Coma
혼수
-
A coma is a state of unconsciousness in which the child’s consciousness does not recover even after waking up loudly or by stimulating the body part.
-
The clarity of consciousness and consciousness of a patient in a coma may differ depending on the severity of the coma.
-
A patient in a coma is not well aware of when he is in, where he is, or who is around him at that time.
-
A patient in a coma develops an abnormality in the sense of consciousness and clarity.
-
That is, depending on the severity of the coma, the clarity of consciousness of the coma may be reduced to mild, moderate, or severe, and disability may occur. Falling into a coma can lead to little or no consciousness.
-
Whatever the cause of the coma, the patient’s consciousness and clarity are severely impaired.
-
And it means there are health problems that can be life-threatening.
-
The coma is classified into stage 1 coma, stage 2 coma, stage 3 coma, stage 4 coma, and stage 5 coma, depending on the degree of consciousness and clarity of consciousness.
-
In a patient in a coma, the severity of consciousness varies by type of coma.
-
In other words, places, times, people, etc., may be perceived dimly or not at all.
-
If a patient in a coma is painfully physically stimulating, it reacts a little or does not react at all, and if you call the child’s name aloud or shake the child’s body to wake it up, the child can react to the extent that the child opens eyes a little, and the child may respond slightly with gestures
-
There are various degrees of consciousness and clarity, such as being absent and unable to wake up a little.
Photo 1-9.
They are said to be in a coma when they are in a state of mind, consciousness, and clarity are impaired, and they are unconscious.
There are many causes of coma.
If you suspect or judge that you are in a coma, first start emergency treatment at the site and seek help from a regular pediatrician, hospital emergency room, medical paramedic, or other people around you. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Classification of coma
-
The coma is classified into 1 to 5 groups, depending on the severity of the disorder of consciousness and level of clarity.
-
Stage 1 coma-Masked coma
-
-
When waking the patient by making a loud voice call the patient’s name or waking the patient by making another loud sound,
-
Or the patient may respond with a word or two when physical stimulation is painfully applied to the body,
-
A coma is a state in which parts of the body, such as limbs, can react by moving a little on their own. It is called a first coma.
-
Stage I coma is a coma in a state of drowsiness/drowsiness/拙吟.
-
-
Stage 2 coma
-
Calling out the patient’s name aloud to awaken it, or waking it up loudly with any other sound,
-
Or the patient may respond with a word or two when physical stimulation is painfully applied to the body,
-
Part of the body, such as limbs, can react slightly by itself, but there is a more severe disorder of consciousness and clarity of consciousness than in the first stage of coma.
-
The second stage of coma is a confusion coma. That’s why it is also called a confused coma.
-
Stage 3 coma-less deep coma
-
Even when the patient’s name is called out loud and awakened, or when the patient wakes up with a loud sound, or when a physical stimulus is applied to the body severely, the patient cannot respond with words at all,
-
Can’t wake up,
-
You cannot consciously move any part of your body, such as limbs. You can move a little unconsciously. A very severe coma, which can make a moaning sound, is called a third coma. This coma is also called a light coma.
-
Stage 4 coma-deep coma
-
When the body is stimulated with physical stimulation, it can react slightly reflexively. It is called a 4th coma.
-
A coma in this state is a severe coma.
-
This coma is also called a deep coma.
-
Stage 5 coma, relaxation, apnea, and paralysis
All the muscles of the body are relaxed and paralyzed; the muscles have no strength at all,
Can’t react at all with words,
Coma in a state in which the entire central nervous system is almost completely lost,
The coma just before death is called stage 5 coma.
This coma is also called flaccid and apneic state coma.
The coma is classified as follows according to the cause of the coma.
Alcoholic coma,
Diabetic coma,
Epileptic coma,
Hepatic coma,
Uremia coma,
Metabolic coma,
The coma is classified as a hypoglycemic coma.
