
• It is good to have a pair of tweezers and a pair of tweezers. • mite snouts, snouts of other insects, bees

Photo 133. Tweezers. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Photo 134. Tweezers. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• When a poison sting is lodged in the skin, it can be removed with tweezers or tweezers.
• Tweezers or tweezers can be used to pick up foreign objects in the nostrils (in the nasal passages), in the mouth, or in the external auditory canal.
• If you cannot pull out a thorn, a piece of wood, or a piece of metal that is embedded in the skin or any part of the body, you can use tweezers or tweezers to pull it out.
Tongue depressor

Photo 135. Tongue depressor.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• If you are sick, sore throat or mouth, or go to the hospital for a health problem, your doctor will often look into your mouth and examine you.
• When looking into the mouth or throat, the view through the tongue is blocked, making it impossible to look closely into the pharynx.
• In this case, you can use the tongue depressor to take a closer look inside the pharyngeal cavity by pressing the bottom of the tongue down, tilting it sideways, or lifting it upwards.
• To find the size of not only the pharynx, but also the inside of the throat, gums, and tonsils, it can be used to widen the field of view by pressing the tongue here and there with a tongue depressor.
• Make sure there is no inflammation in the mouth, pharynx, tonsils, etc.
• It is helpful to use a blood pressure monitor to look closely at the roof of your mouth or your mouth with a light.
• At home, you can use a tongue depressor when you need to look into your child’s mouth or pharyngeal cavity, either by pressing down on your child’s tongue or leaning to the side in the same way.
• If you do not have a tongue depressor that can be used to look into your mouth or into the pharyngeal cavity, you can use a spoon to press down on the bottom of the tongue or tilt it to the side to look into the pharyngeal cavity or mouth. Once used, the tongue depressor should be discarded and the spoon should be sterilized.
• When there is any abnormality in the mouth, the tongue depressor can be used to push the cheeks and tongue in the mouth from side to side and search for abnormalities.
• Sometimes a tongue depressor can be used as a splint when a finger bone is fractured or a knuckle is dislocated.
Suction blub

Photo 136. Intake. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• When a newborn, infant, school-age child, adolescent child, or adult suddenly vomits or loses consciousness, it can be used to secure the airway by aspirating secretions, vomit, or foreign objects in the mouth, pharynx, or nasal passages. This device is called a suction port.
• Even when a foreign object enters the external auditory meatus or the eye, it can be removed by aspiration using the sterile suction port.
• There is a simple suction port (Fig. 136) that can secure an airway by aspirating vomit in the nasal cavity, mouth, or pharynx by pressing and opening the round part of the suction port with your hand, and there is an electric aspirator that can suck vomit, etc. . Power-operated suction devices are mainly used in hospitals.
• You can keep one inlet for home use at home and use it when you need it.
• Once used, the inlet can be thrown away or washed clean, sterilized by boiling in water, and then stored and used again.
• However, the inhaler used for a child suffering from a highly infectious pathogenic disease should be discarded after one use.
• When inhaling secretions or vomit in the nasal cavity through the inhalation port, the suction power is weak and the tip of the inhalation port cannot go deep into the nasal cavity, making it difficult to achieve the original purpose of treatment and inconvenient to use. It is relatively easy to use and has useful therapeutic value.
• When a newborn born in the hospital is discharged home from the neonatal unit, the suction port used in the hospital’s neonatal unit can be brought home and used when needed at home. The intake port brought from the hospital looks clean, but it can be sterilized at least once in boiling water and then stored and used when needed.
Humidifier and room humidity

