정기 소아청소년(0-21세) 건강검진
Periodic well child examination for birth to 21 year old
- 소아청소년 (0~21세/갓 태어나서부터 말기 사춘기까지 즉 신생아, 영유아, 학령기아, 사춘기아 )의 소아 건강검진을 다음 표 5-2에 따라 해준다.
- 5-2의 정보의 대부분 내용은 미 소아청소년과학회지 <Pediatrics, December 2007, Vol 120.#6, p.1378>에서 얻은 자료다.
- 거기에 한국 소아청소년들 건강 검진 진료에 알맞게 저자가 가감한 부분도 있다.
- 독자가 사는 나라와 지방에 따라 의료 정책이나 상황이 다를 수 있으므로 반드시 아래 표 5-2와 같이 일정한 간격으로 건강검진을 해줄 수 없다.
- 그러나 자녀의 소아청소년과 의사와 상의한 후 소아 건강검진을 가능한 한 일정한 간격으로 적절히 해줄 것을 권하고 싶다.
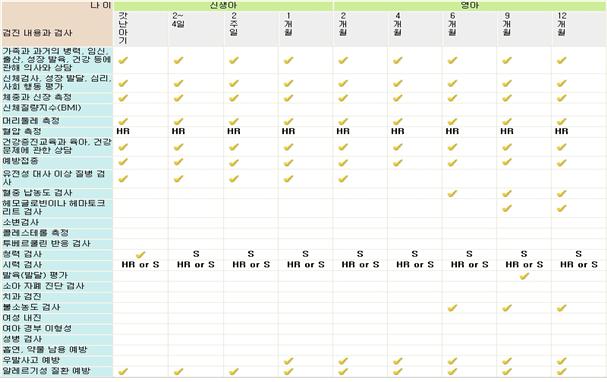
표 1-3. 소아청소년 정기 건강 검진
![]() 상담이나 검진, 또는 임상 검사를 통해 한다.
상담이나 검진, 또는 임상 검사를 통해 한다.
1. S: 상담과 검진을 통해 한다.
2. D: 다각적 검사를 통해 알아본다.
3. HR: 필요에 따라 검사한다.
편의상 다음표는 위에 있는 표를 다시 올린것이다.
Table 5-2 Health checkups for children and adolescents (0-20 years old) that can be received depending on their age at regular intervals 표 5-2. 일정한 간격을 두고 나이에 따라 받을 수 있는 소아청소년(0-20세) 건강검진 내용
|
나이 검진 내용과 검사 |
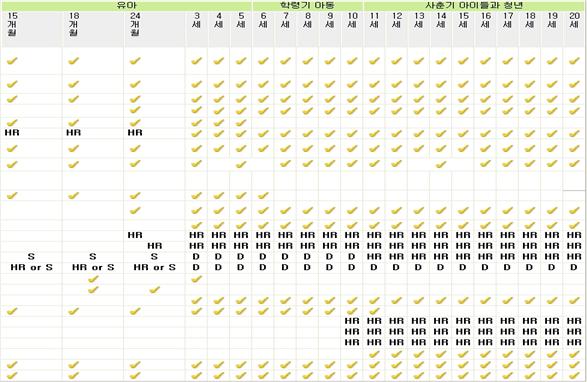
학령기 아동 | 사춘기 아이들과 청년 | |||||||||||||
| 6세 | 7세 | 8세 | 9세 | 10세 | 11세 | 12세 | 13세 | 14세 | 15세 | 16세 | 17세 | 18세 | 19세 | 20세 | |
| 가족과 과거의 병력, 임신, 출산, 성장 발육, 건강 등에 관해 의사와 상담 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 신체검사, 성장 발달, 심리, 사회 행동 평가 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 체중과 신장 측정 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 신체질량지수(BMI) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 머리둘레 측정 | |||||||||||||||
| 혈압 측정 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 건강증진교육과 육아, 건강문제에 관한 상담 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 예방접종 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 유전성 대사 이상 질병 검사 | |||||||||||||||
| 혈중 납 농도 검사 | √ | ||||||||||||||
| 헤모글로빈이나 헤마토크 리트 검사 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 소변검사 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 콜레스테롤 측정 | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR |
| 투베르쿨린 반응 검사 | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR |
| 청력 검사 | D | D | D | D | D | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR |
| 시력 검사 | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
| 발육(발달) 평가 | |||||||||||||||
| 소아 자폐 진단 검사 | |||||||||||||||
| 치과 검진 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 불소농도 검사 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| 여성 내진 | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | ||||
| 여아 경부 이형성 | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | ||||
| 성병 검사 | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | ||||
| 흡연, 약물 남용 예방 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 우발사고 예방 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 알레르기성 질환 예방 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
소스: Pediatrics, December 2007, Vol 120.#6, P.1378
√ 의사와 상담, 진찰, 검사를 통해 한다.