Glasgow coma evaluation item: Glasgow coma scale (GCS)
In 1974, J Ennett Glasgow devised a Glasgow Coma Scale item to visually assess a person’s state of consciousness in a coma.
Specifically explaining the Glasgow coma evaluation item,
Degree of eye-opening,
The degree of verbal response,
The degree of motor response was set as a large evaluation item.
Then, divide each large evaluation item into more subdivided evaluation items,
Then, for each subdivision evaluation item, the score was determined based on the degree of the patient’s reaction state.
If the patient’s reaction status was the best, 1 point was given; 2 points if it was bad, 3 points if it was very bad, and 4 points if it was very bad.
The Glasgow Coma Scale is a clinical information criterion for effectively diagnosing and treating coma by knowing the degree of coma in children with coma according to the total evaluation item-total score.
Table 5 below introduces the Glasgow coma scale items that differentiate between infancy and coma in infancy.
The Glasgow Scale is information for medical professionals, but when someone is in a coma, you can find out what degree of the coma a parent is in and the degree of coma observed in the field more specifically to a regular doctor or emergency room doctor over the phone or verbally It is also important to report on the back, so here is the Glasgow coma scale.
Table 6. Cause of coma
Classification of causes of coma |
혼수의 원인이 될 수 있는 병Diseases that can cause coma |
혼수의 진단Diagnosis of coma |
뇌 등 두 개강 내, 중추신경계의 외상Intracranial trauma, central nervous system injury |
뇌손상, 뇌진탕, 뇌 절상, 경막하 혈종, 경막외 혈종, 뇌 출혈, 간질, 뇌부종, 뇌수종, 고혈압성 뇌 병변, 1차성 감염병이 낫은 후 생기는 엔세팔로파티(뇌병) 등의 뇌 병변Brain injury, concussion, brain cut, subdural hematoma, epidural hematoma, cerebral hemorrhage, epilepsy, cerebral edema, hydrocephalus, hypertensive brain lesions, Encephalon which develops after healing of primary infectious disease Brain lesions such as party (encephalopathy) |
증상징후, 병력, 검진, CT 스캔, MRI 검사 등으로 진단한다.Diagnosed with symptoms, signs, medical history, physical examination, CT scan, MRI, etc. |
뇌 등, 두 개강 내 중추신경계의 병변Lesions of the central nervous system within the cavities of the brain |
뇌부종, 뇌수종, 뇌종양, 고혈압성 뇌 병변, 뇌 혈관염, 다발성 경화증, 1차 감염병이 다 나은 후 2차 병으로 생긴 엔세팔로파티(뇌병) 등의 뇌질환으로including brain edema, hydrocephalus, brain tumors, hypertensive brain lesions, cerebral vasculitis, multiple sclerosis, and brain diseases such as Encephalopati (encephalopathy), which is a secondary disease after the primary infectious disease has healed. |
증상징후, 병력, 검진, CT 스캔, MRI 검사 등으로 진단 한다.Diagnosed with symptoms, signs, medical history, physical examination, CT scan, MRI, etc. |
간질(뇌전증)Epilepsy |
간질, 간질 지속상태epilepsy, status epilepticus |
혈 중 항경련 약 레벨검사, 산소호흡 치료anticonvulsant drug level test in blood, oxygen respiration therapy |
