뇌전증(간질)
Epilepsy(Epileptic seizure)
뇌전증(간질) Epilepsy(Epileptic seizure)
뇌전증(간질)에 관련된 용어
1. 간질(Epilepsy)
재발성이 있는 경련성 질환을 간질이라 한다. 간질을 Epilepsy, Seizure disorder, 또는 Epileptic seizure라고도 한다.
2014 년부터 한국에서는 간질이란 말 대신 ‘뇌전증‘이란 말을 쓰기로
했다. 그러나 편의상 여기서는 간질 또는 뇌전증이란 말을 병용하기로
한다
2. 뇌전증(간질) 발작(Epileptic seizure)
간질이란 병명의 동의어
3. 경련성 질환(Seizure disorder)
뇌신경 세포의 발작적인 방전으로 생기는 간헐적 신경계 장애를 통틀어 경련성 질환이라고 한다. 경련성 질환을 발작성 질환이라고 한다. 간질은 발작성 질환 중 하나이다.
4. 경련(Convulsion)
특히 근육 운동 현상을 동반하는 전신 경련을 의미한다. 즉 강력한 불수의성 근육 수축과 수의근의 연속적 수축을 동반하는 경련
5. 발작(Seizure)
간질 발작 또는 급성 발작이라고 한다.
뇌전증(간질)
-
간질은 거의 모든 가족들 중 적어도 한 사람 정도 간질을 할 정도로 흔한 경련성 질환이다.
-
동서고금을 막론하고 간질이란 병명은 간질이 있는 환아에게는 물론이고 그 환아의 가족 또는 친지들에게도 불미스러운 병명이라고 여긴다.
-
1988년 “소아가정의학백과“를 지으면서 간질이란 병명을 쓰는 대신 경련성 질환이란 병명을 쓰면 어떠냐고 저자가 주장해 본 적도 있다.
-
요즘 한국 의학계에서 간질이란 병명을 다른 신 의학용어로 바꾼다는 뉴스를 들었다. 아주 좋은 생각이다. 대찬성한다.
간질이란 병명대신
1) 뇌신경경련(증) 腦神經痙攣(症),
2) 뇌진증 腦震(症)
3) 뇌전증 腦電症
4) 뇌전류장애증 腦電流障碍(症) 등의 병명을 쓰면 어떻겠느냐는 제의가 한국 의학계에 있는 것 같다.
저자는 이런 병명을 쓰면 어떨까 한번 내 제안한다.
“간질“을 “재발성 경련성 질환“이라고.
뇌전증(간질)의 병인론
-
미국 총인구 중 2백만 명에게 간질 발작이 유발 되고
-
인구의 약 3%에게 일생 동안 한 번 이상 간질 발작이 유발되었고.
-
간질 발작이 재발되는지 이유는 확실히 모른다.
-
간질의 종류에 따라 간질 발작이 유발되는 기전도 다르다.
-
한 개의 대뇌 속에 수백억 개의 뇌신경 세포들이 있다. 무엇을 생각하고 기억하고 감정의 변화에 따라 대뇌의 한 부분에 있는 뇌신경 세포 등에서 정상적으로 전기 에너지가 방출된다. 이 때 방출된 전기 에너지는 대뇌의 한 부분에서 대뇌의 다른 부분으로 일정한 방향으로 흐르는 것이 정상적이다. 그러나 여러 가지 원인으로 다량의 전기 에너지가 대뇌의 한 부분에 있는 뇌신경 세포들에서 방출되어 대뇌의 다른 부분 뇌신경 세포들로 비정상적으로 갑자기 흘러갈 때 간질 발작이 생길 수 있다.
-
대량의 전기 에너지가 양쪽 대뇌 반구에서 비정상적으로 갑자기 방출될 때 전신 대발작이 생길 수 있다. 이런 대발작을 전신 발작이라고 한다. 전신 발작의 대부분은 유전적인 원인으로 생긴다.
-
전기 에너지가 대뇌의 일부분의 뇌신경 세포들이나 여러 부분의 뇌신경 세포들에서 비정상적으로 갑자기 방출되어 전체의 대뇌로 갑자기 흘러갈 때 신체의 일부에 발작이 생길 수 있다. 이런 발작을 부분 발작이라고 한다. 부분 발작은 대뇌의 일부나 여러 부분에 생긴 뇌 손상으로 생긴다고 믿는다.