Photo 137. Humidifier. Humidifiers are not recommended these days. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Until a few years ago, humidifiers were commonly used to treat viral infections of the upper and lower respiratory tracts and respiratory diseases such as asthma, pneumonia, and bronchiolitis, but are rarely used these days.
• After passing through the nasal cavity, the microscopic water droplets from the humidifier enter the throat (in the pharyngeal cavity) and become entangled with each other and cannot enter the trachea, bronchus, or capillary bronchus under the larynx.
• In addition, water aerobic bacteria such as Pseudomonas, Proteus, and Crebosiella that exist in unsterilized humidifiers or water used in humidifiers can infect the respiratory tract and cause Pseudomonas, Proteus, or Crebosiella infections.
• Do not use humidifiers to treat sick children for other reasons.
• When you have a disease, the indoor humidity is too low and the airway is dry. If you have a dry airway and have health problems, you can temporarily increase the indoor humidity with a humidifier, etc., and provide sufficient moisture to the patient to treat the patient’s airway less dry. can
• Rather than using a humidifier to increase the humidity in the room where the child lives, it is necessary to find a way to properly increase the humidity not only in the room but also in the whole house.
• If the patient’s living room is particularly drier and the humidity in the patient’s living room is much lower than the humidity in the other rooms and the humidity in the room cannot be increased further by various means, a humidifier or other means can temporarily increase the humidity in the room.
• Noise generated when the humidifier is operating can be harmful to the patient and family members. end
• If moisture is used for a long time, mold and mold may grow due to high indoor humidity, and the indoor floor may become slippery and may fall.
• The truth is, there aren’t many times when you need to use a humidifier. Cold pack and hot pack
Hot pad (compress) or cold pad(compress)

Photo 138. compress Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• There are hot and cold compresses, dry hot compresses and wet hot compresses, and cold compresses with ice water (see compresses).
• Rubber bags, steam pads, plastic bags, etc.
• ice cubes,
• ice water,
• cold water
• Put hot water
• You can buy a cold or hot compress at a pharmacy or make at home to apply a cold or hot compress.
• You can keep one or two poultice bags at home and use them when you need them.
• A poultice pad with jelly-like chemicals (Picture 138) is available at pharmacies.
• You can buy this type of poultice at the pharmacy and use it whenever you need it.
• You can apply a cold compress after storing a jellied poultice with a chemical substance in the refrigerator.
• Soak the spatula in hot water or boiling water to warm it up, wrap it in a towel, adjust the temperature appropriately, and apply a local compress to the body. There are other ways to warm up and apply a hot compress.
• www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents – See Sprains and Dislocations. bandages

Photo 139. Bandages of different sizes. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Bandages can be used to cover cuts, lacerations or abrasions on any part of the body. • To protect an already existing wound from further damage;
• To stop bleeding from the wound,
• To prevent infection of bacteria in pus from purulent lesions to other parts of the body or to others;
• Bandages can be used to treat skin wounds by bandaging them to prevent pathogens from infecting them;
• Gauze can be immobilized by covering the wound with gauze and wrapping a bandage over it.
• Bandages may be used to splint and immobilize fractures, dislocations, or sprains.
• It’s a good idea to keep a few different sizes of bandages around the house and use them whenever you need them.
• Store one or two elastic bandages other than the usual bandages. [Parents should also become anti-doctors – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing] – Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children – Sprains
• www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Pediatric Emergency Medical Care-Refer to Dislocation
Elastic bandages
• It can be used for first aid for dislocations in limbs.
• When using an elastic bandage, follow your doctor’s instructions.

Photo 140. Different types of disposable bandages and elastic bandages. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Photo 141. Elastic bandage. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Cotton-tipped applicators and Q-tips

Photo 142. Cotton swab. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• A cotton swab is a medical product made of wood or plastic, shorter and thinner than chopsticks and about 3mm in diameter, with cotton wrapped around one or both ends.
• A cotton swab can also be used to wipe pus, bleeding, or mucus from the affected area, such as a boil.
• Use a cotton swab to collect mucus from the pharyngeal mucosa to obtain a blood sample for bacteriological testing.
• Cotton swabs can also be used to remove insects or debris that have entered the conjunctival surface of the eye.
• www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Pediatric Emergency Medical Care-See foreign body of the eye.
• In addition, cotton swabs can be used to remove pus and blood from the ear canal or nasal passages. Never insert a cotton swab deep into the ear canal.
• Swabs can be used for many other therapeutic purposes.
• There are sterile and non-sterile swabs. It’s a good idea to keep non-sterile swabs at home and use them when you need them.
Disposable Band-Aids
• Disposable bandages are called Band-Aids.
• Disposable band-aids are available in many shapes and sizes, including round, square, rectangular, and oblong (see photo 143).
• Apply a disposable band-aid directly to the skin wound, such as blisters, abrasions, lacerations, cuts, or burns, or
• Apply a disposable band-aid to the affected area of the skin that has been thoroughly washed with soapy water.
• It can be treated by attaching a disposable band-aid to the skin wound that has been sterilized with betadine disinfectant.
• It can be used to prevent bacterial infection by covering the wound with a disposable band-aid to prevent bacterial infection in the skin wound caused by trauma.
• It can be used to prevent infection by bacteria by covering the affected area with a disposable band-aid so that the bacteria in the blood pus from impetigo or purulent boils do not infect themselves or others.
• It is a good idea to keep a large number of disposable bandages at home so that they can be used as needed.
• If possible, it will be more convenient to store several types of disposable bandages and use them appropriately as needed.
• [Parents should also become anti-doctors- Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing]-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents-Abrasions,
• See cuts, cuts. Adhesive plaster