S: 상담과 진찰을 통해 한다.
D: 다각적 검사를 통해 알아본다.
HR: 필요에 따라 검사한다.
| 부모와 의사가 상담 |
소아청소년과에서 소아 건강검진을 받기 직전 또 받은 후 정신적․육체적 건강, 성장 발육, 수면, 음식물 섭취, 안전사고 예방, 학교 문제 등에 관해 의사와 포괄적으로 상담한다.
| 신체검사, 체중과 신장 측정, 머리 둘레 측정 |
겉옷은 다 벗고 속옷민 입은 채로 검진 가운을 입고 건강검진을 받는다. 체중, 신장, 머리둘레 등을 재고 체중 치과 신장 치를 성장차트 백분위선에 그려본다.
그 아이의 신장과 체중이 성장차트 백분위선에 따라 계속 자라는지 성장상태를 알아본다. 그리고 발육상태와 영양상태가 정상인지 알아본다.
| 혈압 측정 |
생후부터 3세까지는 필요에 따라 혈압을 측정할 수 있지만 3세 이후부터 소아 건강검진을 받을 때마다 혈압을 기본적으로 측정한다.
| 다음 소아 정기 건강검진을 받을 때까지 부모와 소아청소년과에서 모유수유, 인공영양, 이유식, 수면, 안전사고, 질병의 예방, 소아 성교육 등 소아 건강문제에 관한 상담 |
| 기본 예방접종 |
1) B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자 균 감염에 의한 감염병 예방접종 백신-Hib vaccine 등
2) 디프테리아 파상풍 백일해 예방접종 백신-DTaP vaccine 등
3) 소아마비 예방접종 백신-IPV vaccine 등
4) 홍역 볼거리 풍진예방접종 백신-MMR vaccine 등
5) A형 간염 예방접종 백신-Hep A vaccine
6) B형 간염예방접종 백신-Hep B vaccine
7) 수두 예방접종 백신-Varicella vaccine
8) 결핵 예방접종 백신-BCG vaccine
9) 독감 예방접종 백신-Influenza vaccine 등
10) 뇌수막염 예방접종 백신-MPSV4 vaccine 등
11) 뇌염 예방접종 백신-Encephalitis vaccine 등
12) 폐렴 예방접종 백신-PCV 등
13) 로타바이러스 위장염 예방접종 백신-Rota vaccine 등
14) 사람 유도 바이러스 예방접종 백신-HPV 등
감염병 예방접종을 해준다.
| 특수 예방접종 |
특정 지역, 각 나라, 특별한 상황에 따라, 장티프스, 뎅구엘 열, 일본뇌염, 말라리아, 광견병, 황색 열 등 특수 감염병을 예방하기 위해 특수 백신으로 예방접종을 비 통상적으로 받을 수 있다.
| 유전성 질환과 유전성 대사 이상을 진단하는 검사 |
- PKU(페닐키톤요증),
- 갑상선 기능 저하증,
- 갈락토오스 혈증,
- 호모씨스틴뇨증,
- 겸상적혈구 혈증,
- 고메티오 혈증,
- 타이로신 혈증,
- 단풍시럽뇨병(Maple syrup urine disease),
- 카르니틴/아세틸 Translocase deficiency,
- Carnitine transporter deficiency,
- 카르니틴 팔미틸트랜스퍼라이제 결핍(Carnitine palmitoyltransferase deficiency 1),
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase deficiency II,
- 글루타르산뇨증 (Glutaric acidemia type II, multiple acyl-CoA dehydronenase deficiency),
- 메텔마르니카시데미아(Methylmalonic acidemia),
- 프로피은닉산산혈증(Propionic acidemia),
- 이소발레르산혈증(IVA),
- 글루탄산혈증 1형(Glutaric acidemia type I),
- 3MMC or 3MCC(3 – methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency), HMG(3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coA Lyase deficiency),
- BKT(Beta-ketothiolase deficiency),
- Multiple CoA carboxylase deficiency 등 유전성 질환과 유전성 대사 이상을 조기에 진단 치료 예방하기 위해 피검사 등을 한다.