-
간질 환아 자신이나 간질 환아의 가족들이 간질이란 병명을 듣기 좋아하지 않는 것이 보통이다. 간질이란 병명을 쓰는 대신 발작성 질환 또는 재발성 발작성 질환이라는 병명을 쓰기도 한다.
-
([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질환–신생아 경련 참조)
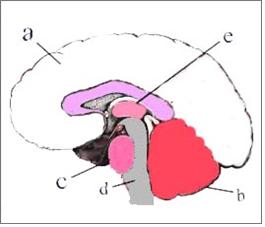
그림 1-11. 뇌 측면 그림
대뇌, 소뇌, 뇌교(교뇌), 연수, 제 3뇌실, 뇌간=중뇌+뇌교+연수
참조문헌 Gray’s Anatomy
뇌전증(간질)의 원인
-
간질의 원인은 확실히 모를 때가 더 많다.
-
그러나 대부분의 간질은 선천성 뇌 기형, 후천성 뇌 질환, 또는 유전성 질환 등이 있다.
-
선천성 뇌 기형, 선천성 뇌염 또는 후천성 뇌염이나 뇌막염, 분만 중 생긴 두부외상, 생후 두부 외상, 분만 중 산소 결핍증 등으로 생긴 뇌 손상이 간질의 원인이 될 수 있다.
-
어떤 원인으로 생긴 뇌 실질 손상으로 생기는 간질을 기질성 간질이라고 한다.
-
대뇌 실질에는 기질적 변화가 없고 간질의 원인을 확실히 모르는 간질을 특발성 간질이라고 한다.
-
요즘은 뇌 CT 스캔 검사, 뇌 MRI 검사, 뇌 초음파 검사, 기능적 뇌 MRI 검사 등의 뇌 영상 검사와 그 외 눈부신 의학의 발달로 뇌 실질을 전보다 더 정밀하게 검사할 수 있고 뇌 실질에 생긴 아주 작은 병변을 정확하게 알 수 있어 간질의 원인을 더 확실히 알아낼 수 있다.
-
이런 저런 이유로, 과거에 특발성 간질이라고 진단받았던 간질이 최근에는 기질성 간질로 판명되는 경우도 많다.
-
많은 부모들이 자녀가 간질을 가지고 있다는 사실 자체를 부끄럽게 생각해서 자녀들이 간질을 가지고 있다는 사실을 당국이나 그 외 다른 사람들에게 알려주지 않는 경향이 있다. 이런 이유로 각 나라의 간질 환아들의 전체 수를 확실히 알 수 없다.
-
실제로 간질 환아들의 수는 통계상 나타난 수보다 훨씬 더 많을 것이다.
-
한국의 간질 환아들의 수는 약 20만 명으로 추정된다고 한다.
-
가족들 중 누군가가 특발성 간질을 가지고 있는 가족 병력이 있는 가족들에게는 특발성 간질을 가지고 있지 않은 가족들에 비해서 특발성 간질에 걸릴 가능성이 더 많다.
-
(포도주색 혈관성 모반 참조.)
1. 임신 중 원인
① 임신 중, 풍진바이러스 감염, 박테리아 감염, 또는 톡소플라스마 원충 감염 등 TORCH 감염이 태아에게 생겼을 때
② 태아의 뇌 손상,
③ 태아에게 심한 황달이 생길 때,
④ 선천성 뇌 기형이 있을 때,
⑤ 태아가 질식 되었을 때,
⑥ 그 외 다른 원인으로 태아의 뇌가 손상 될 때 간질이 생길 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질환–선천성 태아 풍진증후군, 톡소플라스마증 참조.
⑦ 임신 중 임신부가 Methotrexate, Cyclophosphamide, Systemic retinoids(Isotretinoin and etretinate), 또는 Trimethadioneo, Warfarin 등의 약물 치료를 받을 때 태아의 중추신경계에 기형이 생길 수 있다. 즉 임산부가 임신 중 이런 종류의 약물로 치료를 받을 때 그런 약물에 태아가 노출될 때 태아의 뇌에 기형이 생길 수 있고 태어난 아기에게 간질이 생길 수 있다.