뇌 감염병 및, 또는 전신 감염병Brain infectious diseases and/or systemic infectious diseases |
바이러스 뇌수막염이나 뇌염, 박테리아 뇌수막염이나 뇌염, 뇌 농양, 패혈증, 라임 병 등 그 외 여러 종류의 뇌 감염병 및 전신 감염병Viral meningitis or encephalitis, bacterial meningitis or encephalitis, brain abscess, sepsis, Lyme disease, and other types of brain infectious diseases and systemic infectious diseases |
뇌척수액 검사에서 백혈구 수와 단백질 농도가 증가하고 포도당 농도가 감소하는 것이 보통이다. 뇌척수액 세균배양 검사가 중요하다.Increased white blood cell count and protein concentration in cerebrospinal fluid test, and decreased glucose concentration It is common to be. A cerebrospinal fluid bacterial culture test is important. |
출혈로 생기는 쇼크The shock caused by bleeding |
전신 또는 국소 내출혈이나 외출혈로 생기는 쇼크 등Systemic or localized internal or external bleeding may cause shock. |
혈압이 떨어질 수 있고 혈량이 감소될 수 있다.The blood pressure may drop and the blood volume may decrease, |
악성 종양Malignant Tumor |
뇌종양이나 백혈병Brain Tumor or Leukemia |
뇌종양으로 혼수가 생기면 구기, 구토, 두통 등 증상 징후가 생길 수 있고 백혈병으로 혼수가 생길 때는 백혈병과 관련된 여러 가지 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.When a coma occurs due to a brain tumor, symptoms such as vomiting and headache may occur. When a coma occurs due to leukemia, various symptomatic signs related to leukemia may occur. |
처방 약물중독, 습관성 약물중독Prescription drug poisoning, habitual drug poisoning |
아스피린 중독 등aspirin poisoning, etc |
코케인(코카인)이나 그 외 다른 종류의 습관성 약물에 중독될 수 있고 그로 인해 혼수가 생길 수 있다. 혈중 약물농도 또는 소변 약물농도 검사 등이 진단에 가치가 있다. Your child may be addicted to cocaine (cocaine) or other types of addictive drugs, which can lead to coma. Blood drug concentration or urine drug concentration tests are valuable for diagnosis |
중금속 중독Heavy metal poisoning |
수은중독, 납중독 등 중금속 중독이나 그외 Heavy metal poisoning such as mercury poisoning, lead poisoning, |
병력, 증상 징후, 혈중 중금속 농도를 측정해서 진단할 수 있다.It can be diagnosed by measuring heavy metal poisonings such as mercury poisoning, lead poisoning, and other medical history, symptoms, and heavy metal concentration in the blood. |
가스 중독Gas poisoning |
일산화탄소 중독Carbon monoxide poisoning |
카복실 헤모글로빈 농도를 측정하고 산소호흡 치료를 한다.Carboxyl hemoglobin concentration is measured, and oxygen respiration therapy is performed. |
화학물질 중독Chemical poisoning |
알코올 중독Alcohol poisoning |
혈중 알코올 레벨을 측정한 뒤 진단한다.Alcohol poisoning is diagnosed by measuring the level of alcohol in the blood. An alcoholism diagnosis is made by measuring the level of alcohol in the blood. |
알코올 중독Alcoholism |
알코올 중독Alcoholism |
혈중 알코올 농도를 측정해 진단한다.Diagnosis is made by measuring the level of alcohol in the blood |
간, 신장 질환Liver, kidney disease |
간부전증, 신장 부전증, 요독증, 라이증후군 등 Liver failure, kidney failure, uremia, Reye syndrome, etc. Severe dehydration |
병력, 증상 징후, 적절한 임상검사로 진단한다.is diagnosed by medical history, symptoms, signs, and lab tests |
심한 탈수Severe dehydration |
설사 및, 또는 구토 등으로 인한 심한 탈수, 고 나트륨 증, 저 나트륨 증 severe dehydration, history of hypernatremia, hyponatremia by diarrhea and/or vomiting |
