Pineal Gland
송과선(송과체)
영어 내용은 펴온글
Pineal gland-송과체, Hypothalamus- 시상하부, Thalamus-시상
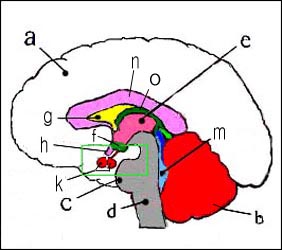
사진 1-1. 뇌하수체와 뇌 측면도.
a-대뇌, b-소뇌, c-뇌교(교뇌), d-연수(숨뇌), f-시상하부, g-간뇌, h-시신경 교차, k-뇌하수체의 전엽과 후엽, m- 제4뇌실, n-뇌량, o- 제 3뇌실.
참고: 이그 림에서 송과체 표시는 없음
What is the pineal gland?
Your pineal gland, also called the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri, is a tiny gland in your brain that’s located beneath the back part of the corpus callosum. It’s a part of your endocrine system and secretes the hormone melatonin. Your pineal gland’s main job is to help control the circadian cycle of sleep and wakefulness by secreting melatonin.
The pineal gland is shaped like a tiny pinecone, which is how it got its name (“pine”-al gland). However, it is pronounced “pin-ee-uhl.”
The pineal gland is the least understood gland of the endocrine system, and it was the last part of the endocrine system to be discovered.
What is the endocrine system?
Your endocrine system is a network of several glands that create and secrete (release) hormones.
A gland is an organ that makes one or more substances, like hormones, digestive juices, sweat or tears. Endocrine glands release hormones directly into your bloodstream.
Hormones are chemicals that coordinate different functions in your body by carrying messages through your blood to your organs, skin, muscles and other tissues. These signals tell your body what to do and when to do it.
The following organs and glands make up your endocrine system:
- Hypothalamus.
- Pituitary gland.
- Thyroid.
- Parathyroid glands.
- Adrenal glands.
- Pineal gland.
- Pancreas.
- Ovaries.
- Testes.
What is melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone that’s mainly produced by your pineal gland. The importance of pineal melatonin in humans is not clear, but many researchers believe it may help to synchronize circadian rhythms in different parts of your body.
Circadian rhythms are physical, mental and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. These natural processes respond primarily to light and dark.
Your pineal gland releases the highest levels of melatonin when there’s darkness and decreases melatonin production when you’re exposed to light. In other words, you have low levels of melatonin in your blood during the daylight hours and peak levels of melatonin during the nighttime.
Because of this, melatonin has often been referred to as a “sleep hormone.” While melatonin is not essential for sleeping, you sleep better when you have the highest levels of melatonin in your body.
Melatonin also interacts with biologically female hormones. Research has shown that it helps in regulating menstrual cycles.
Melatonin can also protect against neurodegeneration, which is the progressive loss of function of neurons. Neurodegeneration is present in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
What does the pineal gland do?
The main function of your pineal gland is to receive information about the daily light-dark (day-night) cycle from the retinas in your eyes and then produce and release (secrete) melatonin accordingly — elevated levels at night (during dark hours) and low levels during the day (during light hours).
Can a person live without a pineal gland?
Yes, you can live without your pineal gland. However, your body may have a difficult time with sleeping patterns and other physiologic functions related to the circadian rhythm without a pineal gland due to a lack of melatonin.
In very rare cases, a person with a pineal tumor may need surgery to remove their pineal gland. This is known as a pinealectomy.
Where is the pineal gland located?
Your pineal gland is located deep in the middle of your brain. It sits in a groove just above the thalamus, which is an area of your brain that coordinates a variety of functions related to your senses.
What is the pineal gland made of?
Your pineal gland consists of portions of neurons, neuroglial cells and specialized secreting cells called pinealocytes. The pinealocytes create melatonin and secrete (release) it directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, the fluid that flows in and around the hollow spaces of your brain and spinal cord, which then takes it into your bloodstream.
How big is the pineal gland?
Your pineal gland is a tiny, cone-shaped gland that’s only about 0.8 centimeters (cm) long. In adults, it weighs about 0.1 grams.
CONDITIONS AND DISORDERS
What conditions and disorders affect the pineal gland?
Your pineal gland’s function and ability to release melatonin can be affected by the following conditions and situations:
- Pineal gland tumors.
- Injuries that affect the pineal gland.
- Pineal gland calcification.
Pineal gland tumors
Pineal gland tumors are very rare, and there are several different types of them. They’re more likely to affect children and adults younger than 40.