그림 1-13. 선천성 태아 풍진 증후군이 있는 태아가 태어난 후 간질이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

그림 1-14. 태아에게 톡소플라스마 원충에 감염되면 생후 간질을 할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
2. 분만 중이나 분만 후 원인
분만 전, 분망 중 태반의 일부가 자궁벽에서 떨어질 때 모체의 피가 태아에게 충분히 공급되지 못하고 그로 인해 태아에게 산소결핍증이 생기고 태아가 질식될 수 있고 태아의 뇌가 손상될 수 있다. 생후 간질이 생길 수 있다.
① 분만 중 태아의 뇌가 질 산도의 압력에 의해 손상될 때,
② 겸자 분만으로 태아의 뇌가 손상될 때,
③ 아주 극도로 작은 미숙 신생아의 두개강 내 출혈이나
④ 만삭 신생아의 두 개강 내 출혈이 생길 때,
⑤ 신생아에게 심한 저혈당증
⑥ 신생아에게 생긴 병적 황달로 뇌가 손상될 수 있고 그로 인해 간질이 생길 수 있다.
⑦ 그 외 다른 이유로 태아들이나 신생아들에게 산소 결핍증이 생겨 태아나 신생아가 질식되고 그로 인해 생긴 뇌 손상으로 간질이 생길 수 있다.
신생아 질식([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질환–신생아 가사 참조).
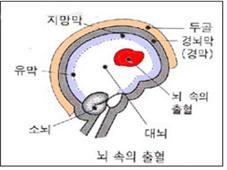
그림 1-15. 두개 강 내 출혈로 인해 뇌손상이 생길 수 있고 그로인해 간질이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
사진 1-16. 갓 태어난 신생아에게 산소 결핍증이 생기지 않게 예방적 치료를 할 때와 갓 태어난 신생아에게 생긴 산소 결핍증을 치료할 때 쓸 수 있는 진보적 신생아 심폐 소생술 치료용 의료기와 산소
분만 전이나 분만 중 자궁 내에서 또는 분만 후 혈중 저산소 농도로 인해 산소 결핍증이 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 뇌 손상이 생길 수 있고 그 후 간질이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
후천성 원인
-
임신과 분만은 정상적으로 이루어졌으나 생후 뇌종양, 뇌진탕, 납 중독, 약물 중독, 두부 외상, 뇌염, 뇌막염, 질식, 그 외 다른 종류의 감염병, 또는 단백질 신진대사 이상 등으로 뇌가 손상되어 간질이 생길 수 있다.
유전성 원인
-
유전으로 간질이 생길 수 있다.
-
병력, 세밀한 신체검사, 피검사, 뇌 X-선 사진 검사, 뇌 CT 스캔 검사, 뇌 MRI 검사, 뇌파검사 등 여러 가지 검사로 간질의 원인을 확실히 찾지 못할 때도 있다.
-
이런 종류의 간질을 특발성 간질이라 하고 특발성 간질의 대부분은 유전으로 인해 생긴다고 추정한다.
그 외 원인
뇌전증(간질)의 분류
간질의 원인과 증상 징후 등에 따라 간질을 다음과 같이 분류한다.
①위에서 설명한 바와 같이 뇌의 실질에 생긴 병변의 유무에 따라 특발성 간질과 기질성 간질로 분류하고
②특발성 간질은 유전 여부에 따라 유전성 간질과 비유전성 간질로 분류하고
③경련 상태와 정도에 따라 전신에 생긴 전신 발작과 신체의 일부에 생긴 부분 발작으로 분류할 수 있다.
1. 전신 발작 분류
1). 대발작
2). 소발작
3). 이완성 발작
4). 근 간대성 발작
5). 점두 경련
2. 부분 발작 분류.
1). 단순성 부분 발작
2). 복합성 부분 발작
Epilepsy (Epileptic seizure) 뇌전증(간질)
Terms related to epilepsy (epilepsy)
1.Epilepsy
Recurrent convulsive disease is called epilepsy.
Epilepsy is also referred to as Epilepsy, Seizure disorder, or Epileptic seizure. Since 2014, in Korea, instead of the word epilepsy, the word’epilepsy’ has been used. did.
However, for convenience, I will use the term epilepsy or epilepsy together here. do
2. Epileptic seizure A synonym for epilepsy
3. Seizure disorder
Intermittent nervous system disorders caused by seizure discharge of cranial nerve cells are collectively referred to as convulsive disorders. Convulsive disorders are called paroxysmal disorders. Epilepsy is one of the paroxysmal disorders.