병력, 검진, 증상 혈중 전해질 농도 검사 등으로 진단한다. physical examination, symptoms, blood electrolyte concentration tests, etc. |
비타민Vitamins |
비타민 과량 또는 비타민 결핍 The diagnosis is based on a history of vitamin excess or deficiency. |
병력, 검진, 증상 징후, 혈중 비타민 농도 검사 등으로 진단한다. medical history and physical examination, symptom, signs, and blood vitamin concentration tests |
고 온도 저 온도 감전사고 등 High temperature, Low temperature, Damage caused by cold temperature, electric shock, |
냉온도로 인한 손상, 악성 고열, 열사 병, 화상 뇌 병변, 방사능 조사, 감전사도 등malignant high fever, heat stroke, burned brain lesions, radiation irradiation, electrocution degree, etc., |
병력, 검진, 증상 등으로 진단한다.are diagnosed by medical history and physical examination, |
전해질 불균형, 수분 불균형Electrolyte imbalance, water imbalance |
전해질 및, 또는 수분(수액) 불균형, 전해질 과다증, 전해질 과소증 Electrolyte and/or water imbalance, electrolyte hyperemia, history of electrolyte hypoplasia |
병력, 검진, 증상 징후, 혈중 전해질 농도 검사를 해서 진단한다.medical history, physical examination, symptoms, signs, and blood electrolyte concentration are used to diagnose |
산소 결핍oxygen deficiency |
익수사고, 산소결핍증 등으로 생기는 질식 사고나 호흡부전증a history of suffocation or respiratory failure caused by an oxygen deficiency, drowning accident, |
병력, 검진, 혈중 산소농도 검사를 해 진단한다. a medical history, physical examination, and a blood oxygen level test |
신진대사 장애Metabolic disorders |
각종 신진대사 장애, 저혈당증, 당뇨병성 케톤 산혈증Various metabolic disorders, hypoglycemia, diabetic ketone acidemia history |
병력, 검진, 혈중 전해질 농도 검사 등을 해서 진단한다. history, examination, blood electrolyte concentration test, etc., are used to diagnose. |
내분비 장애Endocrine disorders |
애디슨 병 Addison’s disease |
병력, 검진, 혈중 전해질 농도 검사, 호르몬, 혈액 농도 검사를 해서 진단한다. medical history, examination, blood electrolyte concentration test, hormone, and blood concentration test to diagnose |
고혈압이나 저혈압Hypertension or hypotension |
심한 고혈압 및, 또는 심한 저혈압으로 인한 병변It is diagnosed by measuring the history of lesions caused by severe hypertension and/or severe hypotension. |
병력, 검진, 혈압을 측정해서 진단한다. medical history, physical examination, and blood pressure. |
정신 안정제나 수면제Mental tranquilizers, sleeping pills |
각종 처방 약물 및 환자 자신이 사서 복용하는 약물 등 various prescription drugs and drugs purchased and taken by the patient themselves |
병력과 검진을 하고 혈중 약물 농도를 검사해서 진단한다.medical history, physical examination, test for blood drug level |
정신 이상Insanity |
히스테리Hysteria |
다른 병으로 인해 혼수가 생기지 않고 정신적 원인으로 혼수 증상이 있으면 히스테리라고 진단할 수 있다. Hysteria can be diagnosed if a coma does not occur due to other illnesses |
알레르기로 인한 쇼크나 그 외 Allergic shock or other |
아나필랙시스, 나무나 풀의 중독anaphylaxis, poisoning of trees or grasses |
독성 나무나 독성 풀을 섭취한 후 중독에 걸릴 수 있고 알레르기로 인해 쇼크가 생기고 혼수상태에 빠질 수 있다. After ingestion of poisonous trees or grasses, you may become addicted, and allergies may cause shock and lead to a coma. |
Myosis and mydriasis
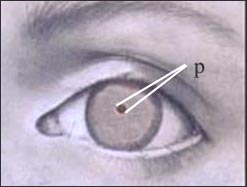
Figure 120.