- 이상 검사는 각 지방이나 각 나라의 보건정책에 따라 다르게 할 수 있고, 또 미국에서도 각 주 보건정책에 따라 다르게 한다.
| 혈중 납 농도 검사 |
납 중독에 걸려 있는지 알아보기 위해 혈중 납 농도 측정 검사를 나라 보건정책에 따라, 또는 상황에 따라 기본적으로 실시한다.
| 헤모글로빈이나 헤마토크릿 검사 |
빈혈이 있는지 알아보기 위해 헤모글로빈 농도를 검사하거나 헤마토크릿 농도를 검사한다.
| 소변검사 |
소변 검사에는 소변 화학검사도 있고 소변 현미경검사, 소변 세균 배양검사 등이 있다.
소변에 당, 단백질, 케톤, 피, 빌리루빈, 박테리아 등의 소변검사가 비정상인지 정상치인지 알아본다.
| 콜레스테롤 측정 |
필요에 따라 혈중 콜레스테롤 농도를 측정할 수 있다.
사춘기가 되기 바로 전 말기 사춘기에 혈중 콜레스테롤 농도를 기본으로 잰다.
| 투베르쿨린 반응 검사, 또는 PPD 검사 |
결핵에 결려 있는지 알아보기 위해서 피부 결핵 반응 검사를 한다.
| 청력 검사와 시력 검사 |
청력이 정상인지 잘 들을 수 있는지, 시력이 정상인지 잘 볼 수 있는지 알아보기 위해 시력과 청력을 주기적으로 검사한다.
| 치아 검사와 불소농도 검사 |
이를 치과에서 정기적으로 검진 받고 있는지, 섭취하는 식수의 불소의 농도가 얼마인지 알아본다. 식수 불소 농도가 권장하는 농도 보다 낮으면 의사의 처방에 따라 불소를 경구로 섭취하든지 다른 방법으로 섭취해 충치를 예방하는데 관해 상담한다.
| 여성 내진 |
성 관계를 하는 사춘기 여아들은 내부 생식기와 외부 생식기를 정기적으로 검진 받고 팹 검사도 받는다.
| 성병검사 |
남여 사춘기 아이들이 감염성 성병에 걸려있는지 알아보기 위해 검사를 받는다.
특히 성 관계를 적극적으로 하는 남녀사춘기아가 소아 정기 건강검진을 받을 때 가능하면 11세부터 성병에 걸려 있는지 알아보는 검진을 받아야한다.
| 여아 자궁 경부 이형성 검사 |
성관계를 하는 사춘기 여아들은 소아 정기 건강검진을 받을 때 내진검사를 받고 자궁 경부 이형성이 있는지 알아보는 검진을 받는다. 역시 가능하면 여아가 11세가 될 때부터 자궁경부 이형성 검사를 받기 시작한다.
| 흡연, 약물 남용 예방 |
흡연을 시작하기 전에 흡연을 하지 않도록 흡연을 시작 하지 않게 교육을 시키고 이미 흡연을 시작한 소아들에게 금연을 하도록 흡연교육 시키는 것에 관해 상담한다.
| 안전사고 예방 |
화상, 낙상, 교통사고, 익사, 중독, 질식, 총기 안전사고 등을 예방하는 것에 관해 상담을 한다.
| 알레르기성 질환 예방 |
기관지 천식, 알레르기성 비염 등 각종 알레르기성 질병이 유발되지 않게 예방교육을 하는 것에 관해 상담한다.
|
수면, 자녀 사랑에 관해 상담한다. |
| 그 외 소아 성장발육, 육아, 질병 등에 관해서도 상담할 수 있다. |
Periodic well-child examination for birth to 21-year-old
정기 소아청소년(0-21세) 건강검진
- Children’s health check-ups for children and adolescents (0 to 21 years old/from newborn to terminal puberty, ie, newborns, infants, school-age hunger, and adolescents) are performed according to the following table 5-2.