4. Convulsion
In particular, it refers to systemic convulsions accompanied by muscle movement. In other words, convulsions accompanied by strong involuntary muscle contraction and continuous contraction of voluntary muscles.
5. Seizure
It is called an epileptic seizure or acute seizure.
Epilepsy
• Epilepsy is a convulsive disorder that is so common that at least one in almost every family member has epilepsy.
• Regardless of the age, the disease is considered to be an unfavorable name not only for the child with epilepsy, but also for the child’s family or relatives.
• In 1988, while building “Encyclopedia of Pediatric Family Medicine”, the author argued that it would be like to use the name of convulsive disease instead of using the name of epilepsy.
• Recently, I heard news that the Korean medical community is changing the name of epilepsy into another new medical term. That’s a very good idea. I approve of it very much.
Instead of epilepsy
1) cranial nerve spasm (symptoms) 腦神經痙攣(症),
2) encephalopathy
3) epilepsy
4) There seems to be a suggestion in the Korean medical community as to what it would be like to write a disease name such as brain current disorder, 腦電流障碍(症). The author makes my suggestion on what to do if you use such a disease name. “Epilepsy” is called “recurrent convulsive disease.”
The etiology of epilepsy
• 2 million people in the US population have epileptic seizures,
• About 3% of the population has had epileptic seizures more than once in their lifetime. • It is not clear why epileptic seizures will recur.
• The mechanism by which epileptic seizures are triggered differs depending on the type of epilepsy.
• There are tens of billions of cranial nerve cells in one cerebrum. As you think, remember, and change your emotions, electrical energy is normally released from the cranial nerve cells in one part of the cerebrum. At this time, it is normal for the emitted electrical energy to flow in a certain direction from one part of the cerebrum to another part of the cerebrum. However, for various causes, an epileptic seizure can occur when a large amount of electrical energy is released from cranial nerve cells in one part of the cerebrum and abnormally and suddenly flows into the cranial nerve cells in other parts of the cerebrum.
• Large amounts of electrical energy can develop abnormally and suddenly in both cerebral hemispheres. These major seizures are called systemic seizures. Most systemic seizures are due to genetic causes.
• A seizure can occur in parts of the body when electrical energy is released abnormally and suddenly from parts of the cerebral nerve cells or from several parts of the cranial nerve cells and suddenly flows into the entire cerebrum. These seizures are called partial seizures. It is believed that partial seizures are caused by brain damage in parts or parts of the cerebrum.
• It is common for children with epilepsy or their family members to not like to hear the name of epilepsy. Instead of using the name of epilepsy, the name of paroxysmal disease or recurrent seizure disease is sometimes used.
• (Refer to www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 6, Newborn growth and development and disease-Newborn spasms)

Figure 1-11. Brain side picture Cerebrum, cerebellum, pons , training, third ventricle, brain stem = midbrain + pons + training References Gray’s Anatomy
Causes of epilepsy
• More often than not, the cause of epilepsy is unclear.
• However, most epilepsy includes congenital brain malformations, acquired brain diseases, or inherited diseases.
• Brain damage caused by congenital brain malformations, congenital encephalitis or acquired encephalitis or meningitis, head trauma during delivery, postnatal head trauma, and oxygen deficiency during delivery can cause epilepsy.
• Epilepsy resulting from damage to the brain parenchyma caused by any cause is called organic epilepsy. • Epilepsy with no organic change in the cerebral parenchyma and for which the cause of epilepsy is unknown is called idiopathic epilepsy.
• Nowadays, brain imaging tests such as brain CT scan, brain MRI, brain ultrasound, functional brain MRI, and other remarkable advances in medicine allow the brain parenchyma to be examined more precisely than before, and the tiny You can accurately identify the lesion, so you can determine the cause of the epilepsy more clearly.
• For one reason or another, epilepsy that was previously diagnosed as idiopathic epilepsy is often found to be organic epilepsy in recent years.
• Many parents are ashamed of the fact that their children have epilepsy, so they tend not to let the authorities or others know that their children have epilepsy. For this reason, the total number of children with epilepsy in each country is not known for certain.
• In fact, the number of children with epilepsy will be much higher than the number statistically indicated.
• The number of children with epilepsy in Korea is estimated to be about 200,000.