Abnormally constricted pupil
If the pupil is abnormally contracted due to a drug or drug addiction, and the diameter of the pupil is less than 2mm,
it is called Myosis.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
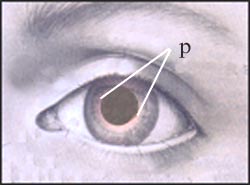
Figure 121. Abnormally enlarged pupil
If the pupil is abnormally enlarged due to drugs or severe brain damage, and the diameter of the pupil is larger than 2mm, it is called mydriasis.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
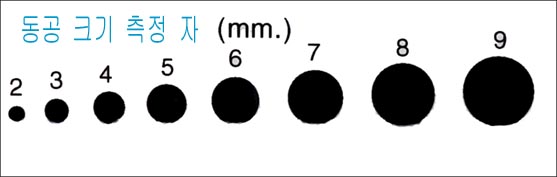
Figure 122.Pupil sizing ruler It is important to know the size of the pupils in your child’s eyes when your childis in drug addiction, brain injury, eye trauma, coma, or at the time of examination.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Table 7. Changes in pupil size in people who are in a coma due to drug or drug addiction
동공 확대(산동)의 원인Causes of pupil dilation (Mydriasis) |
동공 축소(축동)의 원인Causes of pupil constriction (Myosis) |
Aetamine |
메페리딘 meperidine |
암페타민Amphetamine |
메사돈 mesadon |
항히스타민antihistamine |
헤로인, 몰핀 등 오피움Opium such as antihistamine heroin, morphine |
아트로핀Atropine |
Organophosphates |
코케인 Cocaine |
Phenothiazines |
에페드린Ephedrine |
Propoxyphene |
글루테지아마이드 Gluthethiamide |
LSD, Mescaline, PCP 등 Psychedelics |
스코폴라민 Scopolamine |
Thallium |
Com is caused by some primary disease and its cause.
A coma is an asymptomatic sign, not a disease name. Depending on the primary disease that caused the coma and its underlying cause, symptoms of coma and symptomatic symptoms usually appear together according to the severity of the coma.
For example, sepsis can cause shock, which can lead to coma.
Sepsis may have symptomatic symptoms such as high fever, hypothermia, low blood pressure, and spotty skin spots, as well as symptoms of coma.
Shock occurs due to severe bleeding or severe dehydration, and as a result, when in a coma, blood pressure decreases, resulting in hypotension, and the skin of the face and whole body is pale.
In particular, dehydration may result in shock, and signs of dry skin may be present.
When a coma is caused by an abnormally high intracranial pressure (brain pressure) due to cerebral edema or intracranial hemorrhage, the pulse rate may be slow (bradycardia), and blood pressure may be abnormally high (high blood pressure) or low (low blood pressure).
When hepatic coma occurs due to aspirin poisoning, Reye syndrome, liver disease, etc., breathing may be faster and the face may be pale.
When you have an alcoholic coma due to alcoholism, it is common to have a good color and smell of alcohol when you breathe.
When you are in a coma due to brain injury, symptoms of brain damage such as general convulsion, general paralysis, and hemiplegia appear.
When in a coma with diabetic ketoacidemia, it is common to smell acetone when you breathe.
As such, symptomatic signs vary depending on the primary disease and cause of the coma, and various symptoms may appear during the coma.
Photo 1-10. Use an ambulance as needed. If you fall into a coma, you will be taken to a general hospital by ambulance. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
ABCD emergency treatment
-
If anyone suddenly loses consciousness and falls into a coma, it is common to start first aid immediately as follows, regardless of the primary illness that caused the coma or the cause of the coma.
-
It opens the airway (Air way=A).
-
In other words, a secure Airway. Open the breather so that he can breathe (Breathing=B) normally First aid is taken to restore normal cardiovascular function (Circulation=C), and treatment to stop bleeding is performed at the same time.
-
At the same time, what was the primary disease and cause that caused coma (Diagnosis=D).
-
If necessary, the ideal order of coma treatment is to provide appropriate first aid according to the primary disease and cause and degree of coma that caused the coma while taking medication (Drug treatment=D).
-
This is where the word ABCD(D) comes from.
-
To summarize the ABCD first aid measures described above.
-
Airway establishment and breathing recovery,
-
Cardiovascular function/ Circulation
-
Presumed diagnosis
-
Start Drug treatments.
-
In clinical practice, if possible, treatments corresponding to ①~④ should be performed at the same time.
-
This treatment is called the ABCD treatment, or the ABCDD treatment.