- Most of the information in 5-2 was obtained from <Pediatrics, December 2007, Vol 120.#6, p.1378> in the Journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents.
- There are also parts that the author added and subtracted appropriately for medical examination of Korean children and adolescents.
- Medical policies and circumstances may differ depending on the country and region in which the reader lives, so health check-ups cannot be provided at regular intervals as shown in Table 5-2 below. However, after consulting the child’s pediatrician and doctor,
- I would like to recommend that the child health check-up is performed at regular intervals as much as possible.
Table 1-3. Regular health checkups for children and adolescents
표 1-3. 소아청소년 정기 건강 검진


- Consultation, examination, or clinical examination.
- 1. S: Consultation and examination.
- 2. D: Check through multiple inspections.
- 3. HR: Check as needed. For convenience,
The following table is a reload of the table above-Table 5-2.
특히 0세에서부터 6세가 될 때까지의 소아 건강검진 내용과 검사, 양호 등에 관해 구체적으로 더 알아보자.
Table 5-2 Health checkups for children and adolescents (0-20 years old) that can be received depending on their age at regular intervals
|
age/ |
School-age children | adolescent children and youth | |||||||||||||
| 6
years |
7
years |
8
years |
9
years |
10
years |
11
years |
12
years |
13
years |
14
years |
15
years |
16
years |
17
years |
18
years |
19
years |
20
years |
|
| Consult with a doctor about family and past medical history, pregnancy, childbirth, growth and development, health, etc. | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Physical examination, growth development, psychology, social behavior evaluation | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Weight and height measurement | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Head
circumference measurement |
|||||||||||||||
| measurement Blood pressure measurement | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Health promotion education and parenting, counseling on health issues | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Vaccination | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Hereditary metabolic abnormal disease test | |||||||||||||||
| Blood lead level test | √ | ||||||||||||||
| Hemoglobin or hematocrit | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Urine test | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Cholesterol measurement | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR |
| Tuberculin test | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR |
| Hearing test | D | D | D | D | D | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR |
| Vision test | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
| Development (development) evaluation | |||||||||||||||
| Pediatric autism diagnostic test | |||||||||||||||
| Dental examination | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Fluoride concentration test | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Women’s female internal examination | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | ||||
| female cervix dysplasia examination | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | ||||
| STD test | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | HR | ||||
| Smoking and drug abuse prevention | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Accident prevention | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Prevention of allergic diseases | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Source: Pediatrics, December 2007, Vol 120.#6, P.1378
√ Consultation, examination, and examination with a doctor.
S: Do it through counseling and medical examination.
D: Find out through multi-faceted tests.
HR: Inspect as needed.
In particular, let’s learn more about children’s health checkups from 0 to 6 years old, tests, and good.
Parents and doctors consult
Immediately before and after receiving a pediatric health check-up at the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents, comprehensive consultation with a doctor is given on mental and physical health, growth and development, sleep, food intake, prevention of safety accidents, and school problems.
Physical examination, weight and height measurement, head circumference measurement
Take off all your outerwear and wear your underwear while wearing a medical examination gown and undergo a health checkup. Measure your weight, height, and head circumference, and draw the weight and height of the dentist on the percentile line of the growth chart. Determine whether the child’s height and weight continue to grow according to the growth chart percentile. And find out if the state of development and nutrition are normal.
Blood pressure measurement
Blood pressure can be measured as needed from birth to 3 years of age, but blood pressure is basically measured every time
A child undergoes a health checkup from 3 years of age. Consultation on children’s health issues such as breastfeeding, artificial nutrition, baby food, sleep, safety accidents, disease prevention, and pediatric sex education at the parent and child and adolescent department until the next child’s regular health check-up
Basic vaccination as followings
1) Vaccination against infectious diseases caused by infection with Haemophilus influenzae type B-Hib vaccine, etc.
2) Diphtheria tetanus pertussis vaccination vaccine-DTaP vaccine, etc.
3) Polio vaccination vaccine-IPV vaccine, etc.