Photo 144. Band-aids of different sizes. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• A medical product similar to a bandage made with adhesive on one side and non-adhesive on the other side is called a band-aid.
• Emergency sterilization treatment of skin trauma such as abrasions, cuts, and cuts on the skin and covering it with a disposable band-aid;
• Treatment by fixing the gauze covering the affected skin area with a band-aid, or
• The skin trauma may be first bandaged and then a band-aid may be used to further immobilize the bandage.
• Bandages can also be used for splinting.
• There are many types and sizes of band-aids.
• It will be convenient to store one or two large and small bandages and use them appropriately when needed.
Cotton balls

Photo 145. Cotton balls. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Cotton balls is a round ball of cotton with a diameter of 1~3cm.
• Yaksomgu has several types of Yaksomgu made large and small.
• There are sterilized Yaksom balls(Cotton balls), and there are clean Yaksom balls that have not been sterilized.
• There are also bundles of cotton balls sold in large bundles.
• Blood, pus, or body fluids are absorbed well by the Yaksomgu, so the Yaksomgu is mainly used to wash the blood or pus.
• It can be used to treat wounds on the skin or mucosal layer by applying a disinfectant, etc. to the cotton ball.
• It would be good to buy some sterilized small cotton balls, store them, and use them as needed. Nowadays, instead of Yaksomgu, many medical products made with chemical fibers similar to Yaksomgu are used. Gauze
• Gauze is a piece of fabric made from chemical fibers or cotton.
• There are many different sizes, shapes, and thicknesses of gauze.
• There are sterile gauze, gauze that is not sterilized but made clean, and there are gauze of various sizes such as 5x5cm and 8x8cm.
• www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents-See Scratch, Cut
• Skin wounds such as abrasions, lacerations, and cuts can be treated by washing with soapy water and then covering the wound with gauze.

Photo 146. Gauze. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• To protect the wound from bacterial infection, the wound can be treated by covering it with sterile gauze or a disposable band-aid.
• Sterile gauze can be mainly used for cleaning and sterilizing skin wounds. • Other wounds may be covered with gauze to protect them.
• Gauze can also be used to prevent infection of the bacteria in the blood pus from purulent boils, etc. to the patient or others.
• You can store some large and small sterile gauze and use them when needed.