-
Here, ABCD treatment or ABCDD treatment is an abbreviation of the first capital letter of the English described above.
-
For reference, in the case of recent adult CPR, first aid is recommended in the order BACD rather than ABCD.
-
Sometimes, it is inappropriate for a patient in a coma to continue emergency treatment at the site, and continuing first aid treatment at the site may pose a threat to the child’s life or health or may be harmful to the child’s health.
-
For example, in the event of a fire, the child must first be moved to a complete place from the place of the fire.
-
In other words, the child must be moved to a safe place at the accident site.
-
Appropriate ABCDD first aid and treatment should continue while moving.
-
While treating coma as an emergency, it is ideal to find out what is the cause of the primary disease and coma and to treat it according to the cause of the coma and the degree of coma.
-
When you witness a child, adolescent, or adult suddenly in a coma, not only your mother and father, but all the people around you may be embarrassed, but at the same time, calmly and wisely, reasonable and proper first aid and treatment are initiated, and appropriate assistance is provided.
-
You have to ask. As described above, coma cannot be treated uniformly.
-
The primary disease of coma and general coma emergency treatment, regardless of the cause of the coma and the degree of coma, will be described further in detail below.
-
First aid should be done sequentially. It secures an airway so that he can breathe well and opens a blocked airway (breathing box).
-
If you cannot breathe well or need CPR treatment because you cannot breathe, start basic CPR treatment immediately and contact the hospital emergency room or regular pediatric clinic to continue basic first aid and treatment according to their emergency telephone instructions.
-
Depending on the situation, ask for help from a medical paramedic.
-
An ambulance or other means of transport will take him to the nearest and most appropriate general hospital emergency room as quickly as possible.
-
Appropriate first aid will continue at the site until a doctor or medical paramedic arrives to assist.
-
Use the first aid method you have studied at this time. If possible, remove vomit or mucus from the nasal cavity or oral cavity appropriately using suction or a finger to keep the airway open.
-
Tilt your child’s neck slightly back and slightly turn his head and face to the side (you can only perform this treatment if you have confirmed that there is no abnormality in the neck and no possibility).
-
Lay the upper body a little lower than the lower body to secure and open the airways so that you can breathe well (do not use this treatment if you have a cerebral hemorrhage or high brain pressure).
-
Treat the secretions or foreign substances in the mouth, pharyngeal cavity, and airways to easily flow out of the mouth, and treat vomiting or secretions to prevent them from entering the airways, such as the trachea.
-
The nasal discharge or vomit may be inhaled through the inlet.
-
If he is unable to breathe well or can hardly breathe, put your mouth to the patient’s mouth and nose (in the case of newborns or infants), or, in the case of infants or school-age children, provide basic CPR while artificial respiration is performed.
-
Start immediately. Of course, if you have oxygen, oxygen breathing treatment is performed.
-
Depending on the situation, artificial respiration and heart massage are performed at the same time, if there is external bleeding in the limbs and the like, the external bleeding is stopped.
1. If more than one person is in the field One or two people give first aid to a coma, and the other examines the site and surroundings to collect and find information that may be the primary disease of coma and the cause of the coma. The information is used in diagnostic treatment. If there is a clue that it may be the cause of coma and the primary disease of coma, collect it and take it to the hospital to quickly find the primary disease and cause of the coma, and help treat the coma.
2. When you do not know how to give first aid and treatment for a coma, if the child is at the site for a longer period of time, it may be more dangerous; the child should be moved from the site to a safe place. If there is severe external bleeding in the limbs, etc., stop the bleeding with hand pressure or a tourniquet. You can do very common-sense treatment. The whole body of a patient in a coma should not be pressed, pulled, pushed, touched, or moved. Do not touch or move parts of the body carelessly. Especially when there is a fracture of the vertebrae of the neck (cervical spine), you should never move the neck carelessly. When a fracture occurs in a vertebral bone other than the neck bone or other bones in the body, or if a fracture is suspected, the part of the body containing the fractured bone should not be tampered with.