• Families with a family history of someone in their family with idiopathic epilepsy are more likely to develop idiopathic epilepsy than those who do not have idiopathic epilepsy.
• (See wine-colored vascular birthmarks.)
1. Causes during pregnancy
① During pregnancy, when TORCH infection such as rubella virus infection, bacterial infection, or Toxoplasma protozoal infection occurs in the fetus
② fetal brain damage,
③ When severe jaundice occurs in the fetus,
④ When you have a congenital brain malformation,
⑤ When the fetus is suffocated,
⑥ Epilepsy can occur when the fetus’s brain is damaged by other causes. www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 6 Newborn growth and development good and disease-Congenital fetal rubella syndrome, see Toxoplasmosis.
⑦ During pregnancy, when pregnant women receive medications such as Methotrexate, Cyclophosphamide, Systemic retinoids (Isotretinoin and etretinate), or Trimethadioneo, Warfarin, deformities may occur in the central nervous system of the fetus. In other words, when pregnant women are treated with these types of drugs during pregnancy, exposure of the fetus to those drugs can lead to deformities in the fetal brain and epilepsy in the born baby.

Figure 1-13. Epilepsy can develop after a fetus with congenital fetal rubella syndrome is born. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-14. Infecting the fetus with Toxoplasma protozoa can cause epilepsy after birth. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
2. Causes during or after delivery When part of the placenta falls from the uterine wall before delivery or during delivery, the mother’s blood cannot be sufficiently supplied to the fetus, resulting in oxygen deficiency in the fetus, suffocation of the fetus, and brain damage of the fetus. Epilepsy may develop after birth.
① When the fetal brain is damaged by the pressure of the vaginal acidity during delivery,
② When the fetus’s brain is damaged by delivery of forceps,
③ Extremely small intracranial bleeding or
④ When bleeding occurs in the cranial cavity of a term newborn,
⑤ Severe hypoglycemia in newborns
⑥ Pathological jaundice in newborns can damage the brain and cause epilepsy.
⑦ For other reasons, oxygen deficiency occurs in fetuses or newborns, and the fetus or newborn is suffocated, and the resulting brain damage can lead to epilepsy.
Asphyxiation of newborns www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 6 Newborn growth and development good and disease-Newborn baby housework reference).

Figure 1-15. Intracranial bleeding can lead to brain damage, resulting in epilepsy. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-16. Advanced neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation therapy and oxygen that can be used to prevent oxygen deficiency in newborns and to treat oxygen deficiency in newborns. Oxygen deficiency can occur before or during delivery due to hypoxic levels in the uterus or after delivery, which can lead to brain damage, followed by epilepsy. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Acquired causes
• Pregnancy and delivery were normal, but after birth, brain tumors, concussion, lead poisoning, drug addiction, head trauma, encephalitis, meningitis, suffocation, other types of infectious diseases, or protein metabolic abnormalities can cause brain damage and epilepsy have.
Hereditary cause
• Genetic epilepsy can occur.
• In some cases, the cause of epilepsy cannot be clearly identified through various tests such as medical history, detailed physical examination, blood test, brain X-ray examination, brain CT scan, brain MRI examination, and electroencephalography.
• This type of epilepsy is called idiopathic epilepsy and it is assumed that the majority of idiopathic epilepsy is caused by heredity.
Other causes
Classification of epilepsy (epilepsy)
Epilepsy is classified as follows according to the causes and symptoms of epilepsy.
① As described above, according to the presence or absence of lesions in the parenchyma of the brain, it is classified into idiopathic epilepsy and organic epilepsy.
② Idiopathic epilepsy is classified into hereditary epilepsy and non-hereditary epilepsy depending on whether it is inherited or not.
③ Depending on the state and degree of convulsion, it can be classified into generalized seizures and partial seizures.
1. Classification of systemic seizures One). A major seizure
2). Small seizures
3). Relaxation seizures
4). Myoclonic seizures
5). Point cramps
2. Partial seizure classification.
1). Simplicity partial seizure
2). Complex partial seizures
3). Relaxation seizures
4). Myoclonic seizures
5). Point cramps
2. Partial seizure classification.
1). Simplicity partial seizure
2). Complex partial seizures
참조문헌
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-본 사이트의 내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.“
Copyright drleepediatrics.com 2/16/2026