4) Measles mumps rubella vaccination vaccine-MMR vaccine, etc.
5) Hepatitis A vaccine-Hep A vaccine 6) Hepatitis B vaccine-Hep B vaccine
7) Varicella vaccine
8) Tuberculosis Vaccination Vaccine-BCG vaccine
9) Flu vaccination vaccine-Influenza vaccine, etc.
10) Meningitis vaccination vaccine-MPSV4 vaccine, etc.
11) Encephalitis vaccine, etc.
12) Pneumonia vaccination vaccine-PCV, etc.
13) Rotavirus gastroenteritis vaccination vaccine-Rota vaccine, etc.
14) Human-induced virus vaccination vaccine-HPV, etc.
Vaccination against infectious diseases is provided.
Special vaccination
Depending on the specific region, country, and special circumstances, special vaccines can be used to prevent special infectious diseases such as typhoid fever, dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, malaria, rabies, and yellow fever.
Tests to diagnose hereditary diseases and hereditary metabolic abnormalities
- PKU (phenylketonuria),
- Hypothyroidism,
- Galactosemia,
- Homocystinuria,
- Sickle cell anemia
- Hypermethioemia,
- Tyrosinemia,
- Maple syrup urine disease,
- Carnitine transporter deficiency,
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase deficiency 1,
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase deficiency II,
- Glutaric acidemia type II,
- multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency,
- Methylmalonic acidemia,
- Propionic acidemia,
- Isovaleric acidemia (IVA),
- Glutaric acidemia type I,
- 3MMC or 3MCC(3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency),
- HMG(3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coA Lyase deficiency),
- Beta-ketothiolase deficiency (BKT),
- In order to diagnose, treat and prevent hereditary diseases and hereditary metabolic abnormalities such as multiple CoA carboxylase deficiency
at an early stage, blood tests are performed.
The above test can be done differently according to the health policy of each province or country, and in the United States,
it is different according to the health policy of each state.
Blood lead level test
To find out if you are suffering from lead poisoning, tests to measure the concentration of lead in the blood are carried out according to national health policies or by circumstances.
Hemoglobin or hematocrit test
Hemoglobin levels or hematocrit levels are tested to see if you have anemia.
Urine test
Urine tests include urine chemistry, urine microscopy, and urine bacterial culture. Check if the urine test for sugar, protein, ketone, blood, bilirubin, and bacteria in the urine is abnormal or normal.
Cholesterol measurement
If necessary, blood cholesterol concentration can be measured. Just before puberty, at the end of puberty, blood cholesterol levels are measured as a basis.
Tuberculin test or PPD test
A skin tuberculosis test is done to see if you have tuberculosis.
Hearing and vision tests
Check your eyesight and hearing regularly to see if your hearing is normal or you can hear well, and if your vision is normal or you can see well.
Dental examination and fluoride concentration examination
Find out if you are receiving regular checkups at your dentist and what the concentration of fluoride in your drinking water is. If the concentration of fluoride in drinking water is lower than the recommended concentration, consult your doctor about taking fluoride orally or in other ways to prevent tooth decay.
Women’s genital internal examination
Adolescent girls who engage in sexual intercourse are regularly screened for internal and external genitalia and undergo Pap tests.
Venereal disease test
Male and female adolescent children are tested to see if they have an infectious sexually transmitted disease. In particular, when a male and female adolescent child who is active in sexual relations undergoes regular pediatric health checkups, if possible, she should undergo a checkup to see if she has a sexually transmitted disease from the age of 11.
Girls’ cervical dysplasia test
Adolescent girls who engage in sexual intercourse are screened to see if they have cervical dysplasia when they receive regular medical checkups for children.
Before you start smoking,
educate you not to start smoking, and consult with children who have already started smoking to quit smoking.
Prevention of safety accidents
Consultation on prevention of burns, falls, traffic accidents, drowning, poisoning, suffocation, and firearm safety accidents.
Prevention of allergic diseases
Consultation on prevention education so as not to cause various allergic diseases such as bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Talk about sleep and love for your children.
출처 및 참조 문헌
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 그 외
|
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP 미국 소아과 전문의, 한국 소아청소년과 전문의 이상원 저 “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다. “The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.” Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026 |