3. Warm up the coma patient with a blanket so that it does not get cold.
4. If you suspect that you have fallen into a coma due to internal bleeding or dehydration, take it as soon as possible to the nearest hospital emergency room, where you can receive intravenous glucose-electrolyte solution or blood transfusion treatment. Hospital emergency room treatment While performing ABCD first aid, clinical tests such as blood sugar, blood electrolyte concentration, CBC blood test, feces test, gastric juice test, cerebrospinal fluid test, etc., and blood drug test, MRI test, ultrasound test, CT scan test, X-ray photo test, etc.
Find out the cause and start emergency treatment accordingly. If diabetic coma is treated with insulin, intravenous electrolyte solution, oxygen respiration, etc., coma caused by severe dehydration is treated according to the cause of the primary illness and coma, and symptomatic treatment is performed by intravenous injection of glucose electrolyte solution.
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer on
“My baby is very respectful.”.
Q&A. My baby is very respectful…
Q. I’m a parent to a baby named Kim Soon who lives in Suwon… It’s no different. I’m in the hospital now because that baby is so harsh… I still don’t know why…. So I send a melody like this..
Now the baby is in a state of…he can’t see people,,,,the game is severe…he says he has a swollen brain at the hospital…Have you done the examination and don’t know the cause of Badu? I’m worried about what to do…. I’m only thinking about coming to the hospital right now… but please give me some advice…
A. Soon-nim, Hello. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question. If you have more information, such as your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical opinion, clinical examination, etc., before giving an answer, it will be very helpful to me, and I will give you an answer based on the information you provide. I worry a lot, too. Viral encephalitis, Bacterial encephalitis or meningitis, Sepsis, shock from allergic diseases, anoxia Carbon monoxide poisoning, Lead poisoning or other heavy metal poisoning, Chemical poisoning, Severe head trauma, Cerebrovascular rupture, Severe dehydration or anemia, Reye syndrome, Persistent state of epilepsy, Brain damage from any cause
The brain can become swollen and convulsant.
The baby seems to be in a coma. When the brain MRI test, cerebrospinal fluid test, CBC blood test, blood calcium concentration, blood magnesium concentration, blood electrolyte concentration, blood base, and acidity, EEG test, to what degree and what causes the convulsions, why fell into a coma, at least
You can make a presumptive diagnosis. [Parents should also be at least a half-doctor-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Refer to Vol. 12 Pediatric and Adolescent Neurology, Spirit, Behavior, and Sleep Problems.
You will be taken to a hospital and consult with your child’s doctor to determine what causes your convulsions or coma.
May you recover quickly. If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won, MD
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer for “transitional disorder, sleep state”.
Q&A. Conversion disorder, sleep status
Q. This is a 6-year-old girl. Two weeks ago, in the early morning, the child was unconscious with his eyes open, so I contacted 119 and went to the hospital to have an electroencephalogram and blood test, but I was relieved that there was nothing wrong, but two weeks later, this early morning, at the same time, the same symptoms were showing, so I was surprised.
I was surprised to talk while holding my child, and my gaze was concentrated in one place, and the answer was given.
She needs to pass 20 spares before she is in normal condition.
How should I cope?
A. To her sister, Hello. Thanks for the great question. Ideally, diagnosis and treatment should be performed by synthesizing the results of the child’s age and gender, past and current family medical history, symptom signs and medical examination findings, and appropriate clinical tests, but I will respond with the information you have provided. I do not know.
It’s difficult to give a clear answer because I’m not sure what kind of disease caused the symptoms.
If you attach a presumptive diagnosis through the Internet, you may suspect that a girl has such symptoms due to recurrent convulsive disease (epilepsy), drug poisoning, or conversion disorder. What was the doctor’s diagnosis when I first lost consciousness and went to the hospital? After that, how did she treat, Brain MRI
출처 및 참조 문헌
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital, and Community, American Academy of
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey Grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American Heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition-31st 2012
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook, 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other