Pineal tumors aren’t always cancer, but they still cause problems as they grow because they press against other parts of your brain. They can also block the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds and cushions your brain. This blockage raises the pressure inside your skull, which is dangerous and requires treatment.
Injuries that affect the pineal gland
Damage to your pineal gland can cause it to work improperly. Approximately 30% to 50% of people who experience a traumatic brain injury (TBI) have issues with at least one endocrine gland in their brain, which includes the pineal gland and pituitary gland.
A traumatic brain injury can happen when there is a blow to the head. The injury can be penetrating, like a gunshot wound, or a non-penetrating injury, like being struck in the head during a car accident. Concussions are the most common type of TBI.
Pineal gland calcification
Calcification of the pineal gland is quite common. In fact, it’s so common that healthcare providers often use a calcified pineal gland as a landmark on x-rays to help identify different structures of the brain. Calcification happens when calcium builds up in body tissue, causing the tissue to harden.
Your pineal gland tends to calcify as you age. While some calcification is normal, excessive calcification can prevent your pineal gland from functioning properly. Some studies have revealed that the degree of calcification of the pineal gland is higher in those affected by Alzheimer’s disease. There’s a loose link between pineal gland calcification and some migraine and cluster headaches.
More studies need to be done to determine the exact effects of pineal gland calcification.
What are the symptoms of pineal gland problems?
If you have a pineal gland tumor, which are rare, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Seizures.
- Memory issues.
- Headaches.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Vision changes.
What are common tests to check the health of the pineal gland?
Healthcare providers can look at your pineal gland with imaging tests, such as an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or a CT (computed tomography) scan. Providers use these imaging tests to help determine if you have a pineal tumor or cyst.
Providers may also use X-rays to check for pineal gland calcification.
Your provider can also check your melatonin levels with a blood test.
How are pineal gland conditions treated?
Pineal gland tumors may be treated with one or more of the following therapies:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of a pineal tumor is difficult due to its location in the middle of your brain. Because of this, it’s not a common treatment. In some cases, a surgeon might remove the entire pineal gland (pinealectomy).
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy focuses strong beams of energy to destroy cancer cells and prevent them from growing.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells and prevent them from growing.
If you have a condition that causes your pineal gland to secrete less-than-normal levels of melatonin, your provider may have you take an over-the-counter melatonin supplement.
CARE
What can I do to keep my pineal gland healthy?
Researchers and scientists still don’t fully understand the pineal gland and melatonin and their functions. Because of this, there are no known ways to keep your pineal gland healthy.
Why is the pineal gland called the “third eye?”
Since the pineal gland was the last of the endocrine glands to be discovered — and scientists still aren’t fully sure of all of its functions — the pineal gland has long been a “mysterious” organ. The pineal gland was commonly called the “third eye” for many reasons, including its location deep in the center of the brain and its connection to light via the circadian rhythm and melatonin secretion. Many spiritual traditions believe it serves as a connection between the physical and spiritual worlds.
Chakras are prominent in certain forms of Hinduism and Tantric Buddhism. The third eye chakra is considered to be the sixth chakra in your body. It’s believed to be linked to perception, awareness and spiritual communication and linked to the pineal gland. While there’s no scientific evidence to support these claims, many forms of spirituality and cultures emphasize the importance of the third eye chakra and the pineal gland.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your pineal gland is a tiny but powerful gland when it comes to your body’s circadian rhythm. While pineal gland tumors are rare, it’s important to talk to your provider if you’re experiencing symptoms such as memory issues and nausea.
For more information, please visit drleepediatrics.com. search
정보를 더 찾으려면 drleepediatrics.com 방문한 후 Search에서 찾아보세요.
개요
측면에서 본 뇌 중앙의 의료 삽화. 송과선은 뇌의 중앙에 있는 시상 뒤에 위치한 작은 구조입니다.
송과체는 멜라토닌 호르몬을 방출하는 뇌의 작은 내분비선입니다.
송과선이란 무엇입니까?
송과체 또는 뇌단부라고도 하는 송과체는 뇌량의 뒤쪽 아래에 위치한 뇌의 작은 샘입니다. 내분비계의 일부이며 멜라토닌 호르몬을 분비합니다. 송과체의 주요 임무는 멜라토닌을 분비하여 수면과 각성의 24시간 주기를 조절하는 것입니다.
송과선은 작은 솔방울과 같은 모양을 하고 있어 이름이 “소나무”알선입니다. 그러나 “pin-ee-uhl”로 발음됩니다.