Photo 147. Oral and anal thermometers. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• The thermometer has already been explained. This article mainly provides information on thermometers that are commonly used these days.
• A thermometer that can measure body temperature is called a thermometer.
• There are several types of thermometers that can measure body temperature.
• There is also a mercury thermometer made of conventional glass, which has been widely used for a long time.
• It is possible to measure the body temperature of each part of the body.
• Axillary temperature;
• Body temperature;
• Rectal temperature;
• Tympanic temperature;
• Forehead temperature;
• Ear temperature;
• Abdomen temperature;
• Baby temperature,
• There is also an electronic thermometer that can measure oral temperature.
• Ear thermometer to measure ear temperature;
• A tympanic thermometer to measure the eardrum temperature;
• There are various types of electronic thermometers, such as forehead thermometers that measure the temperature of the forehead, and the prices are quite different.
VARIOUS ELECTRONIC THERMOMETER VARIOUS ELECTRONIC THERMOMETER
• ThermoScan pro 4000 ear thermometer;
• Super Temp plus Thermometer,
• Genius Tympanic Thermometer;
• MooreBrand,
• Digital Thermometer;
• Digital Thermometer;
• ZooTemp Thermometer,
• Instant Ear Thermometer,
• Temporal Scanner;
• Temporal artery
• Thermometer;
• Filac 3000 Electronic Thermometer,
• ADTEMP ll Digital Thermometer,
• ADTEMP v Digital Thermometer,
• There are several types of electronic thermometers, such as the ADTEMP 1 mercury replace Digital Thermometer.
• There are also thermometers that look like disposable bandages.
• A thermometer that looks like a disposable band-aid can be placed on the forehead for 1 to 2 minutes and then removed to measure the body temperature.
• There is also an electronic thermometer (computer thermometer) that can measure the body temperature in the ear canal, and although the value is considerable, it is easy to use.
• There is also a thermometer placed in the soother’s nipple that infants suck at. You can take the body temperature by sucking the soother’s nipple.
• Conventional mercury thermometers made of glass that can be taken in the anus, mouth, or armpit are easy to use, inexpensive and practical.
• It’s a good idea to keep one glass mercury anal thermometer and one mercury oral thermometer and use them as needed.
• There are advantages and disadvantages of thermometers.
• Ask your regular doctor to buy an electronic thermometer, keep it and use it
• See when you have a fever.
• See Types of Thermometers and Measuring Body Temperature.
Cups

Photo 148. Cup. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• It is recommended to keep one or two clean or sterile cups that have never been used and can be taken to a hospital or pediatric department with blood samples for various clinical tests, such as urine or feces.
• If possible, it is better to keep one or two clean, sterile plastic cups that can hold as much as 120-240 cc of liquid.
• Sometimes you can keep one or two paper cups at home and use them as needed.
• If you take sputum, blood, feces, urine, pus, vomit, or other diagnostic specimens from home in a cup and take them to the hospital, you can use the specimens to perform necessary clinical tests.
• If possible, it would be better to have one sterile plastic cup.
• When taking liquid medications, keep one or two measuring cups, plastic cups, paper cups, or dosing cups.

Photo 149. A potion measuring spoon that can be used to dispense potions. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Picture 150. A plastic measuring cup that can be used to measure the dose of a potion when feeding it. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 10 Children and Adolescent Kidney and Urogenital System Disorders – See Urinalysis.
Jelly

Photo 151. Jelly. Copyright ⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Jelly is a kind of lubricant and is widely used for various therapeutic purposes.
• Jelly can be used to smooth the tip of the thermometer probe by applying jelly to the probe part that covers the tip of the thermometer that goes into the anus when taking anus temperature with a glass anal thermometer or with an electronic thermometer.
• When examining the anus with a gloved finger, you can apply jelly to the gloved finger.
• Jelly is also used to apply to medical instruments used for examining the anus, rectum, or vaginal cavity to make them easier to enter. See How to take a newborn’s temperature.
• You may want to keep a tube of jelly at home and use it as needed.\
Spoid

Photo 152. Eyedropper. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• When measuring the amount of syrup medicine (syrup) or drop medicine (drop medicine, drop medicine),
• When feeding syrup (syrup) or drops to infants,
• It can be used to inject drops into the ear canal, nasal cavity, or eyes.
• It would be good to keep one or two large and small droppers and use them when needed.
• One drop is called A drop and the total amount of the dropper (pointer) is called Dropper.
• Do not confuse the amount of this drop or dropper.
Triangle sling

Photo 153. Triangle gun. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• The triangular gun is a triangular textile medical device.
• It can be used for emergency treatment by immobilizing a body part with a fractured arm or leg bone, or a dislocated or sprained part.
• It’s a good idea to keep one or two tripods around the house and use them as needed. Safety pin

Photo 154. Safety pin. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Safety pins can be used to fix bandages or triangular tendons used in emergency treatment for trauma such as fractures, dislocations, and cuts.
• Can also be used to temporarily fix torn clothes if necessary.
• Safety pins can also be used to fasten cloth diapers.
• It would be a good idea to keep a few large, sturdy safety pins and use them when needed.
출처 및 참조문헌
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제 6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제 20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026