송과선은 내분비계에서 가장 잘 알려지지 않은 선이며, 내분비계의 마지막 부분으로 발견되었습니다.
내분비계란?
내분비계는 호르몬을 생성 및 분비(방출)하는 여러 땀샘의 네트워크입니다.
땀샘은 호르몬, 소화액, 땀 또는 눈물과 같은 하나 이상의 물질을 만드는 기관입니다. 내분비선은 호르몬을 혈류로 직접 방출합니다.
호르몬은 혈액을 통해 장기, 피부, 근육 및 기타 조직에 메시지를 전달함으로써 신체의 다양한 기능을 조정하는 화학 물질입니다. 이 신호는 몸이 무엇을 해야 하고 언제 해야 하는지 알려줍니다.
다음 기관과 땀샘이 내분비계를 구성합니다.
시상하부.
뇌하수체.
갑상선.
부갑상선.
부신.
송과선.
콩팥.
난소.
고환.
멜라토닌이란 무엇입니까?
멜라토닌은 주로 송과체에서 생성되는 호르몬입니다. 인간에서 송과체 멜라토닌의 중요성은 명확하지 않지만 많은 연구자들은 이것이 신체의 다른 부분에서 일주기 리듬을 동기화하는 데 도움이 될 수 있다고 믿습니다.
일주기 리듬은 24시간 주기를 따르는 신체적, 정신적, 행동적 변화입니다. 이러한 자연적인 과정은 주로 빛과 어둠에 반응합니다.
송과선은 어두울 때 최고 수준의 멜라토닌을 방출하고 빛에 노출되면 멜라토닌 생성을 감소시킵니다. 즉, 낮에는 혈액 내 멜라토닌 수치가 낮고 야간에는 멜라토닌 수치가 최고 수준입니다.
이 때문에 멜라토닌은 종종 “수면 호르몬”으로 불립니다. 멜라토닌이 수면에 필수적인 것은 아니지만 체내에 멜라토닌 수치가 가장 높을 때 잠을 더 잘 잘 수 있습니다.
멜라토닌은 또한 생물학적 여성 호르몬과 상호 작용합니다. 연구에 따르면 월경 주기를 조절하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
멜라토닌은 또한 신경세포의 기능이 점진적으로 상실되는 신경변성으로부터 보호할 수 있습니다. 신경변성은 알츠하이머병 및 파킨슨병과 같은 상태에서 나타납니다.
기능
송과선은 무엇을합니까?
송과체의 주요 기능은 눈의 망막에서 매일의 명암(낮-밤) 주기에 대한 정보를 수신한 다음 그에 따라 멜라토닌을 생성 및 방출(분비)하는 것입니다. 낮 동안(밝은 시간 동안) 낮은 수준.
사람이 송과선 없이 살 수 있습니까?
네, 송과체 없이 살 수 있습니다. 그러나 멜라토닌이 부족하여 송과선이 없으면 신체가 수면 패턴 및 기타 생리적 기능에 어려움을 겪을 수 있습니다.
매우 드문 경우지만 송과체 종양이 있는 사람은 송과체를 제거하기 위해 수술이 필요할 수 있습니다. 이것은 송과체 절제술로 알려져 있습니다.
해부
송과선은 어디에 있습니까?
송과체는 뇌의 한가운데 깊숙이 위치해 있습니다. 그것은 감각과 관련된 다양한 기능을 조정하는 뇌 영역인 시상 바로 위의 홈에 있습니다.
송과선은 무엇으로 만들어졌습니까?
송과체는 뉴런의 일부, 신경교 세포 및 송과체라고 하는 특수 분비 세포로 구성됩니다. 송과체 세포는 멜라토닌을 생성하고 뇌척수액으로 직접 분비(방출)합니다. 뇌척수액은 뇌와 척수의 빈 공간과 그 주위를 흐르는 액체로 혈류로 들어갑니다.
송과선의 크기는 얼마입니까?
송과체는 길이가 약 0.8cm에 불과한 작은 원뿔 모양의 샘입니다. 성인의 경우 무게는 약 0.1g입니다.
상태 및 장애
어떤 상태와 장애가 송과체에 영향을 미칩니까?
송과체의 기능과 멜라토닌 방출 능력은 다음 조건과 상황에 의해 영향을 받을 수 있습니다.
송과선 종양.
송과체에 영향을 미치는 부상.
송과선 석회화.
송과체 종양
송과체 종양은 매우 드물며 여러 유형이 있습니다. 그들은 어린이에게 영향을 줄 가능성이 더 큽니다.